Science & Tech
-

Harsh past might bare its teeth
Early adversity leads to higher aggression and fearfulness in adult canines, study says

-

What will AI mean for humanity?
Scholars from range of disciplines see red flags, possibilities ahead
-
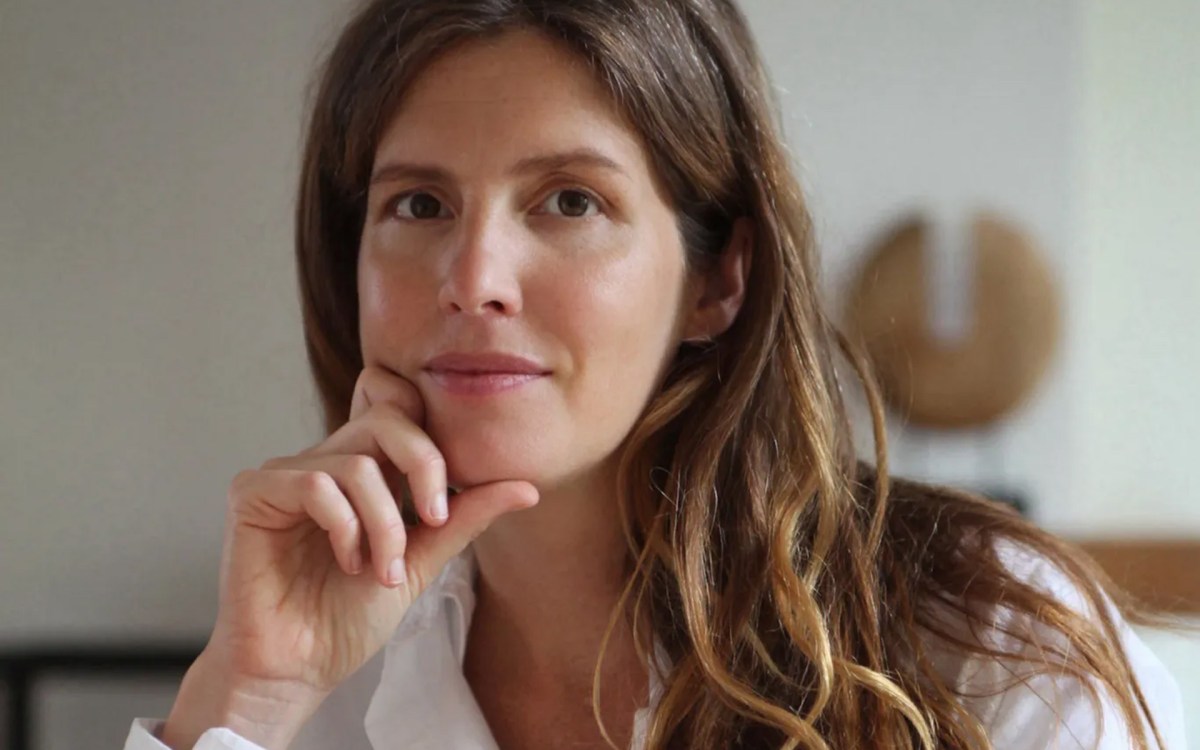

‘Human exceptionalism is at the root of the ecological crisis’
Saving the planet requires getting over ourselves, argues author of ‘The Arrogant Ape’
-
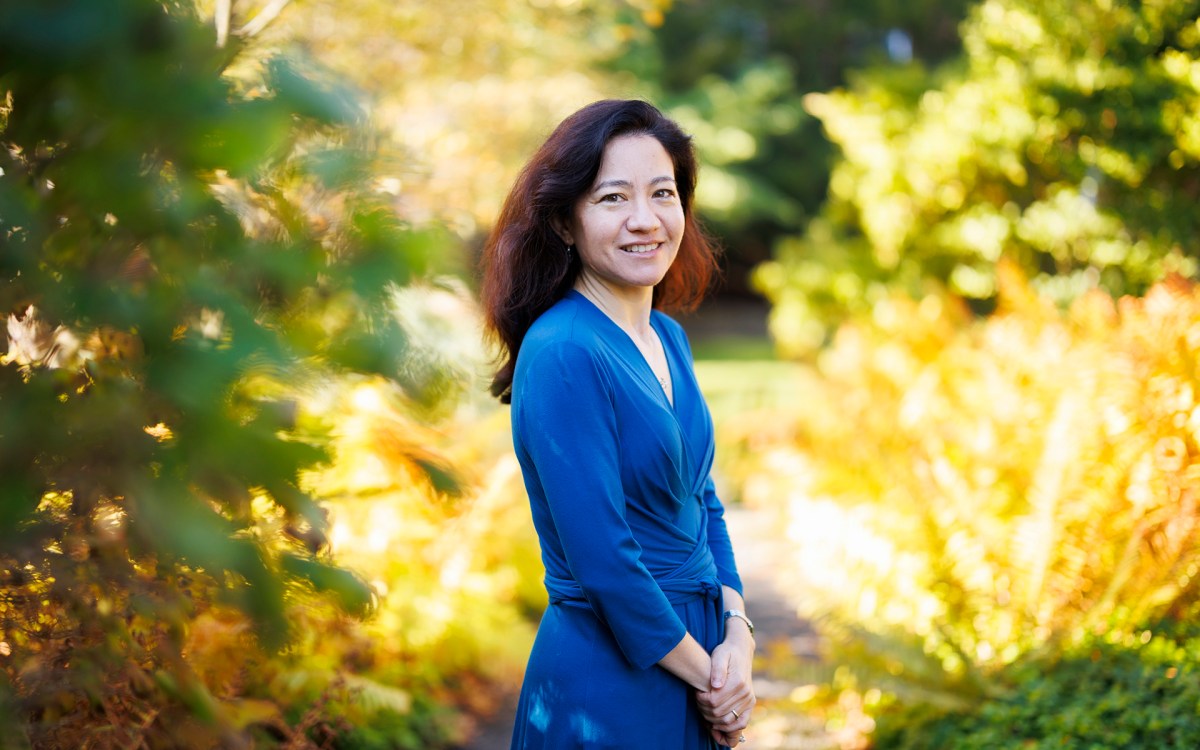

Lauren Williams awarded MacArthur ‘genius grant’
Math professor honored for theoretical breakthroughs with sometimes surprising applications across phenomena such as tsunamis, traffic
-

-
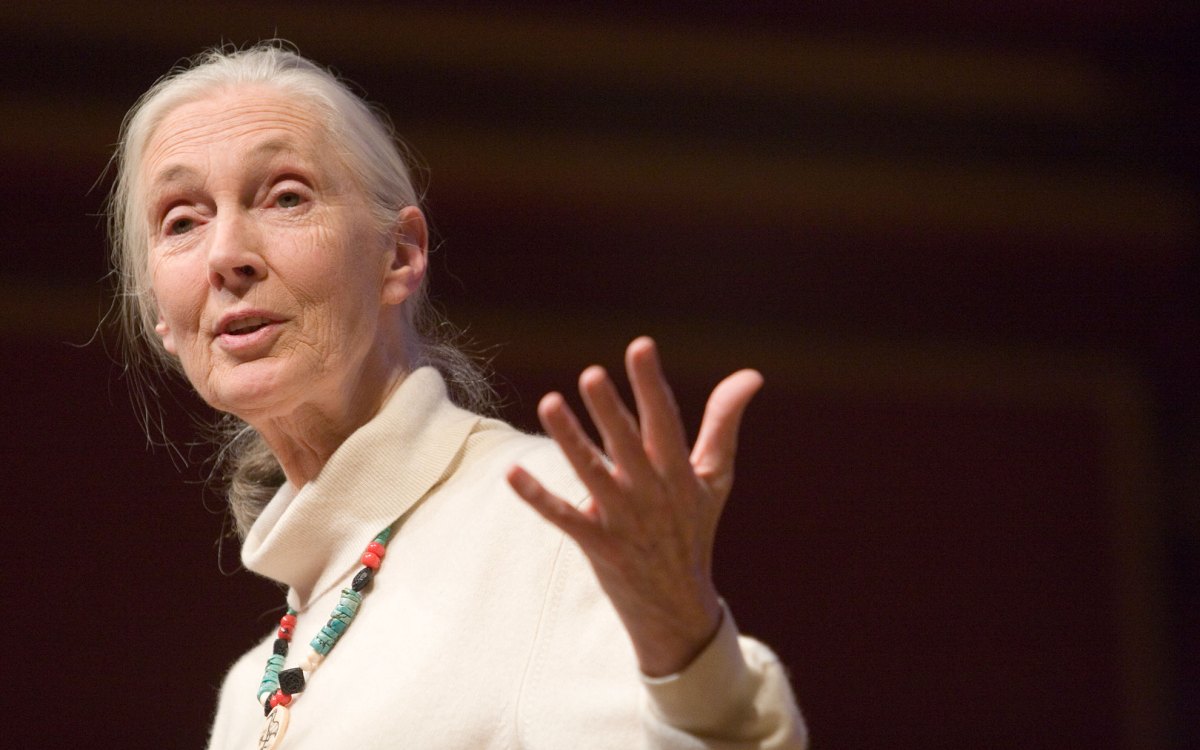

‘She had a sense of caring for everybody that she encountered.’
Richard Wrangham remembers his teacher and colleague Jane Goodall as a force of science, empathy, and hope
-
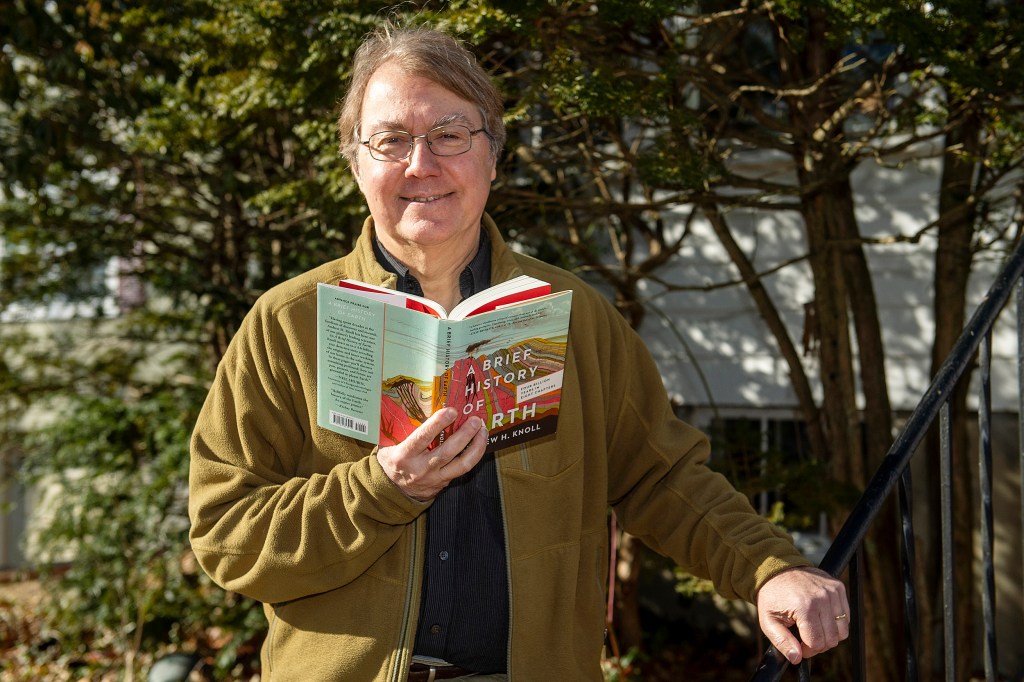
6 things to know about Earth
Andrew Knoll, Harvard’s Fisher Research Professor of Natural History and author of the recent popular science book “A Brief History of Earth: Four Billion Years in Eight Chapters,” shares six facts about the Earth.

-
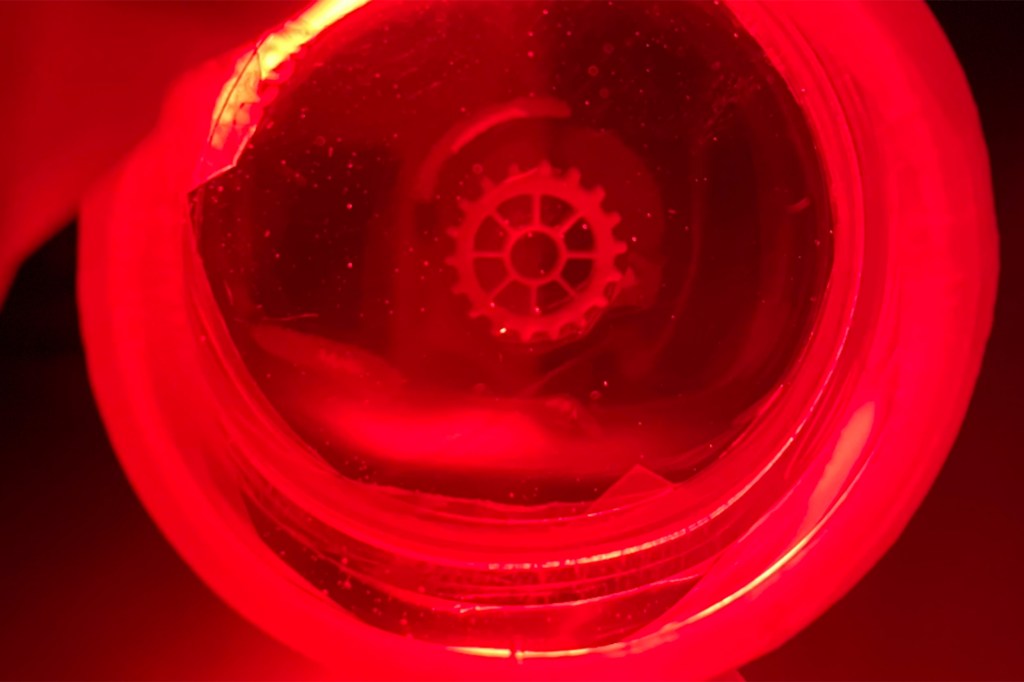
Making 3D printing truly 3D
Harvard researchers present a new method of volumetric 3D printing.

-
Forgetting, fast and slow
Forgetting generates changes in the brain and does not reverse the learning process, Harvard study finds.

-
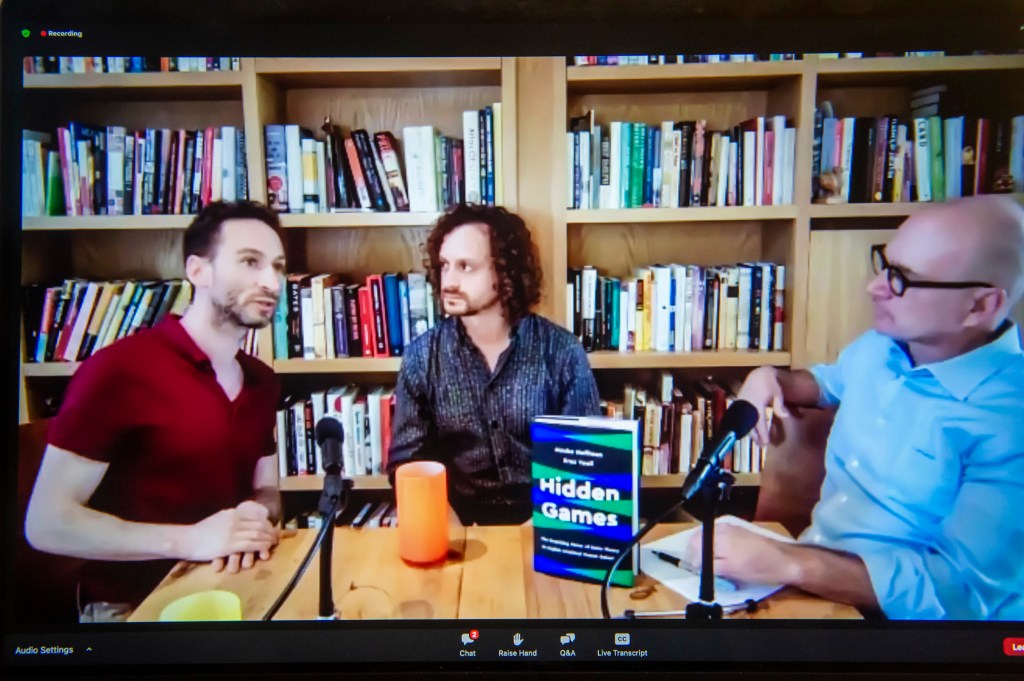
Altruism may not seem to make sense until you dig deep
In their new book, two Harvard scholars suggest that a subconscious process can help us understand everything from our aesthetic tastes to our altruism.
-
It’s not easy being your brain
Stephen Fleming, author of “Know Thyself: The Science of Self-Awareness,” explains the importance of “thinking about thinking.”

-
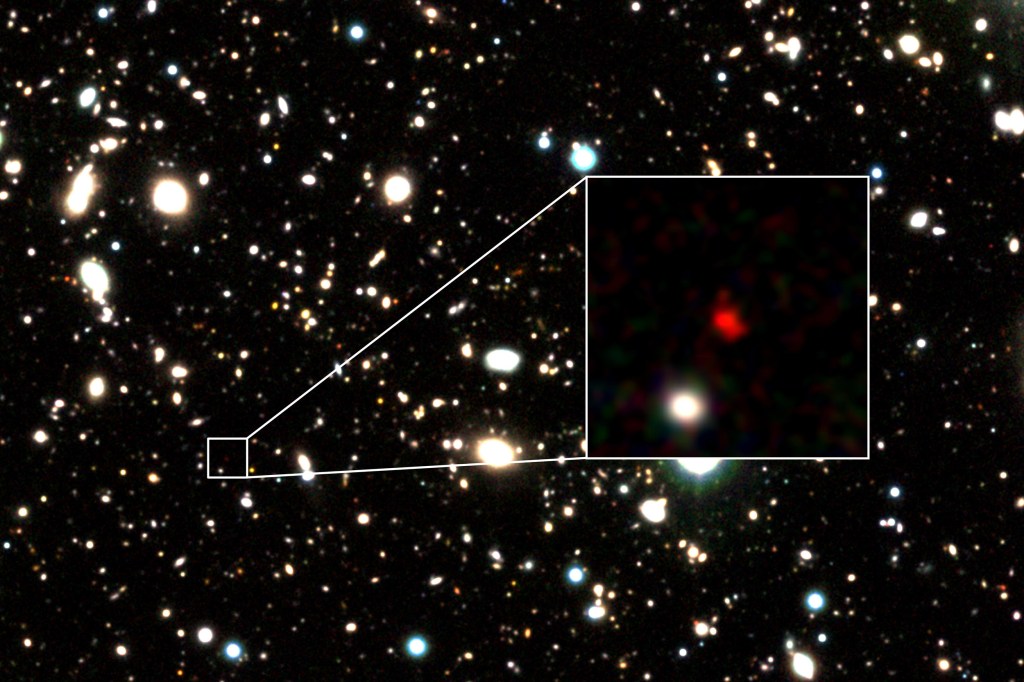
Scientists have spotted farthest galaxy on record
A galaxy, some 13.5 billion light-years away, is now considered the most distant astronomical object ever spotted, leaving scientists to speculate exactly what the galaxy is.

-
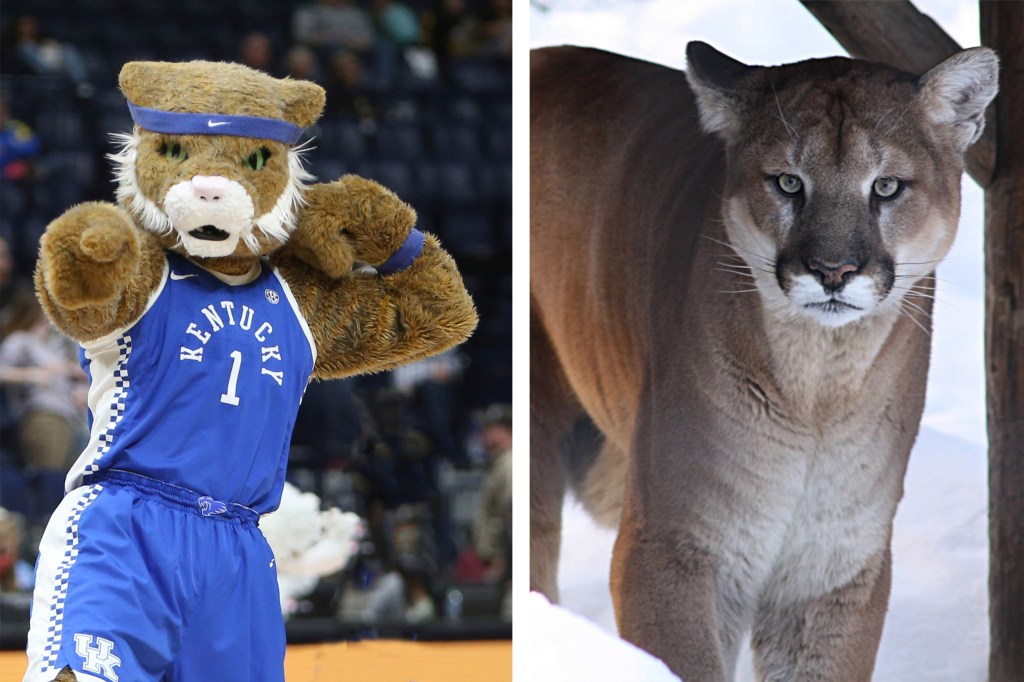
You call that a wildcat?
Hopi Hoekstra documents whether NCAA team mascots are really what they say they are. Here’s a bracket-buster: Many of them aren’t.

-
Whimsical steampunk tour of quantum thermodynamics
New book uses examples of a genre that blends futuristic technology with Victorian style to explain concepts of revolutionary new science.

-
What’s a little envy between friends?
The feeling can eat you alive — but only if you let it

-
Anthropologist describes supernatural adventures
Studying the paranormal can contribute to anthropology, says Jack Hunter in Harvard talk.
-
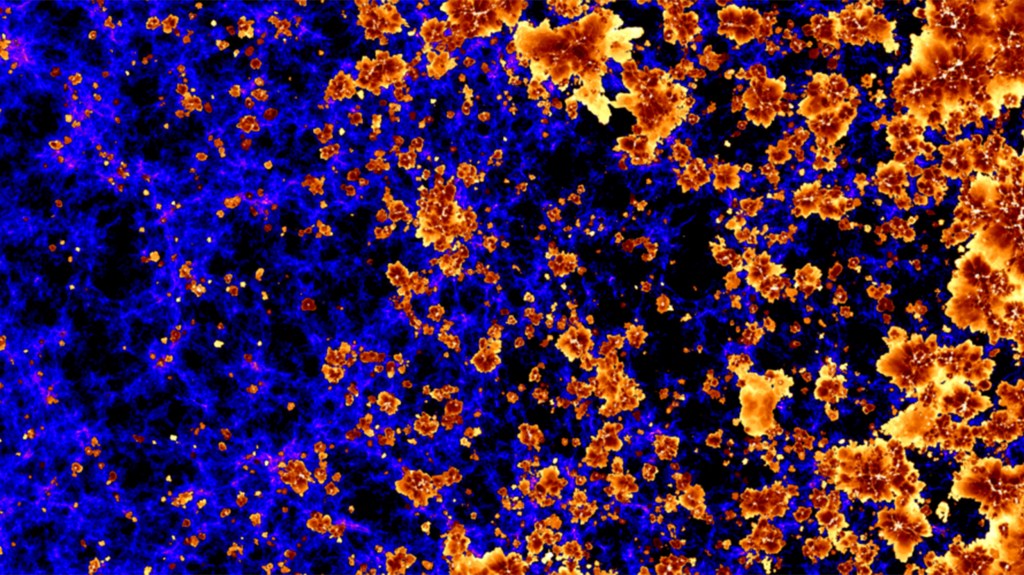
A glimpse into the universe’s first light
Using one of the world’s largest supercomputers, high-resolution simulations were created that show 1 million galaxies forming some 13 billion years ago.
-
Unlocking potential of quantum technologies
Chemical biology professor works to crack secrets of new states of matter.
-
Yes, cat is both dead, alive
Jacob Barandes’ new class combines philosophy and physics to look at quantum theory.

-
Oh, if I could talk to the aliens
Harvard astrophysicist and psychologist explore the possibility of life beyond our solar system and what to do should aliens arrive on Earth ready to engage.

-
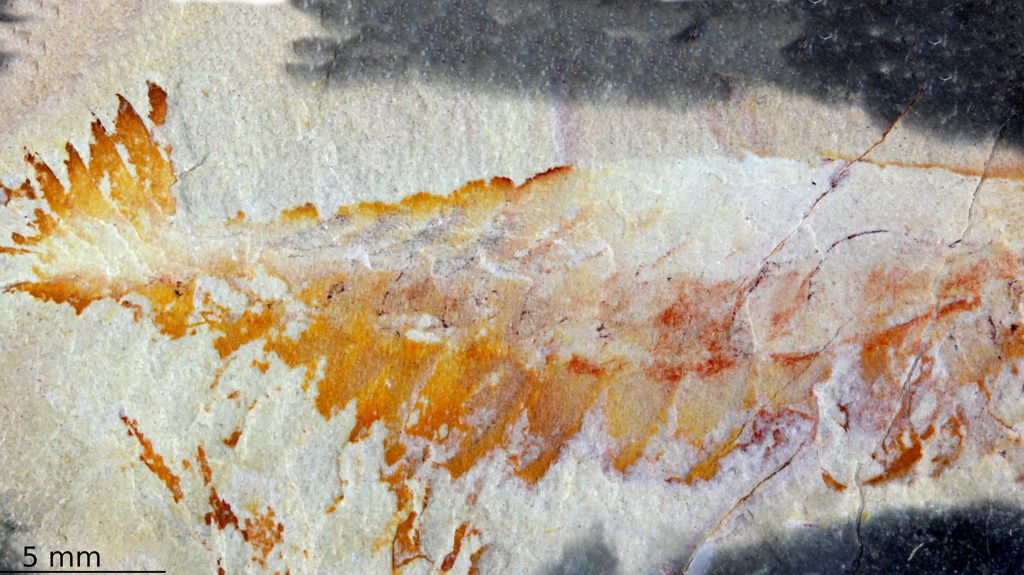
With a tip of hat to Stephen Jay Gould
Research done at Harvard unveils only the second “weird wonder” fossilized Opabinia, first popularized by the late evolutionary biologist.

-
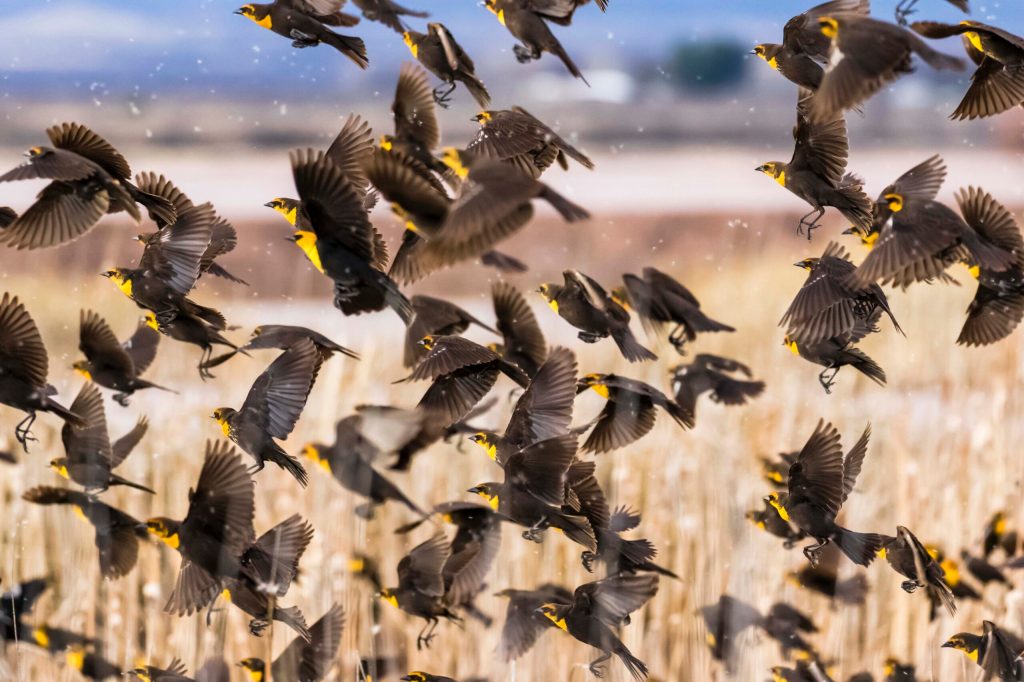
Those birds that crashed and died? It wasn’t fumes.
After internet theorists react to viral video, Harvard researchers answer with science.

-
Tech on a plate
Larissa Zimberoff, author of “Technically Food,” examined new ways of producing what we eat and drink in a discussion sponsored by the Food Literacy Project at Harvard.
-
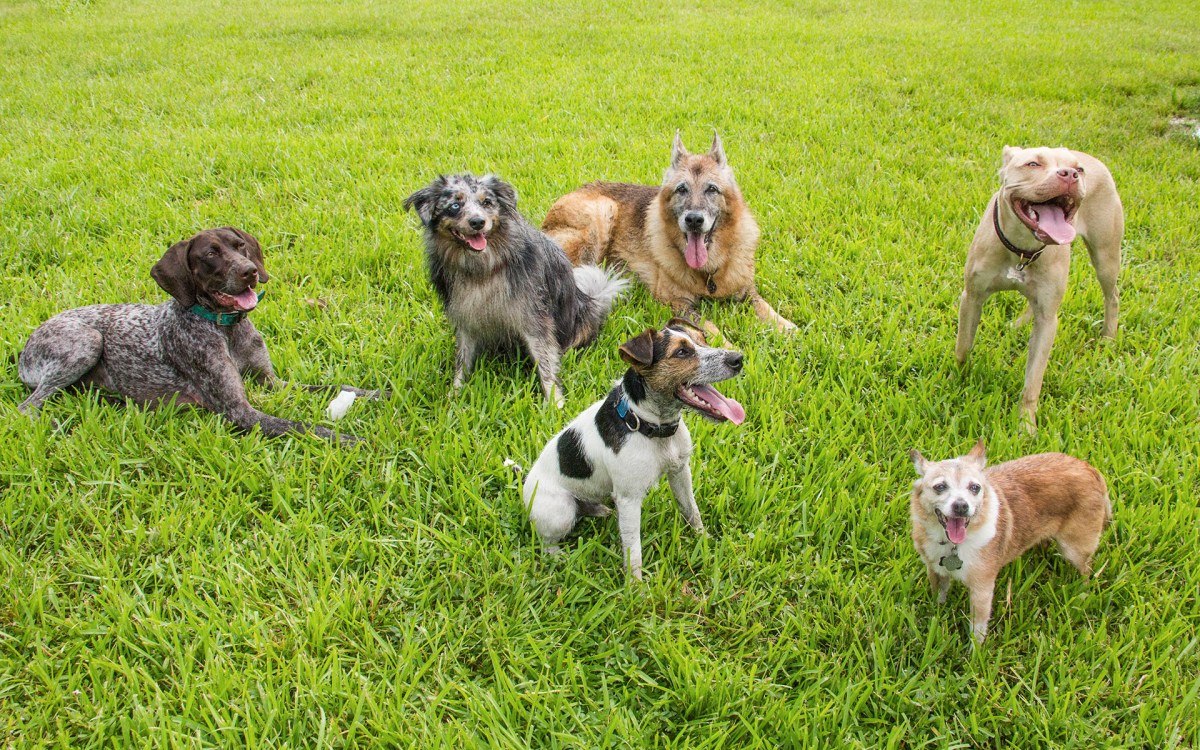
Does your dog care if you die?
Any owner would say yes. Here’s what the science says.

-
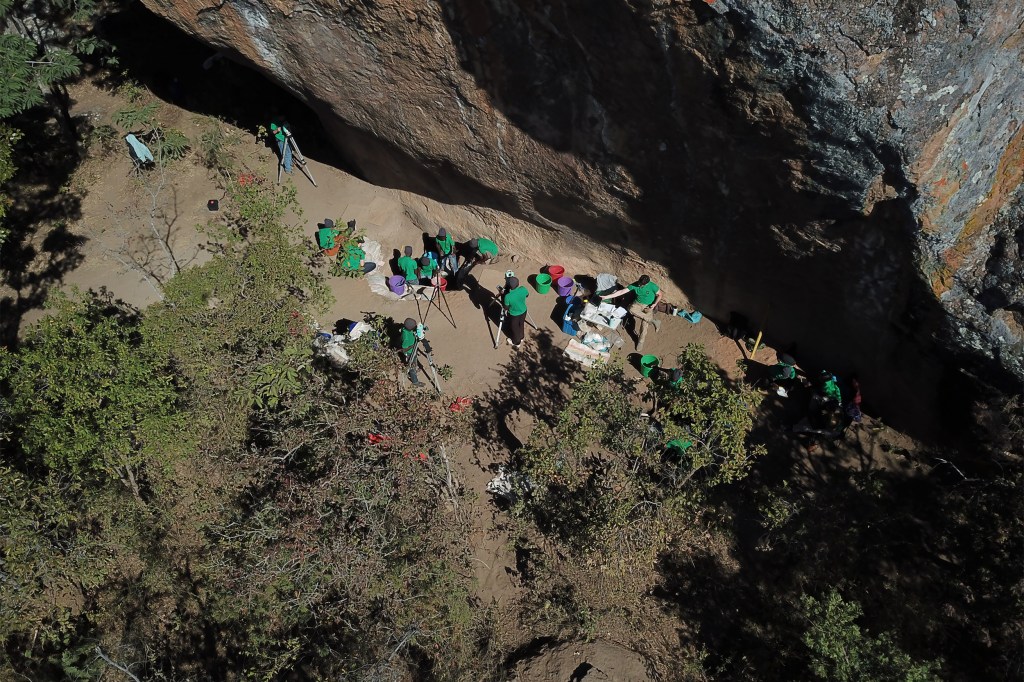
Was Facebook the original social network? Not by a long shot
New research produces earliest DNA from Sub-Saharan Africa and a more complete look at ancient peoples.

-
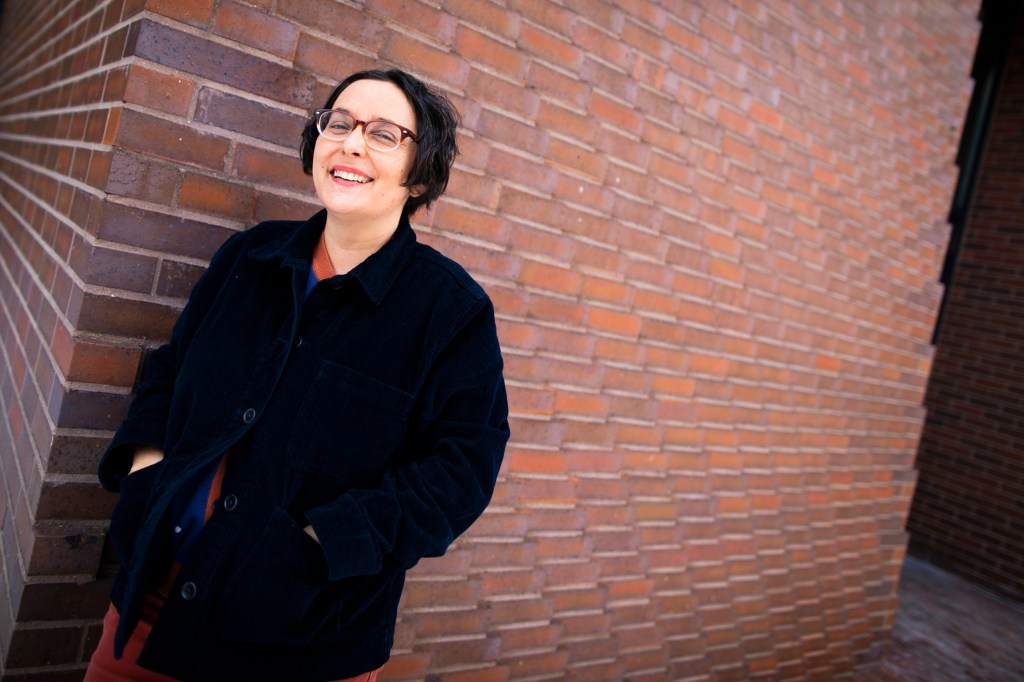
New Faculty: Gabriella Coleman
Anthropology Professor Gabriella Coleman studies the rich, deep world of hackers.

-
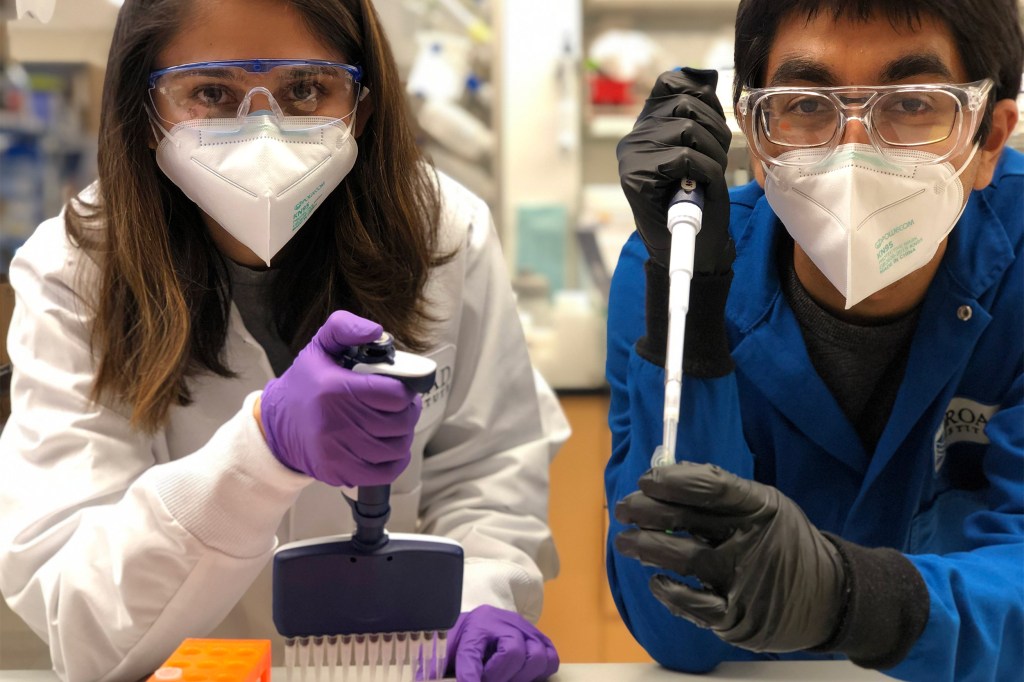
Drug delivery system offers hope for treating genetic diseases
A team of researchers has developed a new drug delivery system that was able to edit genes associated with high cholesterol and to partially restore vision in mice.

-
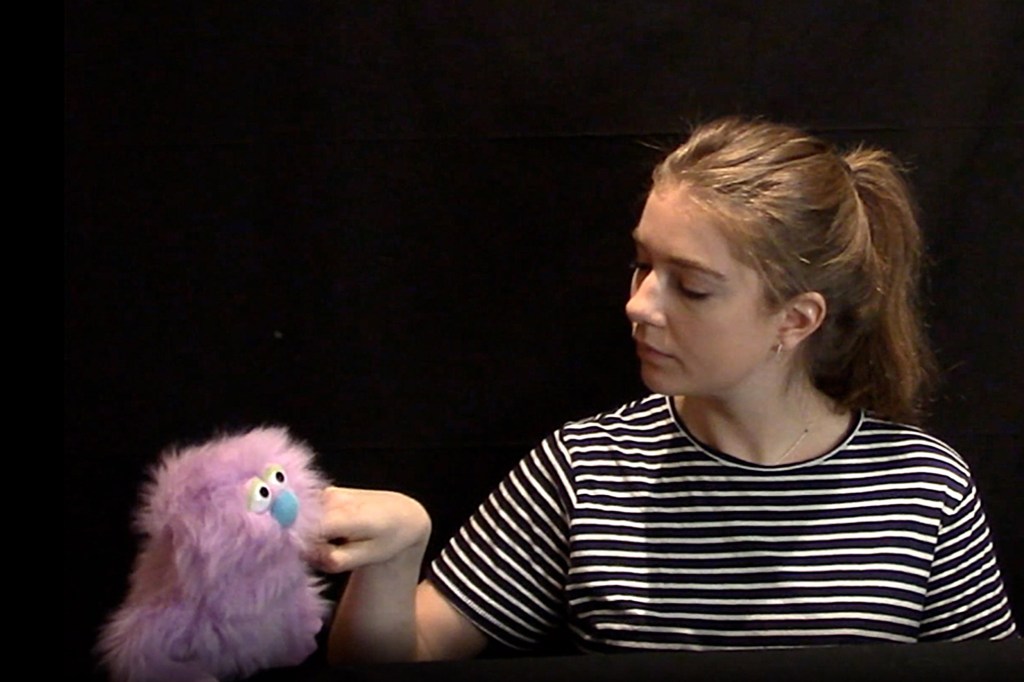
When babies see people swap spit, they know what’s what
Infants deduce that people are in a close relationship if they witness interactions like kissing and taking bites of each other’s food.

-
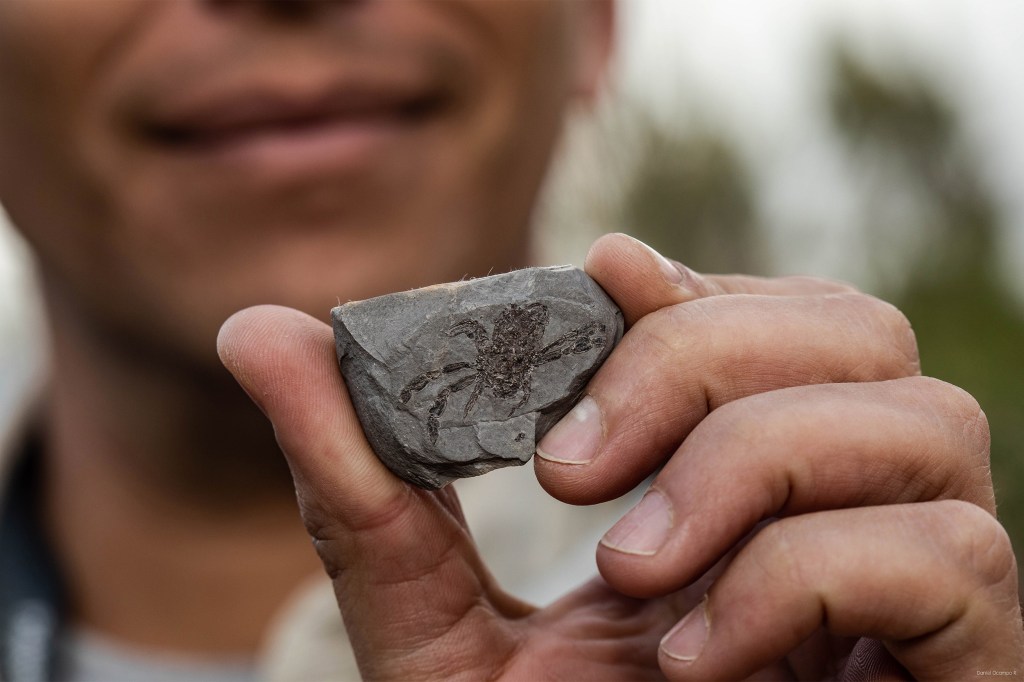
The ‘platypus’ of crabs
A crab that swam the seas 95 million years ago was believed to be an active predator with sharp vision as opposed to today’s bottom-dwellers with limited vision.

-
Reminders from Hollywood on memory, amnesia, personality
Psychology, philosophy scholars mine psycho-thriller “Memento” for its lessons on function of recall, how it shapes who we are.

-
Should married couples live apart?
Separate takes from husband-and-wife psychiatrists on distance, drift, and how to stay connected
-
Logic or emotion: Which is more valuable?
Neither thinking nor feeling is superior, according to Leonard Mlodinow’s new book, which argues that the two are inextricably linked.
-
Back in days of great floods
Harvard researcher explains how overflowing rivers billions of years ago helped shape what Mars looks like today.

-
What it takes to be a scientific breakthrough
Harvard Medical School Professor Anthony L. Komaroff explains the difference between a scientific advance and a true breakthrough.
-
A different kind of queen’s gambit
The n-queens challenge dates back to 1869. After working on the problem for about 5 years, mathematician Michael Simkin has an almost definitive solution.

-
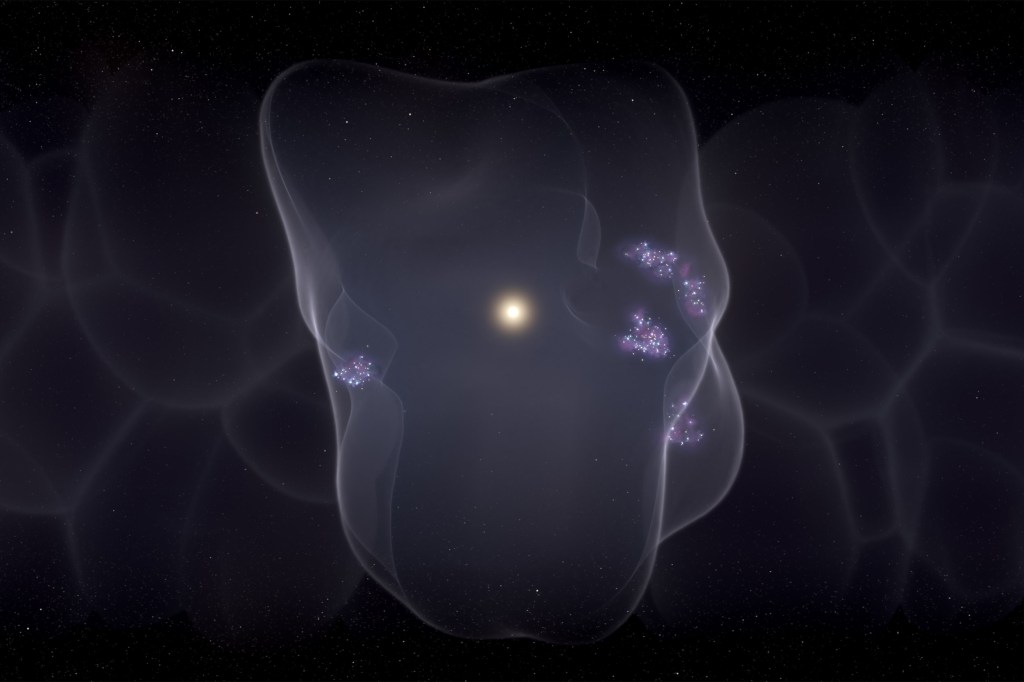
How a bubble gives birth to young stars
Scientists have shown how a chain of events led to the creation of the vast bubble that is responsible for the formation of all young stars within 500 light-years of the sun and Earth.



