Health
-
Lin Test
text with link. This is a quiz. Some text Name Name Quo modo autem philosophus loquitur? Tecum optime, deinde etiam cum mediocri amico. Invidiosum nomen est, infame, suspectum. Name Name…
-

Gender-affirming care is rare, study says
Fewer than 1 in 1,000 transgender youth receive hormones or puberty blockers

-

Nature offers novel approach to oral wound care
Slug’s sticky mucus inspiration behind adhesive hydrogel that can seal wounds in wet environment

-

Time for a rethink of colonoscopy guidelines?
Change informed by new findings would help specialists focus on those most at risk, researcher says

-
Should pharmacists be moral gatekeepers?
‘The problem is not opioids,’ says author of ‘Policing Patients’ — it’s overdose, pain
-

The deadly habit we can’t quite kick
Actions by tobacco companies worry researcher even amid ‘dramatic decrease’ in smoking among young Americans

-
Longevity benefits of Mediterranean diet know no boundaries
In a study of adults in the U.K., those who adhered closely to a Mediterranean lifestyle had a 29% lower risk of all-cause mortality and a 28% lower risk of cancer mortality.

-
Vaginal bacteria must eat to survive — but how?
Chemical analysis brings understudied microbiome into sharper focus.
-
Daily soft drink linked to increased risk of liver disease
Study finds women who consumed sugar-sweetened beverage daily had higher risk of developing liver cancer, chronic liver disease.

-
Mental health ills are rising. Do mood-tracking apps help?
Public health data specialist says they can raise patient awareness, but there are pitfalls.

-
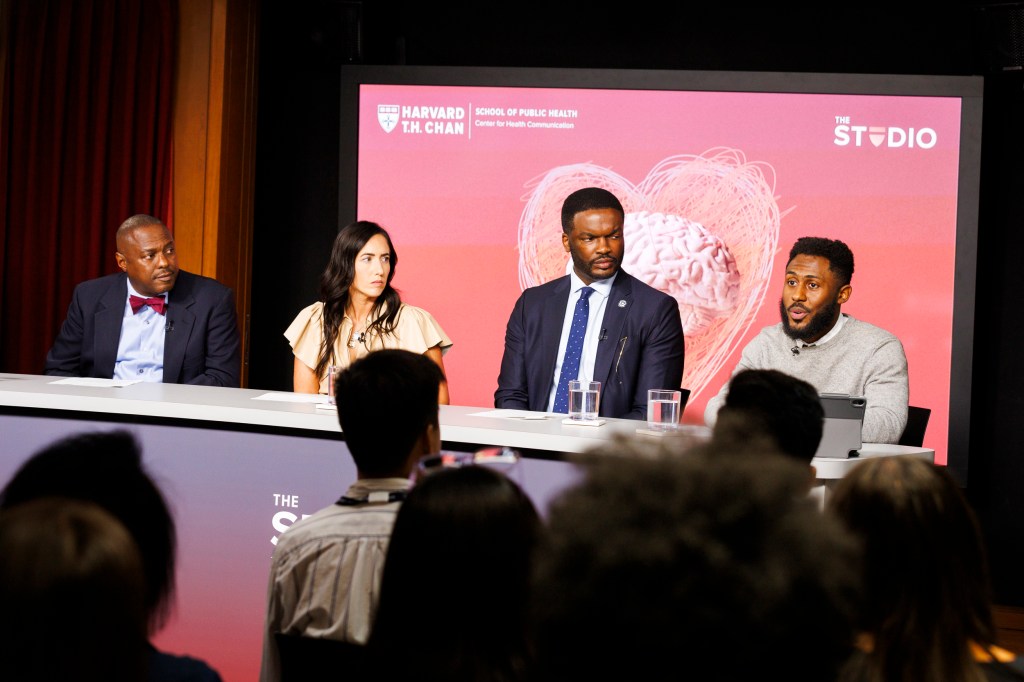
Strong, silent, and suffering inside
Mental health experts, Indianapolis Colts owner discuss efforts to end the stigma around asking for help.

-
Extending lives of old mice by connecting vessels to young ones
Connecting circulatory systems allowed animals in study to live 6-9 percent longer, lowered their biological age.

-
Turns out lowly thymus may be saving your life
Study suggests organ plays vital role in immune health, particularly cancer prevention
-
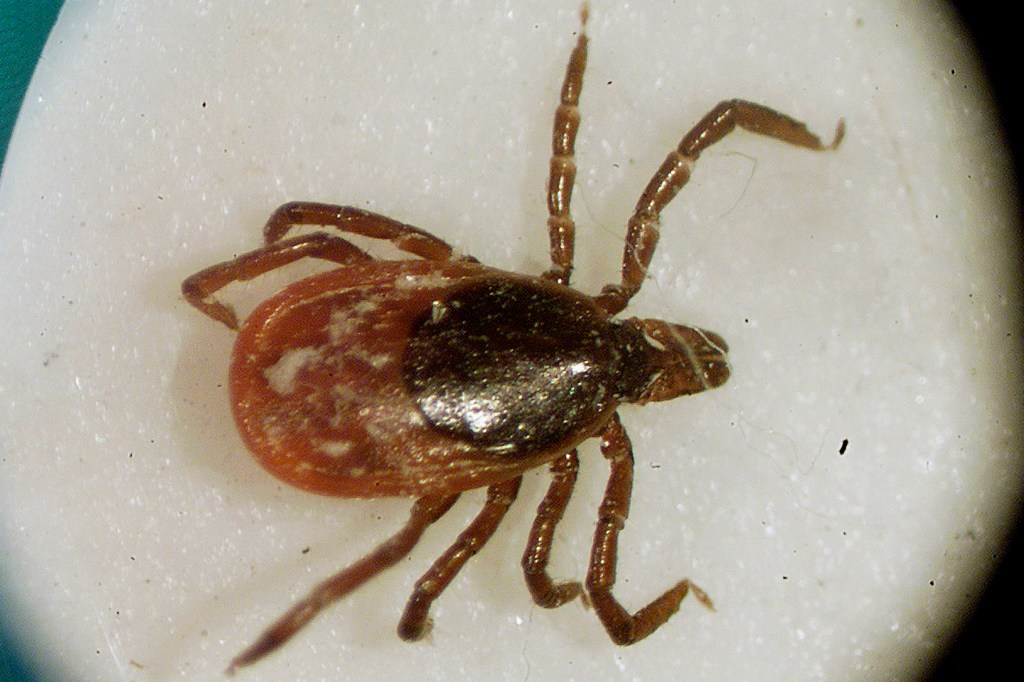
So why does my dog get Lyme disease vaccine, and I don’t?
Science can protect your dog, but not you. Expert explains why ’90s vaccine for humans disappeared and details efforts to develop a new one.

-
COVID-19 came from animals. Why aren’t we working to prevent new scourge?
A new study suggests we are as vulnerable as ever to the emergence of another virus as deadly, or even more so, than COVID-19.

-
Too busy for daily exercise? Study finds same benefits for ‘weekend warriors.’
Study finds similar health benefits for those who concentrate workouts 1-2 days a week.

-
Keep the dog cool
Science has shown that violence among monkeys, rats, and mice increases when the weather is warm. Now it seems we can add dogs to the list.

-
How did E-ZPass help expectant mothers who live near toll booths?
Anupam Jena and Christopher Worsham sift data to find hidden forces at work in healthcare in new book.

-
Are new weight-loss drugs the answer to America’s obesity problem?
Some doctors call them a godsend, particularly as part of wider treatment plan; others warn against halting research into root causes of obesity.
-
The social life of a dermatologist
It might be jarring when a friend, or complete stranger, pulls down their shirt while you’re trying to eat dinner. It’s also an opportunity.

-
Seem like Lyme disease risk is getting worse? It is.
The risk of Lyme disease has increased due to climate change and warmer temperature. A rheumatologist offers advice on how to best avoid ticks while going outdoors.

-
Another study links omega-3s and health
Alpha-linolenic acid — an omega-3 fatty acid found in many nuts, seeds, and oils — showed the strongest link to slowing the progression and premature death of people living with ALS.

-
Feeling anxious? Stuck? Problem is psychological avoidance
In her new book, professor of psychiatry Luana Marques says that too many mistake symptoms for underlying problem

-
More evidence moderate drinking is good for your heart. Also: a reason.
A new study offers an explanation for why light to moderate alcohol consumption may be associated with lower risk of heart disease.

-
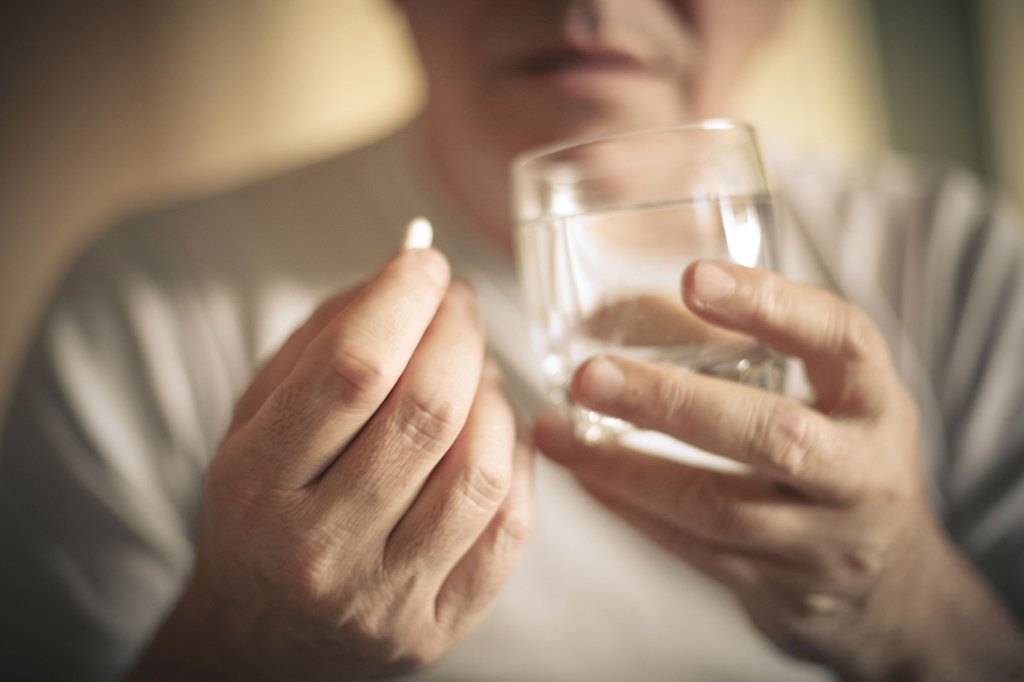
Your memory might benefit from a multivitamin
Can a simple multivitamin stave off age-related cognitive decline? A recent study says yes.

-
Birth control for cats?
A single dose of a naturally occurring hormone prevented ovulation and conception in female cats for at least two years.

-
Start of new era for Alzheimer’s treatment
Neurologist explains why recent trial of the drug lecanemab may offer hope for those with deadly disease.
-
Ketamine found effective in treating severe depression
A new study finds ketamine as effective as electroconvulsive therapy (without its major side effects) for the treatment of nonpsychotic, treatment-resistant depression.
-
The brain on ketamine
It’s a powerful antidepressant, but science needs more answers on out-of-body experiences and other “dissociative effects,” says the first author Fangyun Tian.

-
Estrogen a more powerful breast cancer culprit than we realized
A Harvard Medical School study shows the sex hormone estrogen — thus far thought to be only a fuel for breast cancer growth — can directly cause tumor-driving genomic rearrangements.
-
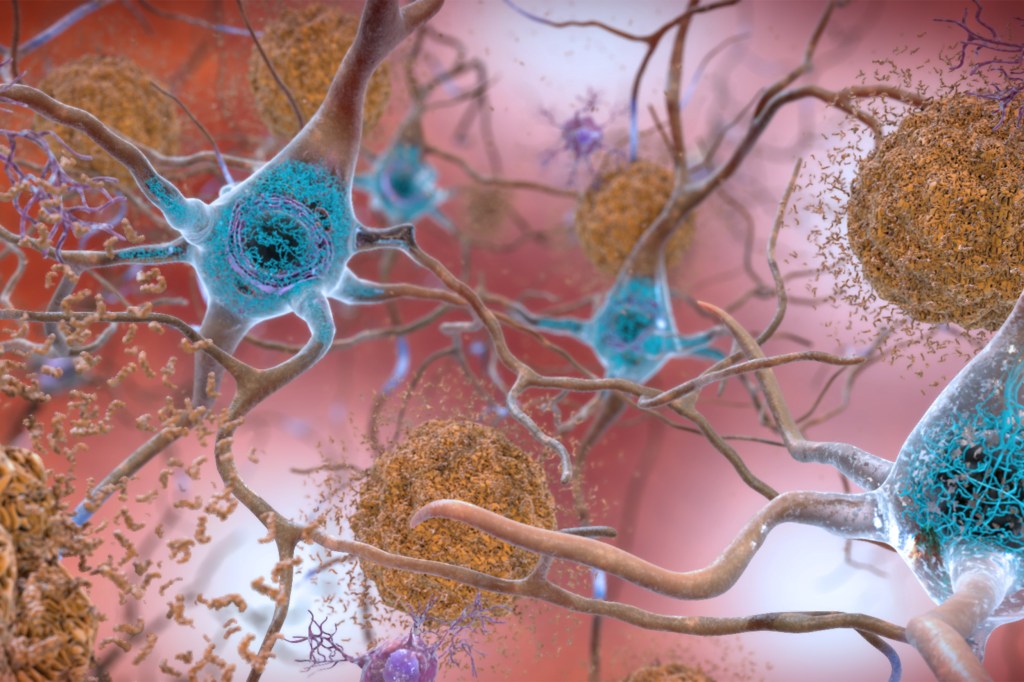
Newly identified genetic variant protects against Alzheimer’s
Researchers identified a first-of-its-kind patient with a genetic predisposition for early-onset Alzheimer’s disease who remained cognitively intact more than two decades beyond the expected age of memory impairment.
-
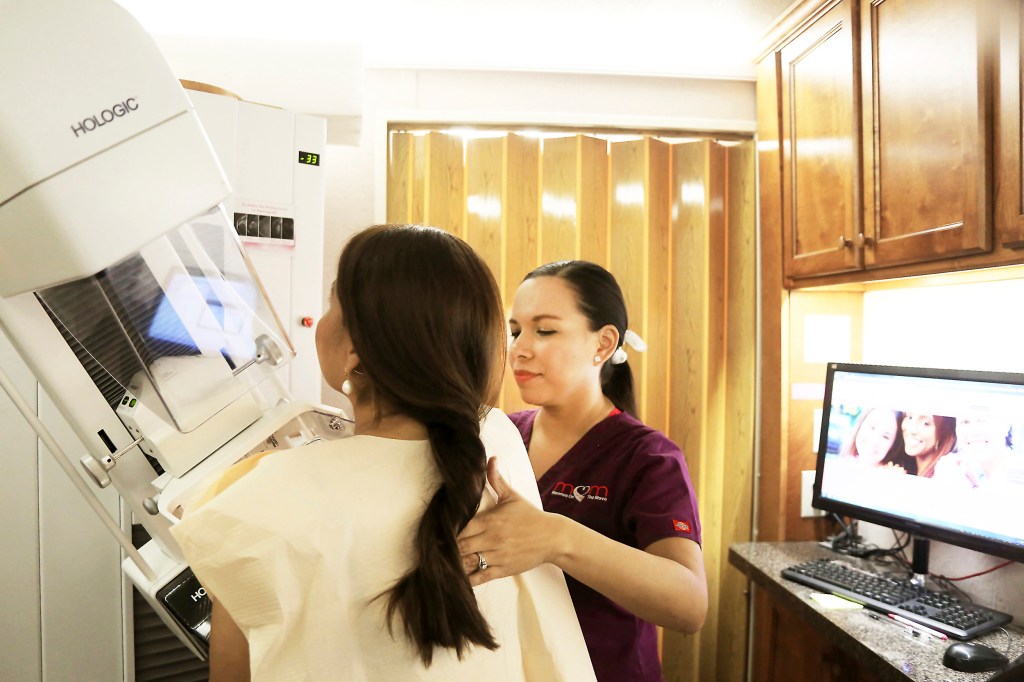
When to get first mammogram? Doctor explains latest advice.
Guidance shifts amid troubling breast cancer trends in young and Black women.
-
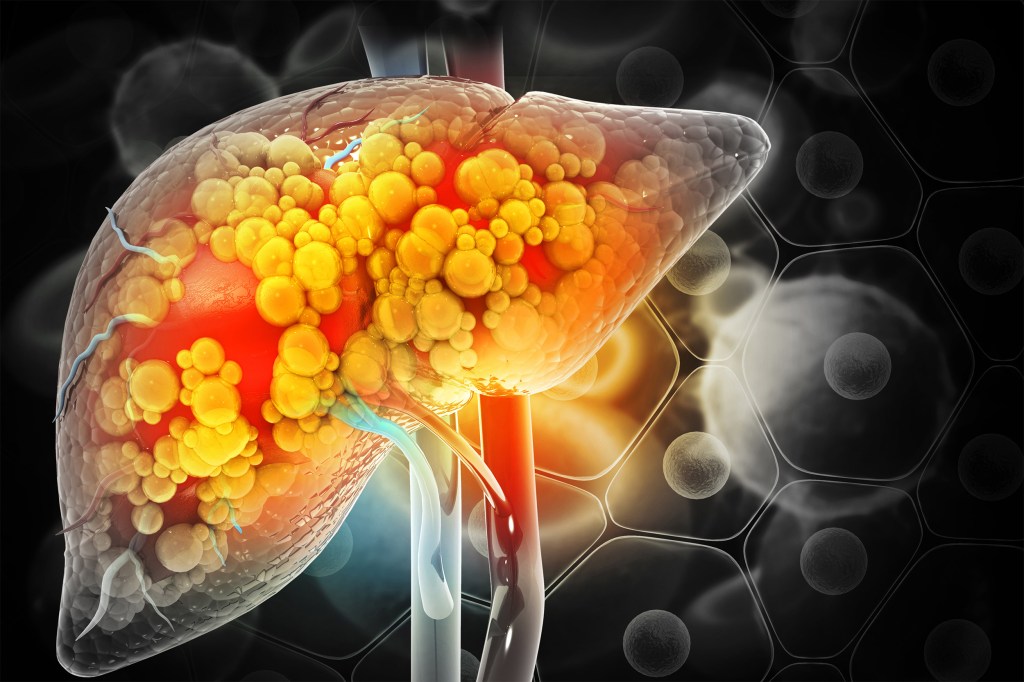
Deaths from alcohol-related liver disease soared during COVID
During the pandemic, American Indian and Alaska Native populations experienced nearly six times the mortality of white people from alcohol-associated liver disease.
-
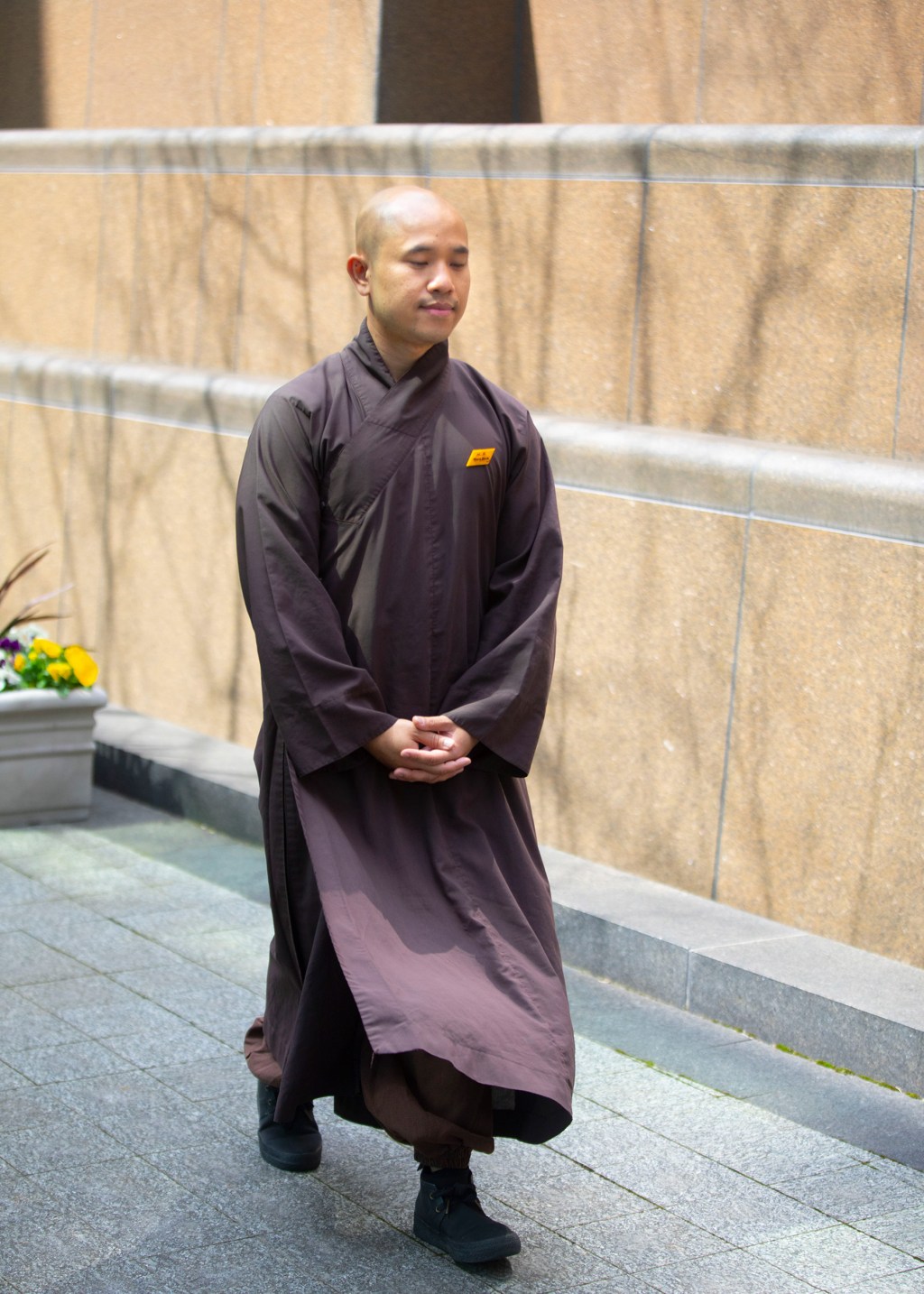
‘Happiness is not a destination … Happiness is the way’
Harvard Chan School of Public Health celebrates opening of $25 million Thich Nhat Hanh Center for research, approaches to mindfulness.

-
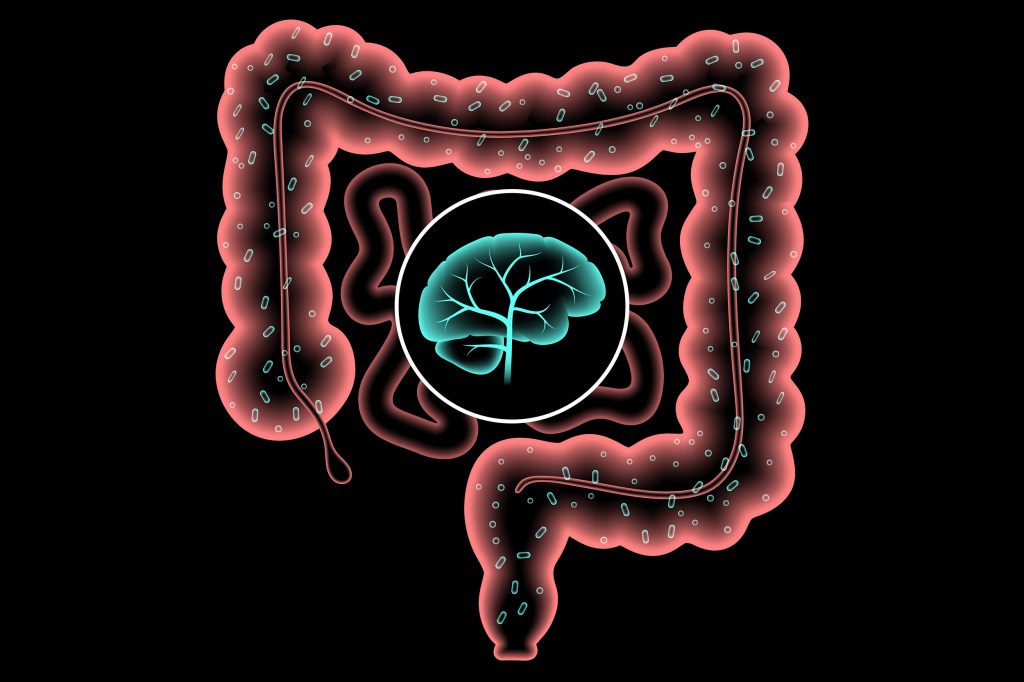
Expanding our understanding of gut feelings
Women who suppressed emotions had less diverse microbiomes in a study that also found a specific bacterial link to happiness.
-
The promising weirdness of biological age
More than you might assume, say researchers who studied three triggers of severe physiological stress: pregnancy, COVID, and surgery.