Health
-
Lin Test
text with link. This is a quiz. Some text Name Name Quo modo autem philosophus loquitur? Tecum optime, deinde etiam cum mediocri amico. Invidiosum nomen est, infame, suspectum. Name Name…
-

Gender-affirming care is rare, study says
Fewer than 1 in 1,000 transgender youth receive hormones or puberty blockers

-

Nature offers novel approach to oral wound care
Slug’s sticky mucus inspiration behind adhesive hydrogel that can seal wounds in wet environment

-

Time for a rethink of colonoscopy guidelines?
Change informed by new findings would help specialists focus on those most at risk, researcher says

-
Should pharmacists be moral gatekeepers?
‘The problem is not opioids,’ says author of ‘Policing Patients’ — it’s overdose, pain
-

The deadly habit we can’t quite kick
Actions by tobacco companies worry researcher even amid ‘dramatic decrease’ in smoking among young Americans

-
U.S. men die nearly six years before women, reflecting largest gap since 1996
Analysis finds COVID-19 and ‘deaths of despair’ behind trend that has been growing since 2010

-
Benefits of work-life balance extend to heart health, study suggests
Intervention benefits older, lower-wage workers at higher risk, novel Chan School study finds

-
Waistline growing? Eat more veggies — but not this kind.
Study adds starchy variety to list of culprits contributing to middle-age weight gain

-
Research shows working out gets inflammation-fighting T cells moving
Activated by regular exercise, immune cells in muscles found to fend off inflammation, enhance endurance in mice

-
How being stigmatized can harm health
Professor of Psychology Mark L. Hatzenbuehler’s course, “Stigma, Discrimination, and Health,” examines the wide-ranging problem that touches on sexuality, body weight, immigration, and poverty.

-
Hot yoga potent antidepressant in study
In a randomized controlled clinical trial, heated yoga sessions led to reduced depressive symptoms in adults with moderate-to-severe depression.

-
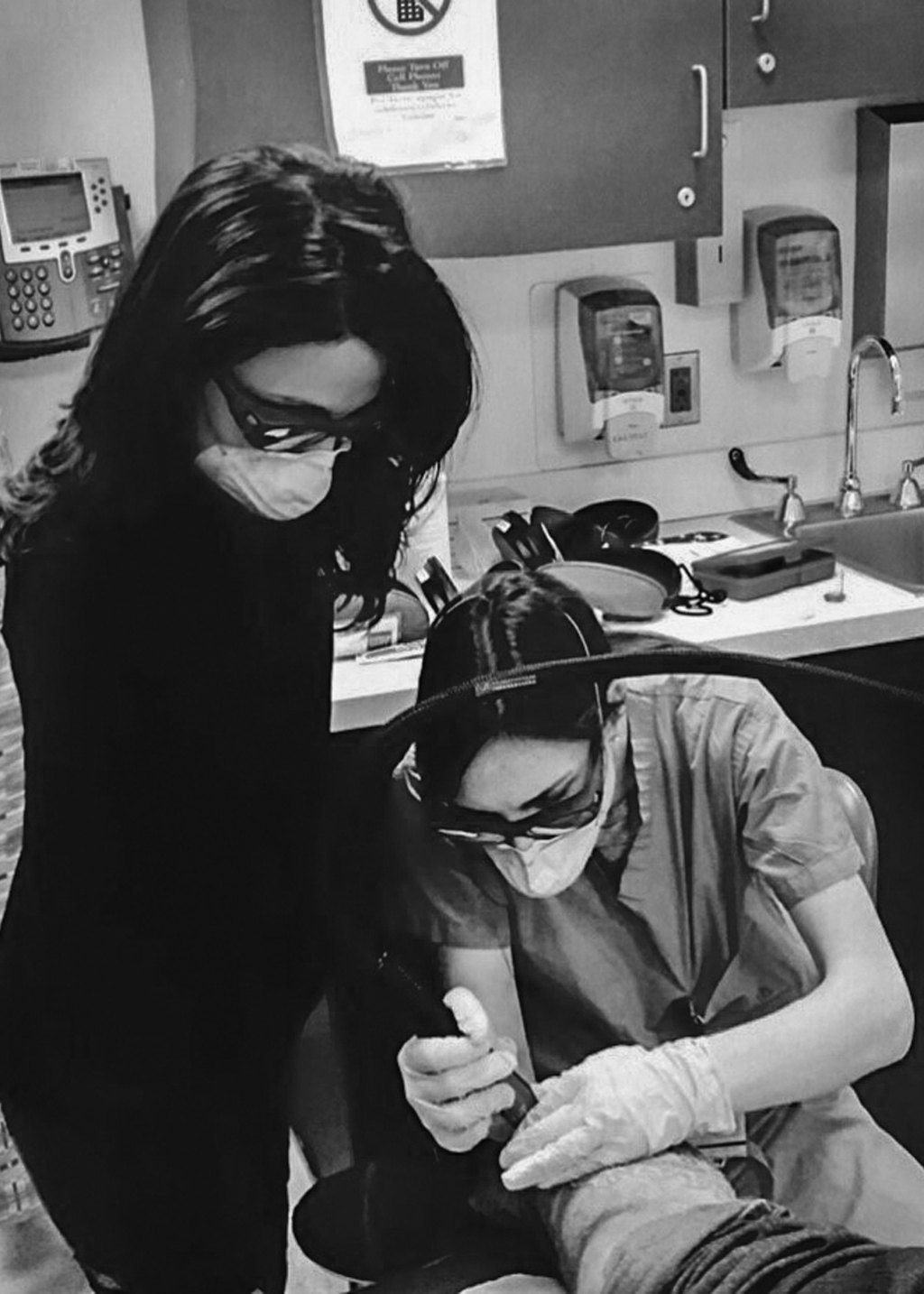
Erasing reminders of stigmatizing, traumatic past
Harvard Medical School-Mass General dermatologists use lasers to remove gang, trafficking tattoos, stigmatizing and often traumatic reminders of the past.

-
Worries about depressed men and IVF are unfounded
New study reveals no correlation between anxiety, regardless of antidepressant use, and IVF outcomes or live birth rate.
-
Study finds link between breastfeeding, rise in adult colorectal cancer risk
Mothers should not halt practice of breastfeeding, which offers many benefits to infants, as much more research is still needed, scientists say.
-
You think you’re fighting your anxiety, but you’re making it worse
An emotion many avoid and view as an illness may actually help us thrive, psychologist David Rosmarin says.

-
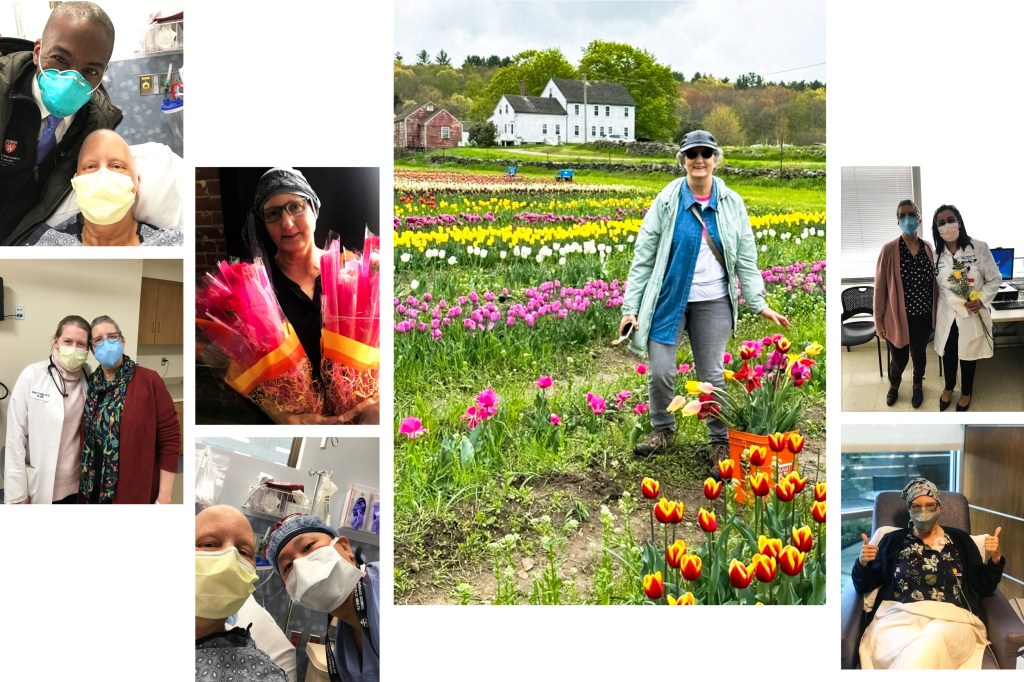
Gift of tulips: Surviving breast cancer
Bobbie Collins, a writer for Harvard Medical School, shares a firsthand account of her bout with the disease.

-
How social isolation, loneliness can shorten life
A new study shows that social isolation and loneliness are not same thing but can be connected, sometimes in surprising ways.

-
Wedding gift from her doctors — the ability to smile again
A complicated brain tumor surgery left Rebecca Grasso with facial paralysis. But thanks to a series of nerve transfers at Harvard-affiliated Mass Eye and Ear, she was able to smile at her wedding.

-
Less rest, more stress for the weary
New study highlights a correlation between women who sleep less than eight hours at night and developing a greater risk for hypertension or high blood pressure.

-
Tab for liver disease tied to drinking projected to double over 20 years
Researchers say planners, policymakers need to be looking to ramp up intervention programs, improve treatment.

-
Is organic better?
Not if you follow the evidence, researcher says

-
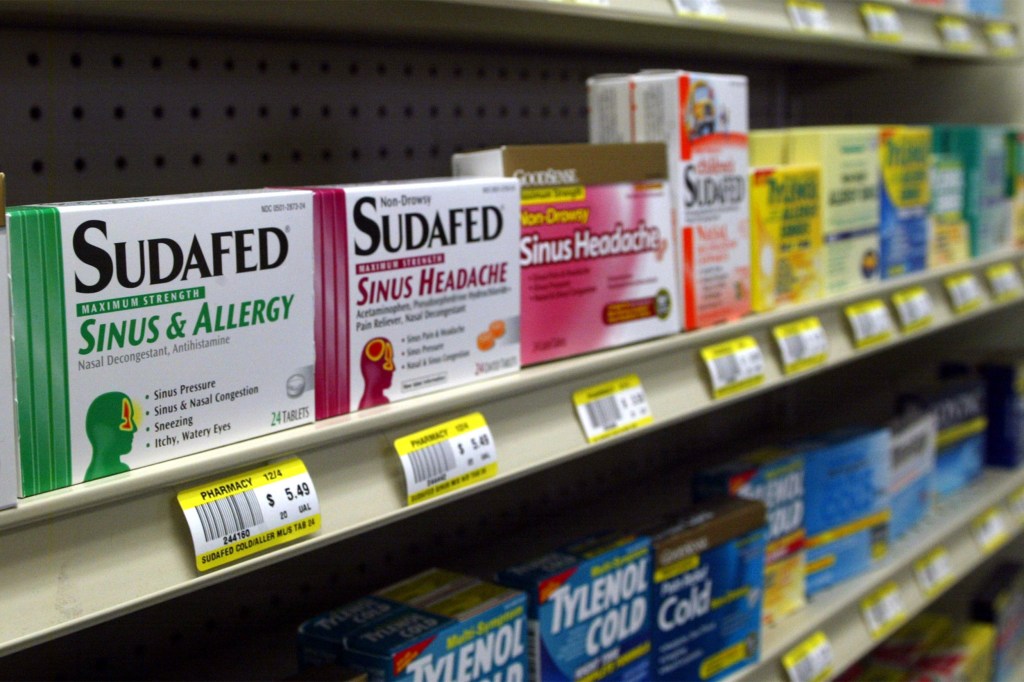
Why are ineffective oral decongestants still on store shelves?
Drug regulation expert explains how the problem was discovered, next steps for FDA, and the questions it raises about other products, supplements.

-
Not getting enough sleep? That’s only half the battle.
Researchers find regularity also plays key role in long-term health and daily performance.

-
Seizing the chance to stop a suicide
New Harvard-MGH initiative to provide caregivers with lab-tested tools for identifying, treating those most at risk.

-
The night owl’s disease problem
A new study has an important message for night owls.

-
Next spat with your partner, try silence
If you’re doing all the talking, then you’re probably doing it wrong, says negotiation expert.

-
Think twice before saying ‘cult’
Survey shows intense support for ex-president in face of indictments, but common claim among MAGA critics falls short of scientific rigor.

-
These doctors aren’t sweating AI — yet
Board exam for pediatric specialty stumps ChatGPT, at least in some areas.

-
How durable is your immunity?
William Hanage, an associate professor of epidemiology, talks about hybrid protection, vulnerability of older people, and the wisdom of Taylor Swift.

-
Microdevices turn brain tumors into tiny labs
A microdevice has been designed that can be implanted into tumors to conduct dozens of experiments at once to study the effects of new treatments on some of the hardest-to-treat brain cancers.

-
Surge in ‘abortion travelers’ to Mass. post-Dobbs
Women are traveling from states as far away as Texas for care, finds Brigham and Women’s study.
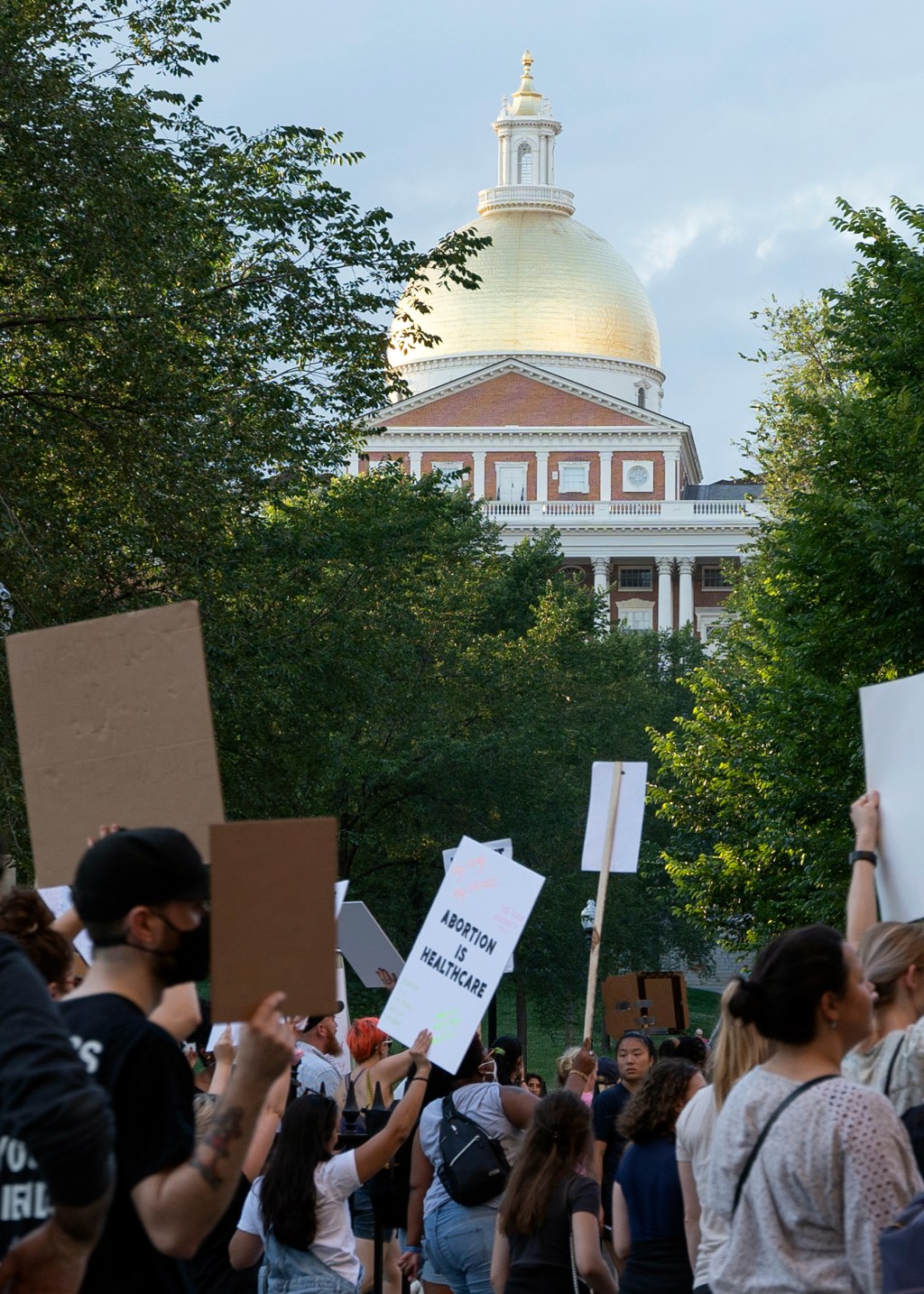
-
Need cancer treatment advice? Forget ChatGPT
New research finds in about a third of the cases AI chatbot provided medically inappropriate recommendations for cancer treatment.

-
The eye as we’ve never seen it
Researchers’ atlas pinpoints where disease-causing genes are expressed, raising hope for inroads against glaucoma and macular degeneration.

-
Engineered probiotic developed to treat multiple sclerosis
Researchers are working on a new approach to target autoimmunity in the brain — a condition at the core of several diseases, including multiple sclerosis.
-
The road that ends with Alzheimer’s
Genetic detective work sheds light on SORL1 gene offering possible new treatments, especially for patients not responsive to existing therapies.