Health
-
Lin Test
text with link. This is a quiz. Some text Name Name Quo modo autem philosophus loquitur? Tecum optime, deinde etiam cum mediocri amico. Invidiosum nomen est, infame, suspectum. Name Name…
-

Gender-affirming care is rare, study says
Fewer than 1 in 1,000 transgender youth receive hormones or puberty blockers

-

Nature offers novel approach to oral wound care
Slug’s sticky mucus inspiration behind adhesive hydrogel that can seal wounds in wet environment

-

Time for a rethink of colonoscopy guidelines?
Change informed by new findings would help specialists focus on those most at risk, researcher says

-
Should pharmacists be moral gatekeepers?
‘The problem is not opioids,’ says author of ‘Policing Patients’ — it’s overdose, pain
-

The deadly habit we can’t quite kick
Actions by tobacco companies worry researcher even amid ‘dramatic decrease’ in smoking among young Americans

-
Grandma’s workouts may have made you healthier
Researchers found that grandmothers’ exercise habits likely impact their grandchildren’s health.

-
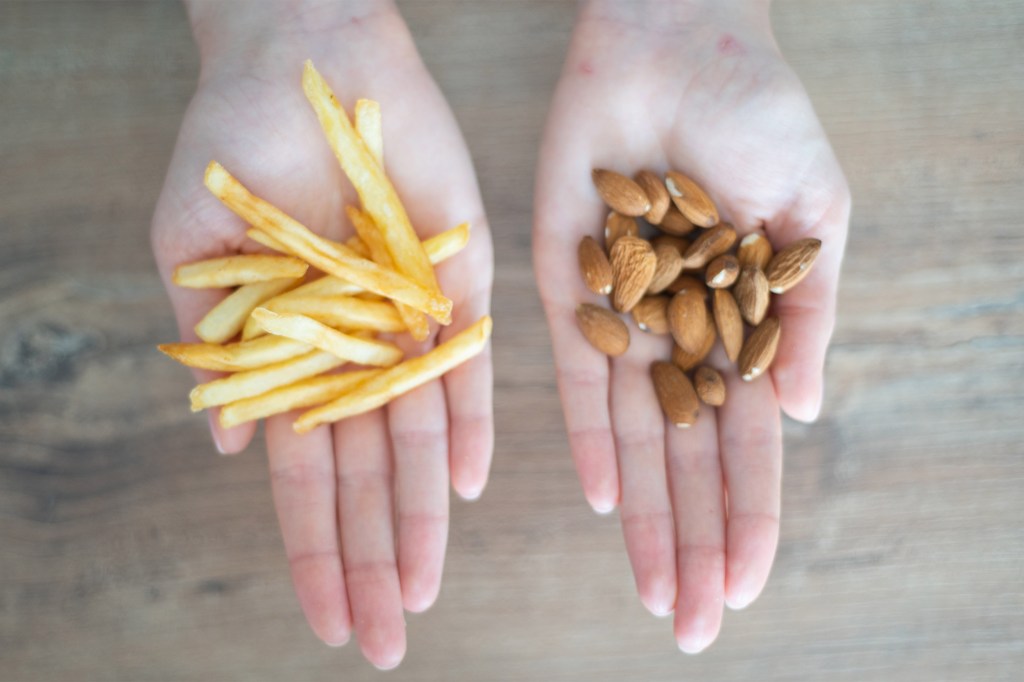
Sorry, fries are no match for almonds
A Harvard expert challenges a new study that suggests there is little difference between eating a 300-calorie serving of french fries and a 300-calorie serving of almonds every day for a month, in terms of weight gain or other markers for diabetes risk.

-
How a bioethicist and doctor sees abortion
Director of Medical School’s Center for Bioethics discusses ethical dimensions of abortion and how a ruling against Roe might affect providers.

-
Women can reduce risk of colon cancer
Researchers found a lower risk of colorectal cancer in women who started endoscopy screenings at age 45 compared to those who had not undergone screening at all.
-
Examining a lesser-known dementia driver
A fourth disorder that causes dementia has been added to the list. It’s called LATE and is estimated to cause about 15 to 20 percent of all dementias.

-
How to break a bad habit
Harvard experts say breaking an unhealthy habit can be done. It takes intent, a little white-knuckling, and some effective behavior modification techniques.

-
Hallmarks of Alzheimer’s found well before diagnosis
A new study shows the impact of early amyloid-β and tau protein accumulation on disrupting brain connections important for memory. These disrupted connections were present even before signs of cognitive impairment were observed.
-
Skull channels shown to protect brain from infection
Researchers have found that “brain water” can exit through tiny channels to reach the skull’s bone marrow, which can detect infection or injury.

-
Subvariants cause for alarm, hybrid immunity hard to beat
Harvard scientists give their read on recent COVID data from the U.S. and South Africa.
-
Snapshot of pandemic’s mental health impact on children
Psychiatric epidemiologist warns crisis too recent for conclusive results but shares some surprising, troubling early indications.

-
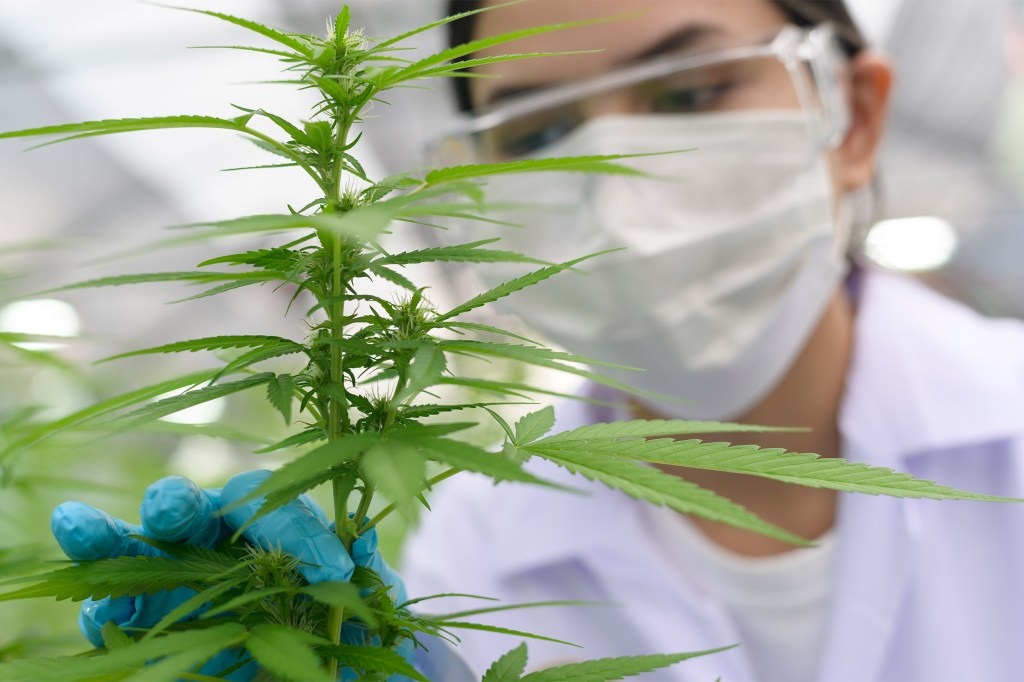
It may be increasingly legal, but it doesn’t mean cannabis is safe
Neuroscientist says the jury’s still out on effects on neurodevelopment of fetuses, teens.

-
In Alzheimer’s victims, somatic mutations are both more and different
A new study by Harvard-affiliated researchers finds that patients with Alzheimer’s disease have both more and different somatic mutations — alterations in DNA — in their brain cells than people without Alzheimer’s disease.
-
Infertility linked to increased risk of heart failure in women
A new study finds that a woman’s history of infertility is associated with increased risk of heart failure.

-
Genetic risk scores developed for six diseases
Newly developed polygenic risk scores, which add up hundreds or thousands of genetic risk factors for six common diseases, can aid physicians and patients in making individualized disease screening and prevention decisions.

-
Understanding aphasia
Sometimes language problems — also known as aphasia — are the first symptom of progressive brain disorders.

-
Women see gains, Black men see losses in U.S. medicine
Diversity in U.S. medicine is not keeping pace with population changes, particularly among Black men, according to a new report.

-
What’s next for the CDC?
Five former CDC directors convened for a panel about the future of the agency.
-
Eating one avocado a week may lower heart disease risk
A Harvard study finds that people who eat two or more servings of avocado each week may lower their risk of cardiovascular disease compared to people who rarely eat avocado.

-
Siren call of daylight saving must be resisted, scientists say
Research, experience point to cancer link and other risks, suggesting standard time would be better year-round choice.

-
HIV drug shows promise against metastatic cancer
A drug widely used in HIV therapy has shown to stop disease progression in 25 percent of patients with fourth-line metastatic colorectal cancer.
-
Cost of distancing may outweigh benefits for healthy adults
Harvard experts say loneliness, isolation raise risk of depression, anxiety, heart ills.

-
The price of a pre-pandemic lifestyle
Scientists conducted a simulation study that projected the future of the COVID-19 pandemic in every state.

-
Bringing the cancer fight back down to earth
Halving deaths and other Biden goals are in reach, experts say, but let’s forget about “moonshot” and focus on resources and prevention.

-
Robots may have upper hand in prostate surgery
A new study provides clarity when comparing short-term differences following a traditional vs. robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy.

-
Large alcohol study challenges heart health claims
A large study challenges the theory that light alcohol consumption benefits heart health.

-
‘We need to rethink how we are studying cancer metabolism’
Insights into how cancer cells adapt and rewire their metabolism to achieve growth and survive was accompanied by a call for tools to study this on a nearly single-cell level, according to a new paper in Nature Communications.
-
Milk used to be simple
Pea, potato, and pistachio milk? Supermarkets now sell multiple kinds of plant-based milks made from nuts, beans, grains, vegetables, or fruit. So how healthy are they?

-
Omicron subvariant taking hold, but so far, life goes on
Subvariant is rising in the region, but no sign of dramatic surge in cases that other nations have experienced.

-
Medical marijuana may trigger substance abuse
Obtaining a medical marijuana card to use cannabis products to treat pain, anxiety, or depression symptoms led to the onset of cannabis use disorder while failing to improve symptoms, says a new study.

-
What’s behind post-COVID brain fog?
Experts trying to unravel why patients who recover from COVID-19 find they still have brain fog as part of their long COVID experience.


