Health
-
Lin Test
text with link. This is a quiz. Some text Name Name Quo modo autem philosophus loquitur? Tecum optime, deinde etiam cum mediocri amico. Invidiosum nomen est, infame, suspectum. Name Name…
-

Gender-affirming care is rare, study says
Fewer than 1 in 1,000 transgender youth receive hormones or puberty blockers

-
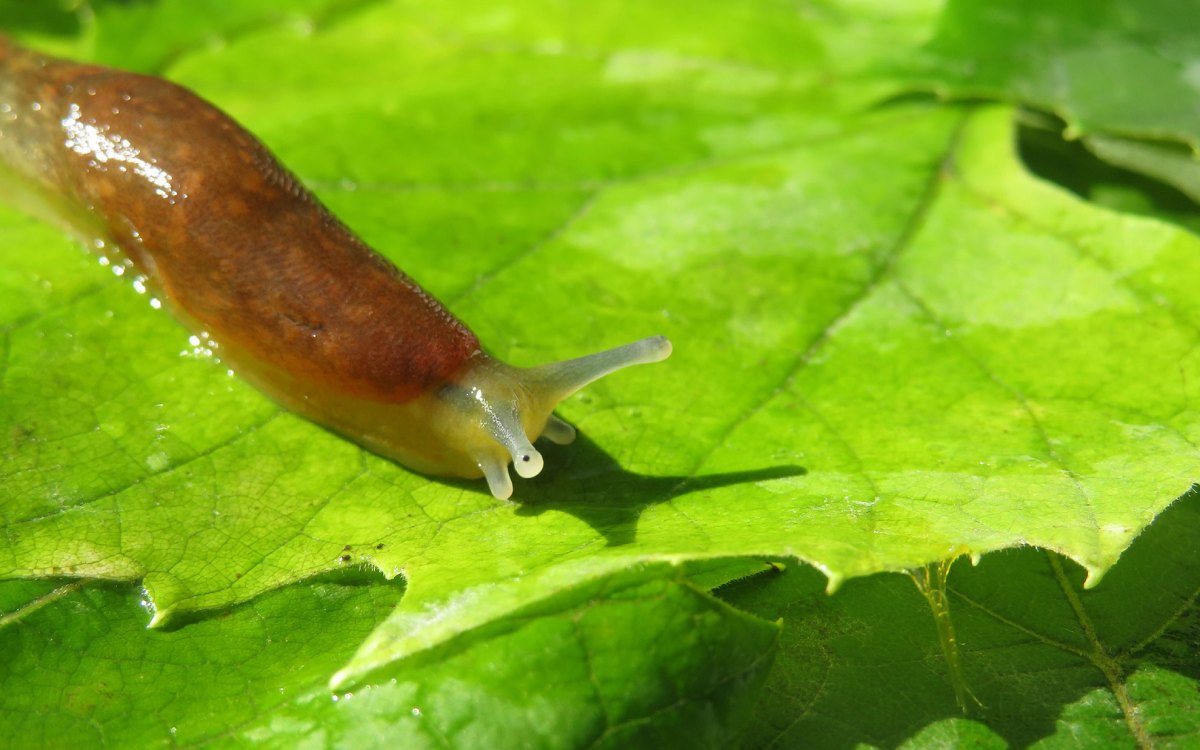

Nature offers novel approach to oral wound care
Slug’s sticky mucus inspiration behind adhesive hydrogel that can seal wounds in wet environment

-

Time for a rethink of colonoscopy guidelines?
Change informed by new findings would help specialists focus on those most at risk, researcher says

-
Should pharmacists be moral gatekeepers?
‘The problem is not opioids,’ says author of ‘Policing Patients’ — it’s overdose, pain
-

The deadly habit we can’t quite kick
Actions by tobacco companies worry researcher even amid ‘dramatic decrease’ in smoking among young Americans

-
60 minutes of exercise per day needed for middle-aged women to maintain weight
If a middle-aged or older woman with a normal body mass index wants to maintain her weight over an extended period, she must engage in the equivalent of 60 minutes…
-
Replacing those saturated fats
In a new study, researchers at the Harvard School of Public Health find that replacing saturated fats with polyunsaturated ones is likely to help reduce the risk of heart disease.

-
Polyunstaturated fats may cut risk of heart disease
Although for nearly 60 years people have been urged to decrease their consumption of saturated fats to prevent heart disease, there has been surprisingly little scientific evidence that doing so actually decreases the risk of coronary heart disease events
-
“Good” cells can go “bad” in a “bad neighborhood”
Normal.dotm 0 0 1 375 2142 Harvard University 17 4 2630 12.0 0 false 18 pt 18 pt 0 0 false false false The general theory of cancer development holds…
-
Playing on our instincts
Assistant clinical professor of psychology Deirdre Barrett says that many of today’s ills come from intentional overstimulation of natural human impulses, giving people hard-to-resist appetites for everything from fighting to sex to unhealthy foods.

-
Epstein-Barr Virus implicated as a cause of MS
Researchers from the Harvard School of Public Health, Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, and a team of collaborators have observed for the first time that the risk of multiple…
-
War-related stress associated with increased risk of asthma
The trauma experienced during war may increase the risk of developing asthma, according to the results of a new study by Harvard researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH), Harvard…
-
Right this way! See it! Taste it!
Former FDA commissioner David Kessler says overeating has to be attacked the same way that tobacco was in the past, by making it socially unacceptable.

-
Alzheimer’s-associated protein may be part of the innate immune system
Amyloid-beta protein – the primary constituent of the plaques found in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients – may be part of the body’s first-line system to defend against infection.…
-
It’s all in the cortex
Research suggests that the brain’s lateral prefrontal cortex plays an important role in showing how well someone can rebound emotionally the day after an argument.

-
Infant mortality down, ailments persist
José Cordero, dean of the University of Puerto Rico’s School of Public Health, said that the progress made in the 20th century on infant mortality has revealed new health concerns stemming from that success: how to reduce birth defects and provide care for the greater number of children who are surviving them.

-
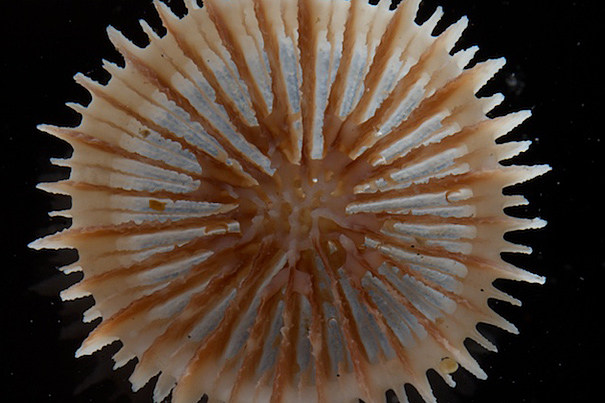
Deep thinking
The Museum of Comparative Zoology’s invertebrate collection continues to expand, as biology professor Gonzalo Giribet brings home samples from the deep ocean in the North Atlantic.

-
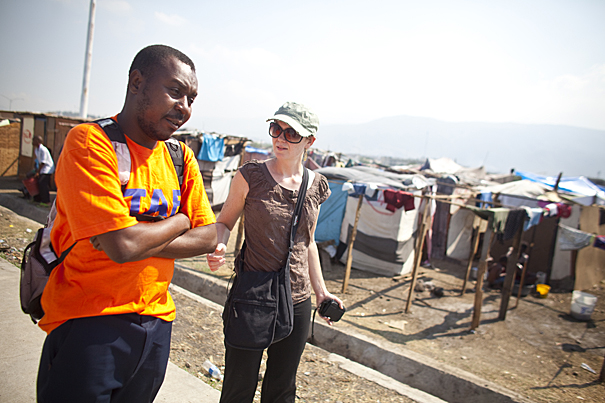
Reflections on a catastrophe
Assistant Professor of Medicine Louise Ivers shares her story of being caught in the Jan. 12 earthquake that devastated Port-au-Prince, Haiti.

-
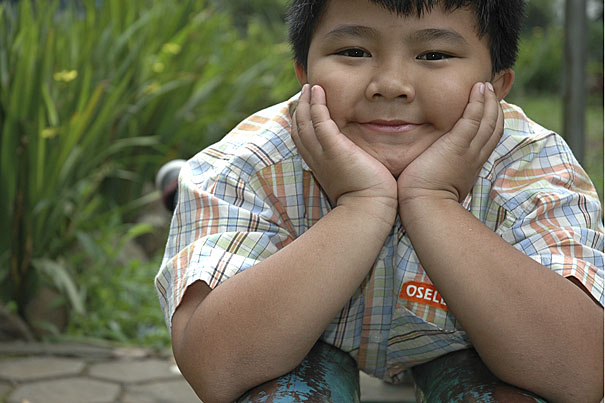
Weighing the risk factors
Risk factors for childhood obesity may be evident before birth and are more likely to occur in African-American and Hispanic children than in Caucasian children. Researchers studied 1,826 mother-child pairs from pregnancy through the child’s first five years of life.

-
Efforts to prevent childhood obesity must begin early
Normal 0 0 1 751 4281 35 8 5257 11.1282 0 0 0 Efforts to prevent childhood obesity should begin far earlier than currently thought — perhaps even before birth…
-
Hey squash, time for your close-up
Bruce Smith, of the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History, discusses the rise of agriculture in a talk at the Harvard Museum of Natural History.

-
Memories are made of this
In a lecture, neuroscientist Eric Kandel ’52 said that researchers have learned that short-term memory, the ability to recall things for minutes or hours, is fundamentally different from long-term memory, which holds information for weeks, months, even a lifetime.

-
Report from Haiti
Nearly a month after a massive earthquake devastated Haiti, paramedic Anthony Croese looked into the crowd outside a destroyed orphanage near Port-au-Prince and spotted an emaciated baby cradled in his father’s arms.
-
A molecule that destroys normal metabolism is found
Overeating in mice triggers a molecule once considered to be only involved in detecting and fighting viruses to also destroy normal metabolism, leading to insulin resistance and setting the stage…
-
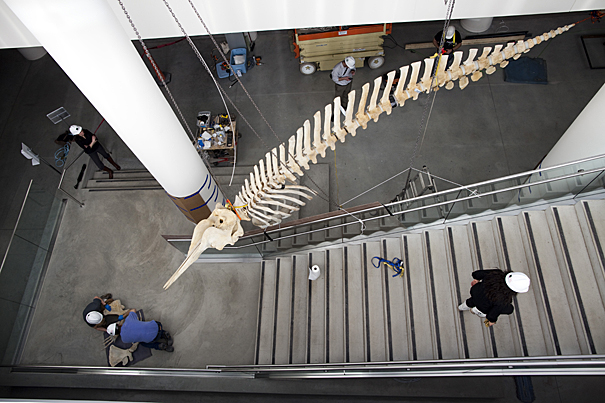
New life for old whale exhibit
Skeletons of whales diving and breaching are enlivening the lobby of Harvard’s new Northwest Laboratory building, bringing the killer whale and bottlenose whale specimens new prominence more than 70 years after they were last exhibited.

-
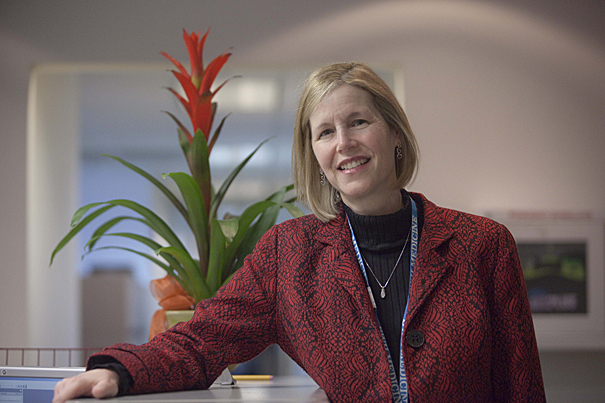
The hunt for healthy answers
JoAnn Manson leads a nationwide study to assess whether vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids can boost immunity and protect against ailments from heart disease to cancer.

-
Open innovation challenge seeks solutions to type 1 diabetes
The best scientific insights, which ultimately may lead to the solution of the world’s great puzzles, do not always come from the experts in the fields in question. Sometimes they…
-
Looking at cooking
Harvard biology professor Richard Wrangham talks about the importance of cooking in human origins.

-
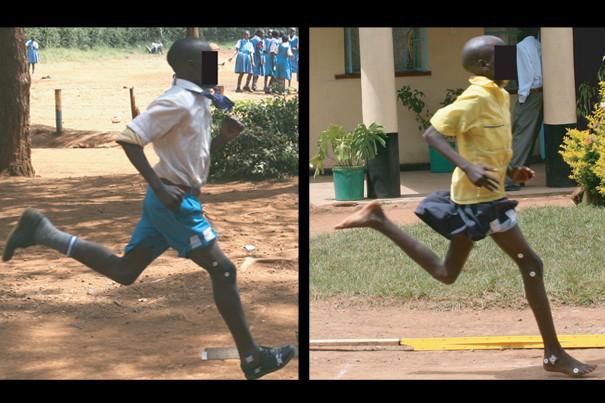
Perfect landing
New research suggests that barefoot running is far less stressful on feet than running in shoes, if runners learn how to alter their strides properly to reduce impact.

-
Blood tells old cells to act young
Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI) researchers at the Joslin Diabetes Center (JDC) have taken a major step toward eventually understanding — and perhaps slowing — the aging process. In a series…
-
Genes linked to breast cancer drug resistance
Harvard researchers at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have discovered a “gene activity signature” that predicts a high risk of cancer recurrence in some breast tumors that have been treated with…
-
U.S. birth weights dip
A study that analyzed data from 36,827,828 U.S. babies born at full-term between 1990 and 2005 has found that birth weights decreased by up to 2.78 ounces during that time frame.

-
Study finds decline in birthweight of full-term infants
Thirteen-pound babies may make headlines, but they aren’t the norm. In fact, U.S. infants are getting smaller, according to Harvard researchers at the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute’s Department of…
-
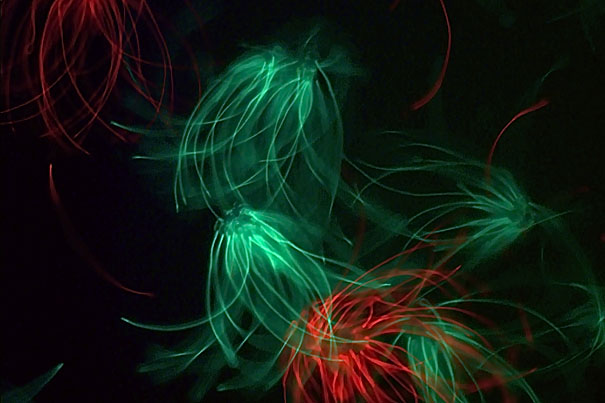
Sperm competition, cooperation
Some mouse sperm can discriminate between their brethren and the competing sperm from other males, showing an unusual behavioral complexity.

-
Zebrafish point the way
A new technique for screening drugs’ effects on zebrafish behavior is pointing Harvard University scientists toward unexpected compounds and pathways that may govern sleep in humans.


