Health
-
Lin Test
text with link. This is a quiz. Some text Name Name Quo modo autem philosophus loquitur? Tecum optime, deinde etiam cum mediocri amico. Invidiosum nomen est, infame, suspectum. Name Name…
-

Gender-affirming care is rare, study says
Fewer than 1 in 1,000 transgender youth receive hormones or puberty blockers

-

Nature offers novel approach to oral wound care
Slug’s sticky mucus inspiration behind adhesive hydrogel that can seal wounds in wet environment

-

Time for a rethink of colonoscopy guidelines?
Change informed by new findings would help specialists focus on those most at risk, researcher says

-
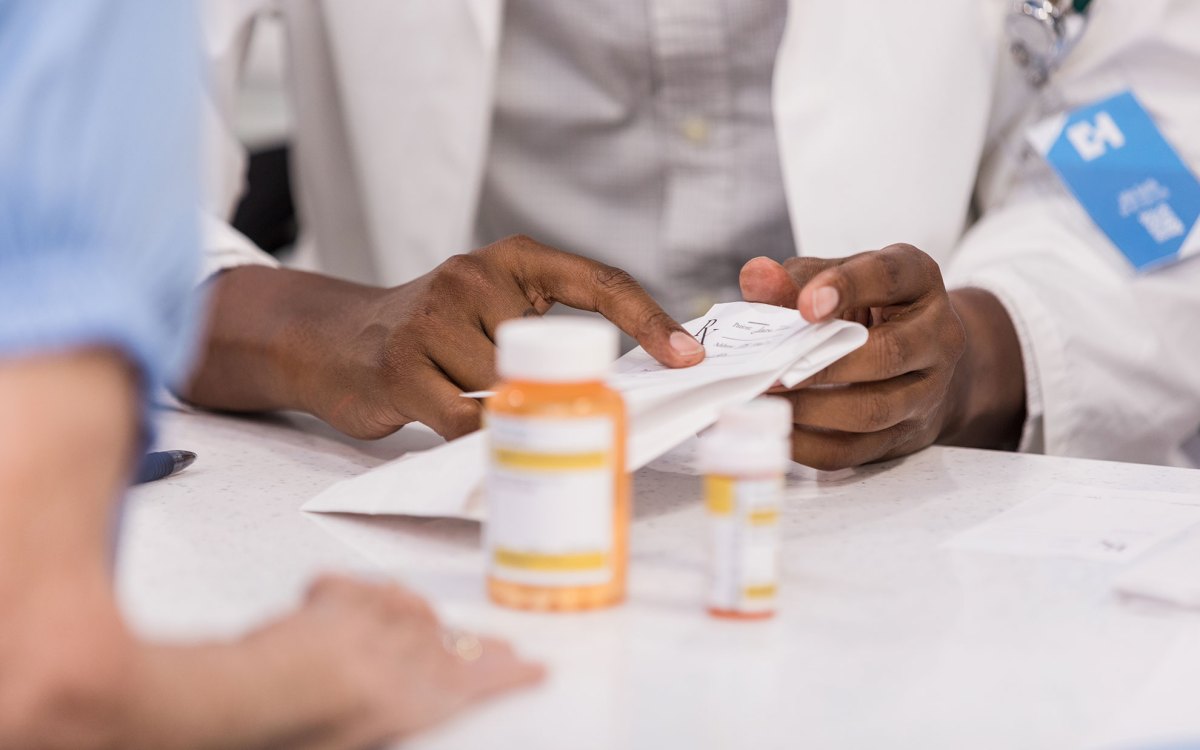
Should pharmacists be moral gatekeepers?
‘The problem is not opioids,’ says author of ‘Policing Patients’ — it’s overdose, pain
-

The deadly habit we can’t quite kick
Actions by tobacco companies worry researcher even amid ‘dramatic decrease’ in smoking among young Americans

-
Why some people are resistant to Alzheimer’s
A new study provides insights on why some people may be more resistant to Alzheimer’s disease than others.

-
Racial disparities found in culturally competent cancer care
A new study from Harvard-affiliated Dana-Farber Cancer Institute finds that non-white minority survivors are less likely than non-Hispanic whites to be seen by cancer specialists who share or understand their culture.
-
How a doctor learned to become a caregiver
Harvard Professor Arthur Kleinman’s wife, Joan, began to struggle with a rare form of early Alzheimer’s disease at 59.

-
Study suggests how measles depletes body’s immune memory
A new Harvard study shows measles wipes out 11 percent to 73 percent of antibodies against an array of viruses and bacteria, depleting a child’s previous immunity, which underscores the importance of measles vaccination.
-
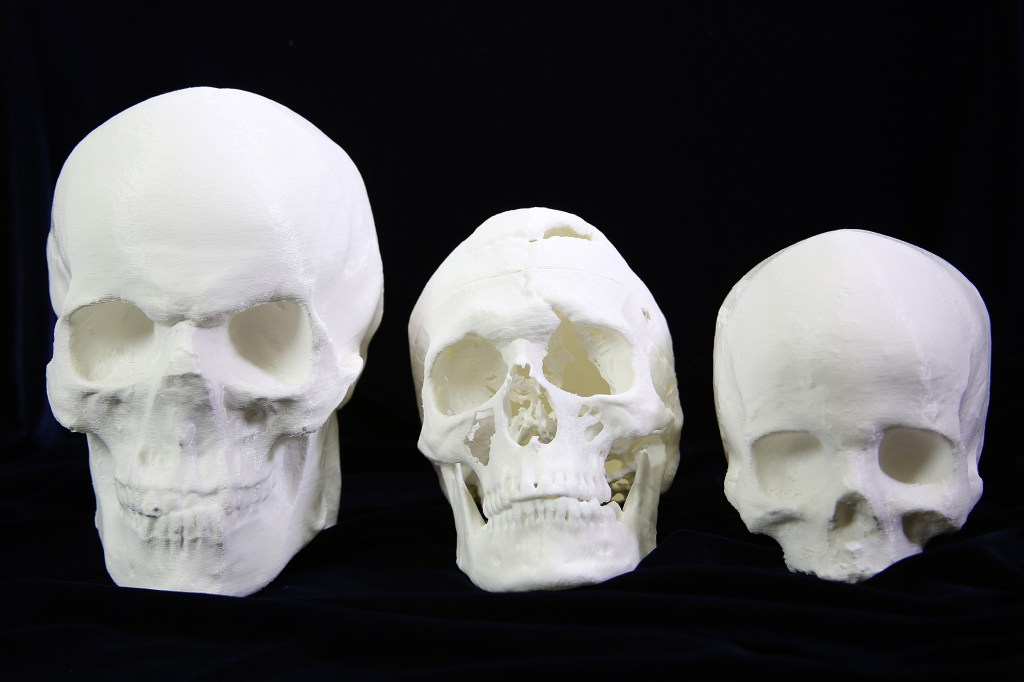
Bringing the Bone Box back to life
Countway Library is looking to revive the Bone Box program, which originally let anatomy students check out real human bones.
-
Power and pitfalls of gene editing
CRISPR gene-editing technology has conquered the lab and is poised to lead to new treatments for human disease. Experts consider the promise and peril at Radcliffe.

-
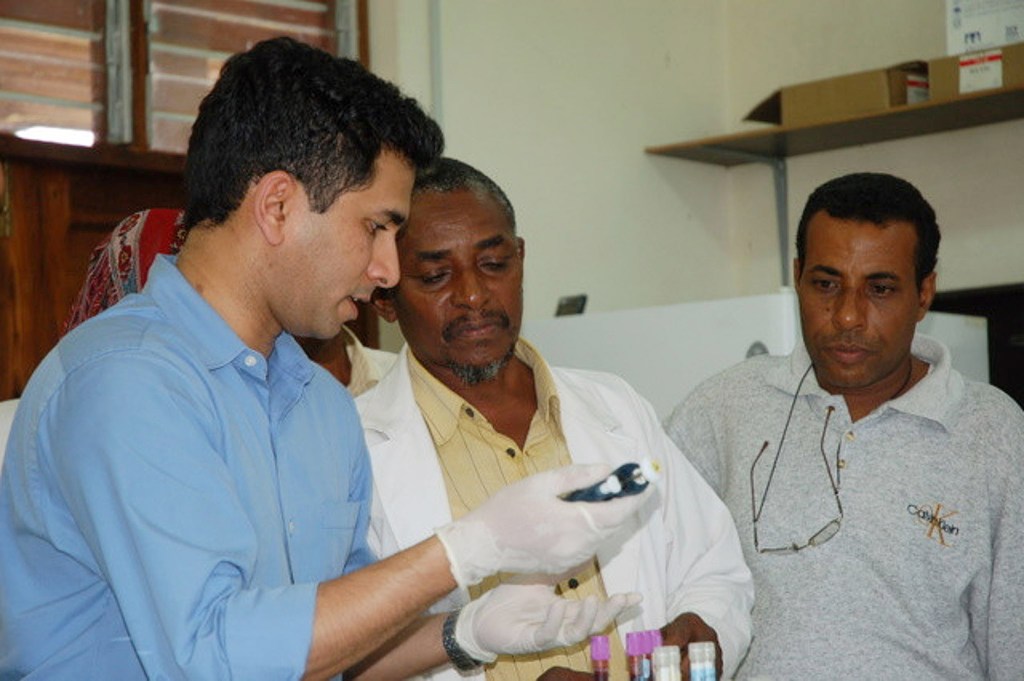
A timely triage test for TB
A team of researchers has developed a point-of-care TB test that costs only $2 and gives results in about 30 minutes, lowering the barrier to care in low-resource settings and potentially saving millions of lives.

-
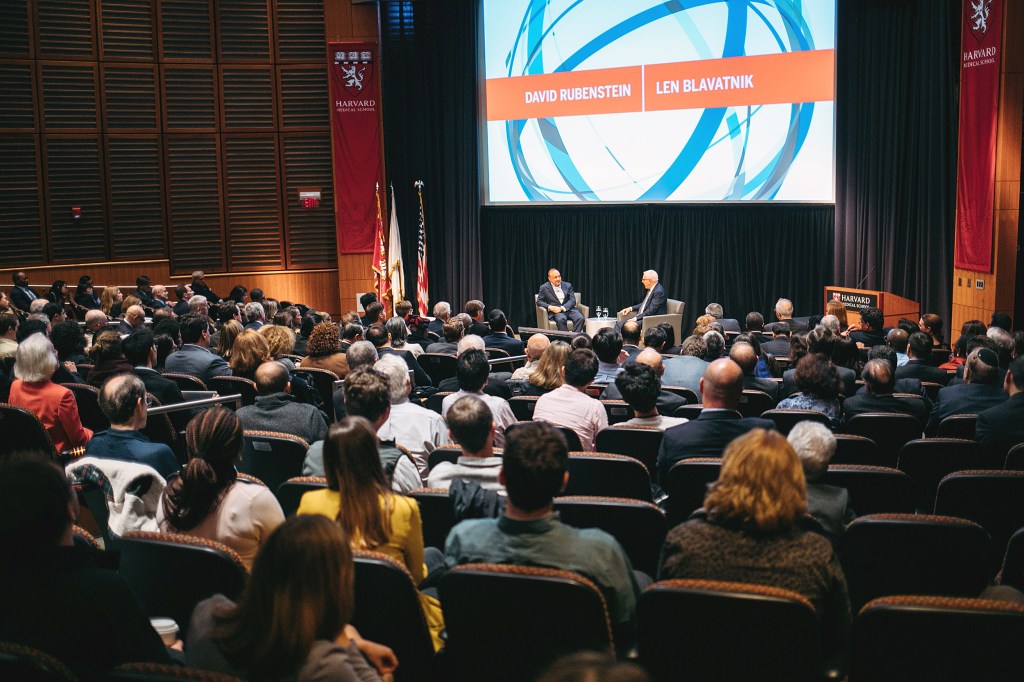
The speed of discovery
One year after the Blavatnik Family Foundation announced a $200 million commitment to Harvard Medical School, philanthropist Len Blavatnik spent the day at HMS visiting with scientists to learn more about research taking place on campus.

-
Learning not to fear
A study using mindfulness meditation showed changes over time in neural responses to pain and fear. The researchers found that changes in the hippocampus after mindfulness training were associated with enhanced ability to recall a safety memory, and thus respond in a more adaptive way.

-
Stigma of opioids a hurdle to solving crisis
“Can you think of all the tax dollars it’s cost for you to go to detox?” the doctor asked Raina McMahan when she arrived at the clinic in Revere seeking…

-
Bringing women to the forefront of global health
A Harvard panel on women in the global health workforce examines ways to keep pushing for gender equity.

-
Harvard to launch center for autism research
Created with $20 million gift, the Hock E. Tan and K. Lisa Yang Center for Autism Research at Harvard Medical School will aim to unravel the basic biology of autism and related disorders.

-
Specialists take on opioid crisis
A conference sponsored by Harvard and the University of Michigan will examine the role that stigma plays in the nation’s opioid crisis and ways it slows and alters responses.

-
Michael Pollan wants to change your mind
Author and Harvard professor Michael Pollan talks about his new book on psychedelic drugs, “How To Change Your Mind,” at HubWeek.

-
You are what you eat — and how you cook it
Scientists have recently discovered that different diets — say, high-fat versus low-fat, or plant-based versus animal-based — can rapidly and reproducibly alter the composition and activity of the gut microbiome, where differences in the composition and activity can affect everything from metabolism to immunity to behavior.

-
Omega-3 fish oil rises to top in analysis of studies
Harvard study finds that greater cardiovascular benefits may be achieved at higher doses of omega-3 fish oil supplementation.

-
Expressing genes
Harvard University staff member Marnie Gelbart is the director of programs for the Personal Genetics Education Project (pgEd) at Harvard Medical School, and is a co-principal investigator of Building Awareness, Respect, and Confidence through Genetics (ARC), a five-year NIH-funded project through which pgEd is developing curricula on identity and inclusion working with teachers in urban Massachusetts and rural South Dakota communities.
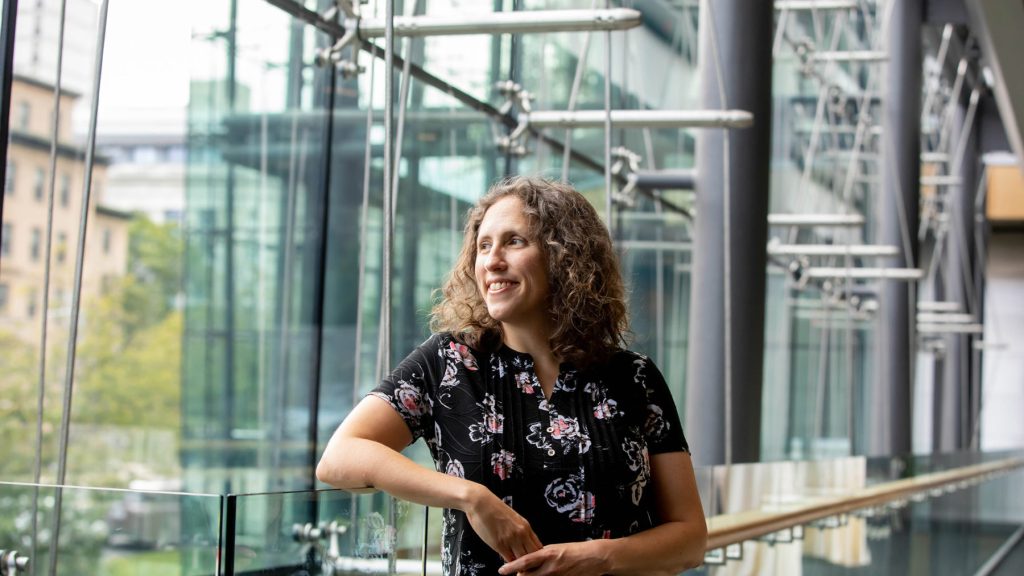

-
Trust, belonging, keys to mental health of students of color
Experts gathered at the Harvard Chan School said despite progress at making college student bodies more diverse, work still needs to be done to make students of all backgrounds feel welcome, a key step in heading off increased rates of mental illness such students experience on campus.

-
Protein, fat, or carbs?
Researchers applied new techniques to old samples from a 2005 dietary study to show that a focus on eating healthy rather than obsessing over a single nutrient can improve heart health.

-
PTSD linked to increased risk of ovarian cancer
A new study finds that women who have greater numbers of PTSD symptoms are at an increased risk of developing ovarian cancer.

-
Mental health as a diversity issue
Faculty of Arts and Sciences Diversity Summer Panel focuses on the impacts of mental illness in the workplace and what can be done about it.
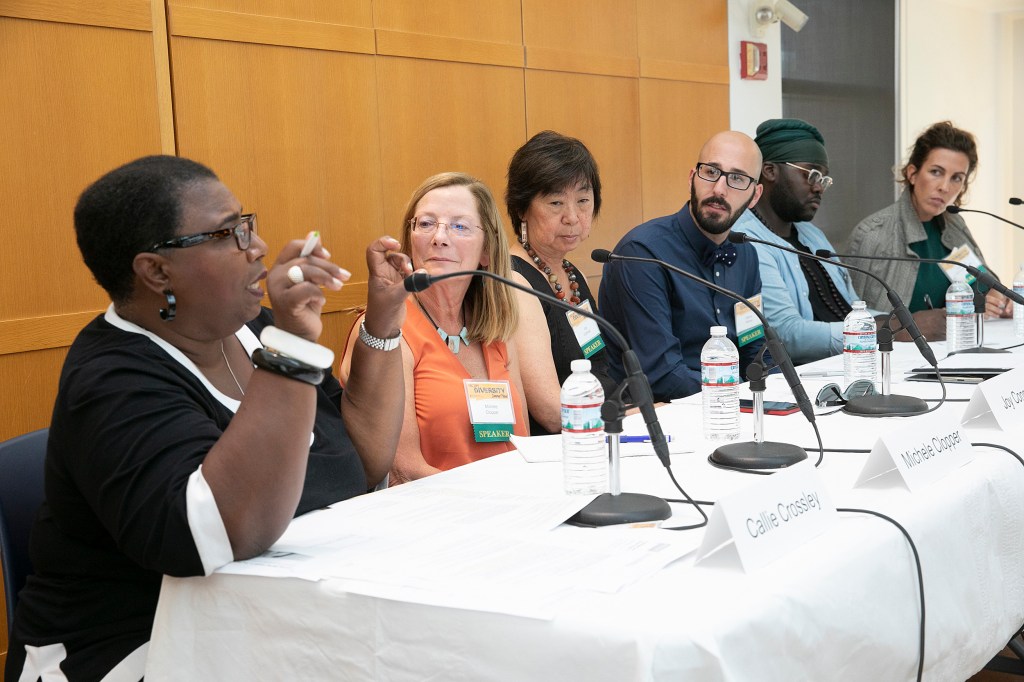

-
Probiotic hydrogels heal gut wounds that other treatments can’t reach
Harvard researchers have developed hydrogels that can be produced from bacterial cultures and applied to intestinal surfaces for faster wound healing.
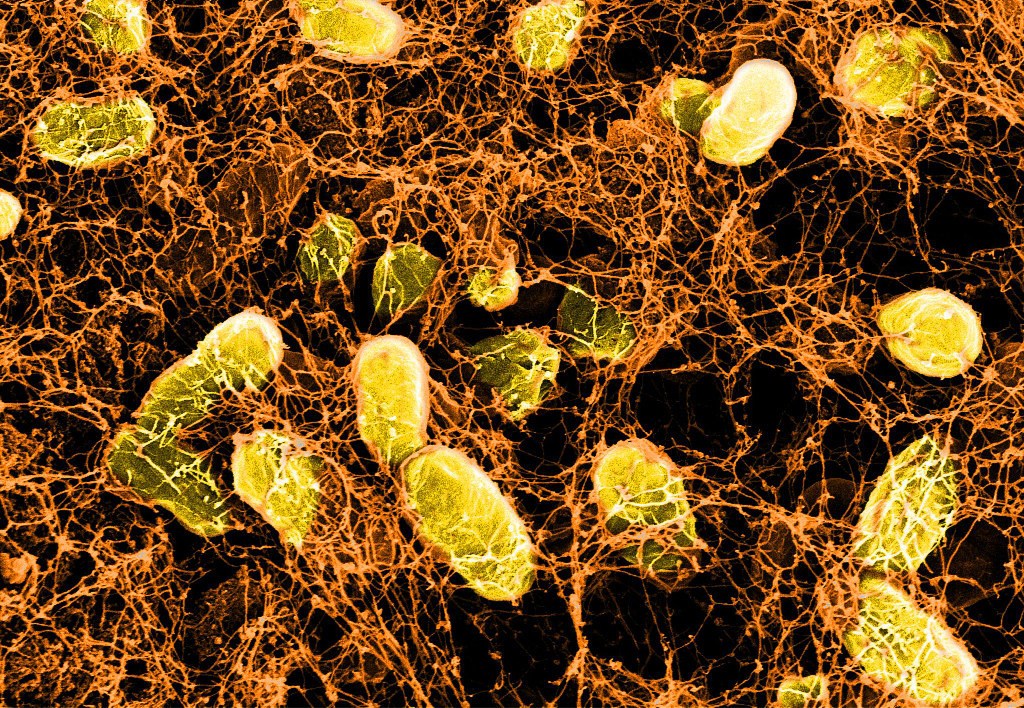
-
At the corner of med and tech
Undergraduate Michael Chen, who created an extraordinary program to help treat TB, also works with a student program to treat ordinary patients.
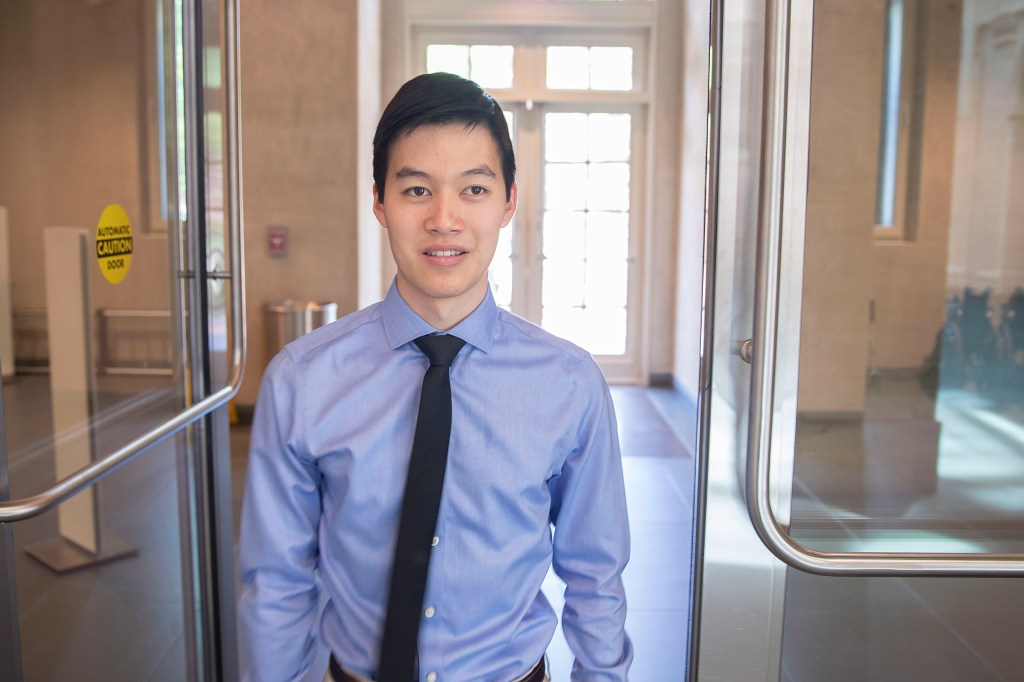

-
What fuels prejudice?
A postdoctoral fellow working in the lab of Psychology Professor Matt Nock,Brian O’Shea is the lead author of a study that suggests racial tension may stem not from different groups being exposed to each other, but fear of a different sort of exposure — exposure to infectious diseases. The study is described in a July 15 paper published in Social Psychological and Personality Science.
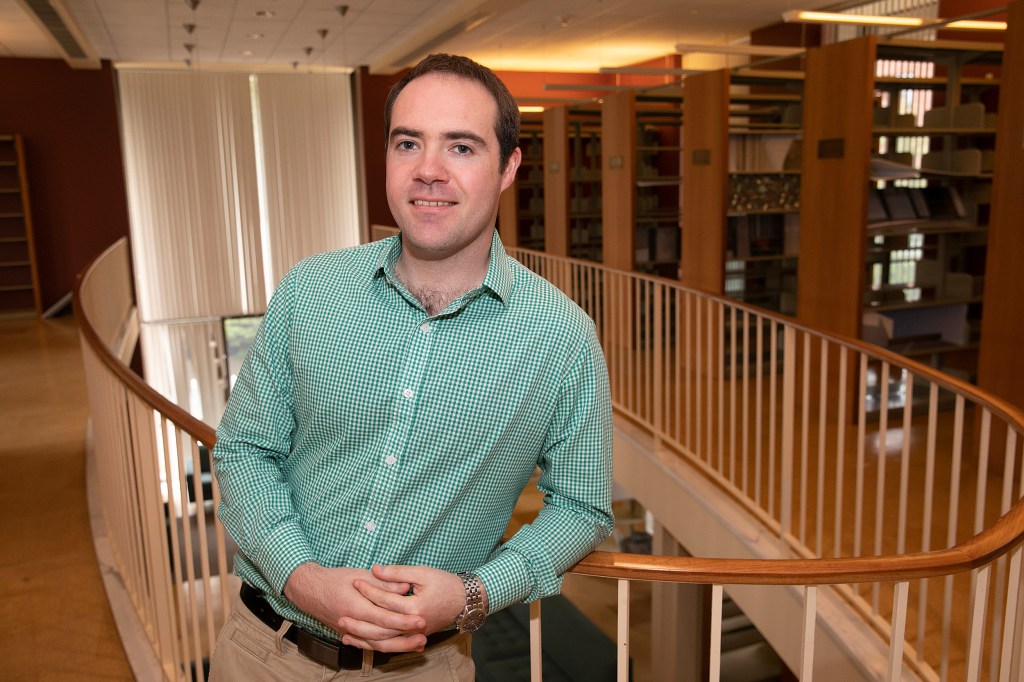

-
CBD rollout shines light on Wild West of supplements
A marijuana derivative called cannabidiol, or CBD, has begun making its way into supplements and even into foods, a use that runs afoul of an FDA designation of the compound as a prescription drug. A Harvard Medical School associate professor says CBD’s tangled legal status may provide an opportunity not only to clear up its status, but to bring clarity to the entire supplements industry.

-
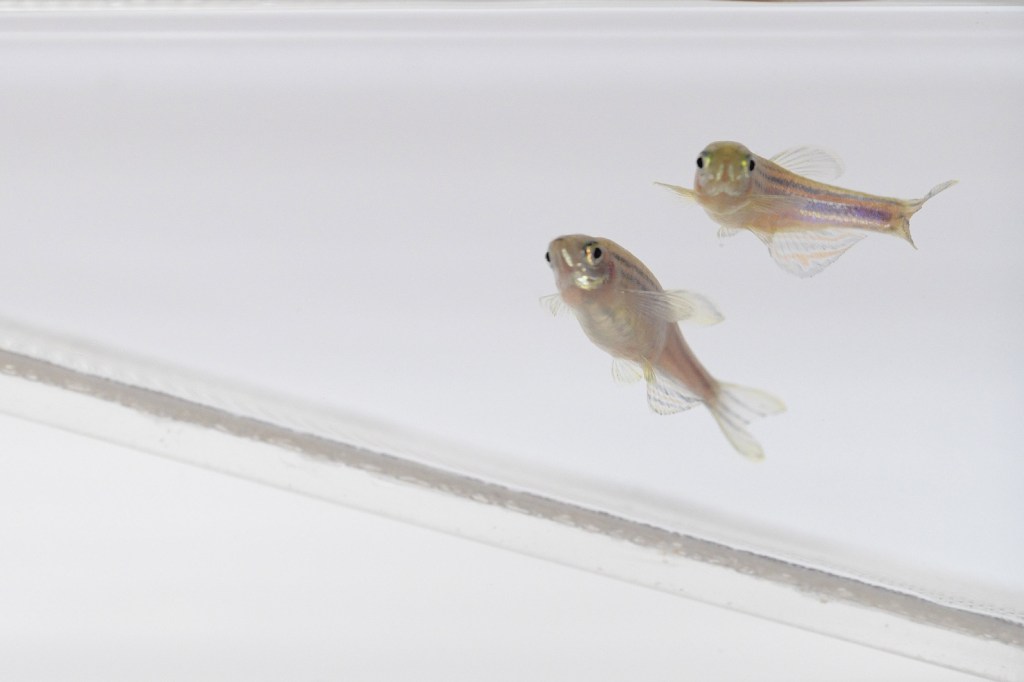
How biology affects behavioral decisions
Researchers have found that when making decisions that are important to the species’ survival, zebrafish choose to mate rather than to flee from a threat.

-
Want to quit smoking? There’s the e-cigarette
A new study provides critical population-level evidence demonstrating that using e-cigarettes daily helps U.S. smokers to quit smoking cigarettes.

-
Growing support for plant-based diet
A new meta-analysis shows that people who follow predominantly plant-based diets with greater adherence have a 23 percent lower risk of developing Type 2 diabetes than those who follow these diets with lower adherence.

-
It takes a community to make compost
Harvard’s Arnold Arboretum partners with local businesses on environmentally responsible composting program.

-
Treating runaway health costs
Study led by Harvard researchers finds that a long-term trial of a capped-payment system encouraged preventative care and discouraged unnecessary spending


