Science & Tech
-

Harsh past might bare its teeth
Early adversity leads to higher aggression and fearfulness in adult canines, study says

-

What will AI mean for humanity?
Scholars from range of disciplines see red flags, possibilities ahead
-

‘Human exceptionalism is at the root of the ecological crisis’
Saving the planet requires getting over ourselves, argues author of ‘The Arrogant Ape’
-

Lauren Williams awarded MacArthur ‘genius grant’
Math professor honored for theoretical breakthroughs with sometimes surprising applications across phenomena such as tsunamis, traffic
-

-

‘She had a sense of caring for everybody that she encountered.’
Richard Wrangham remembers his teacher and colleague Jane Goodall as a force of science, empathy, and hope
-
5 ways to learn new things in the new year
Adults can continue to learn new things if they follow a few simple rules.

-
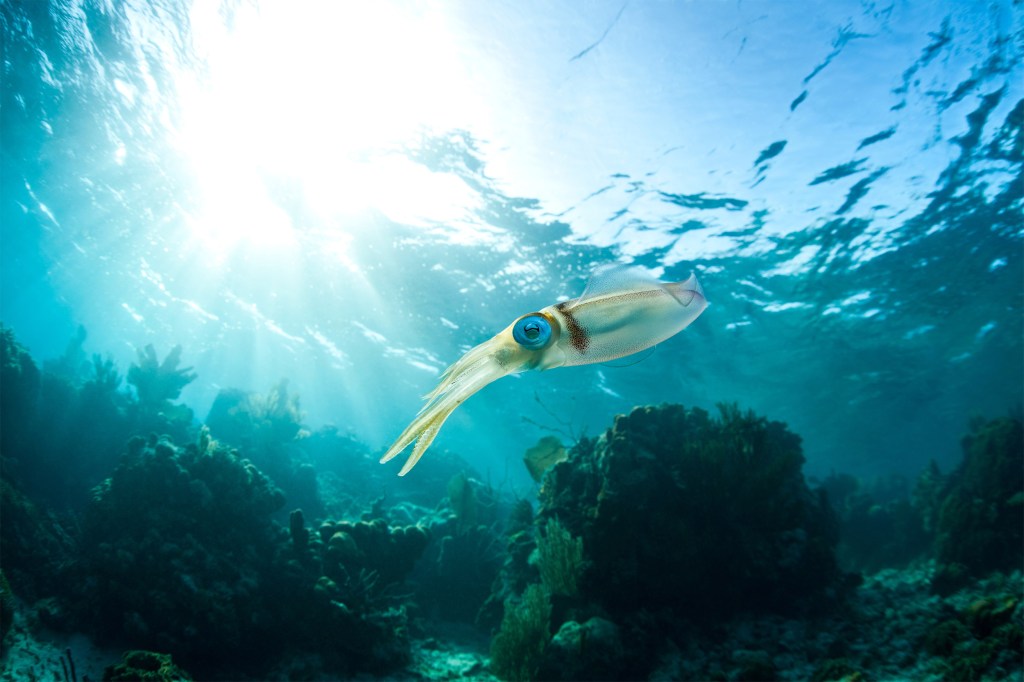
Seeing squid more clearly
Harvard researchers shed new light on squid eye development and convergent evolution.

-
Turns out smarter kids are made, not born
A study co-authored by experts at the Graduate School of Education found that mothers with positive mindsets can mitigate the negative effects of maternal stress on mother-child interactions and help promote children’s healthy development.

-
Gut-brain connection in autism
Researchers have identified a possible mechanism linking autism and intestinal inflammation in mouse models.

-
Geneticists’ new research on ancient Britain contains insights on language, ancestry, kinship, milk
Two new studies highlight technological advances in large-scale genomics and open windows into the lives of ancient people.

-
Twin gene-editing system gives twice the efficiency
A new gene-editing technique that enables larger edits than earlier ones could create new ways to study and treat genetic diseases, such as hemophilia or Hunter syndrome.

-
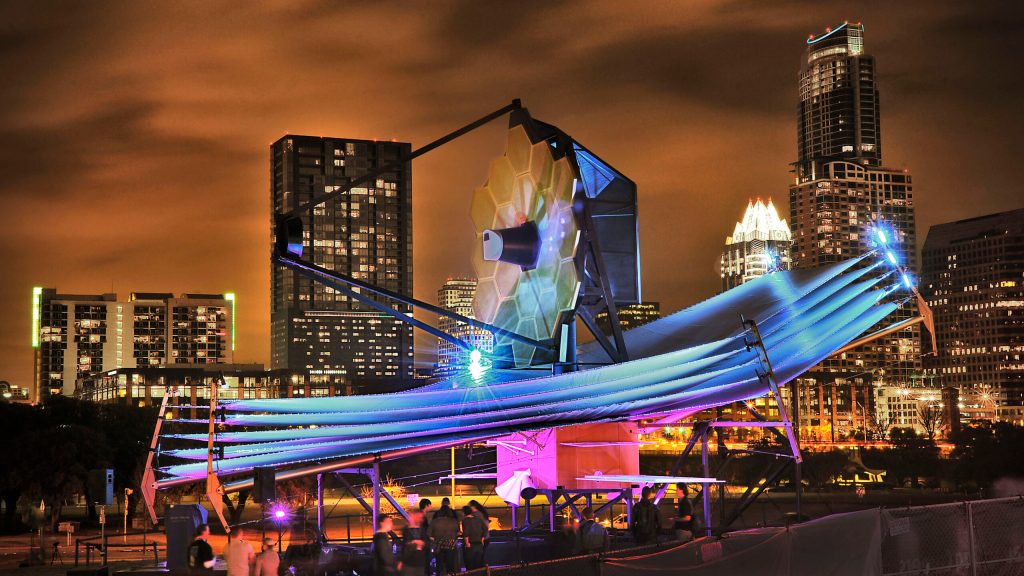
Telescope to help tell the story of the universe
Harvard astrophysicist details the most ambitious space probe NASA ever built.

-
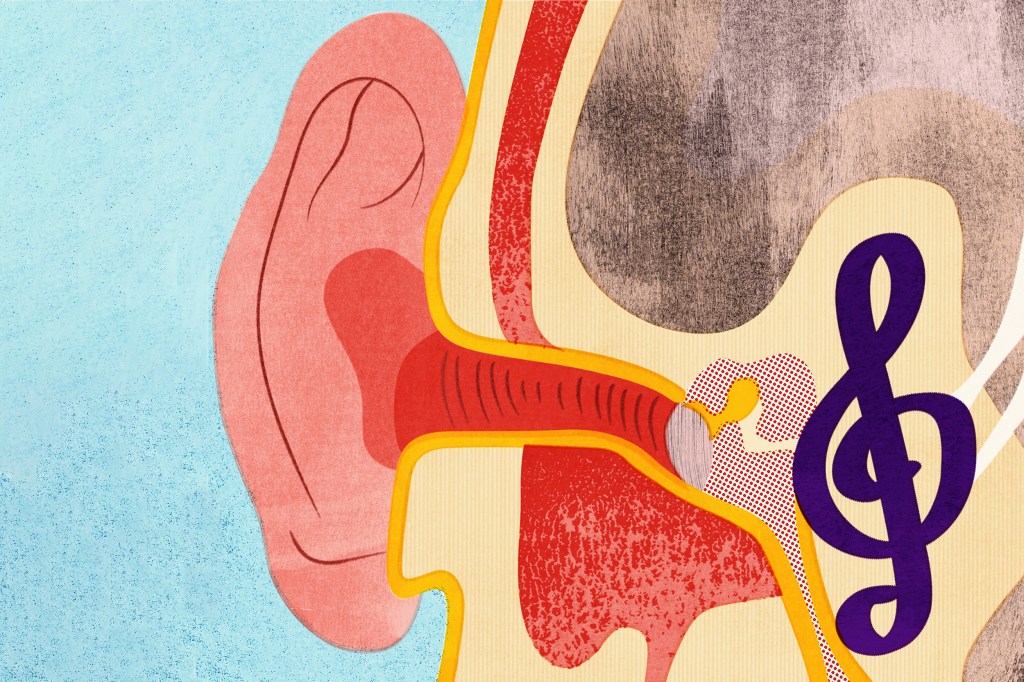
Why that song is stuck in your head
Brain scientist explains earworms
-
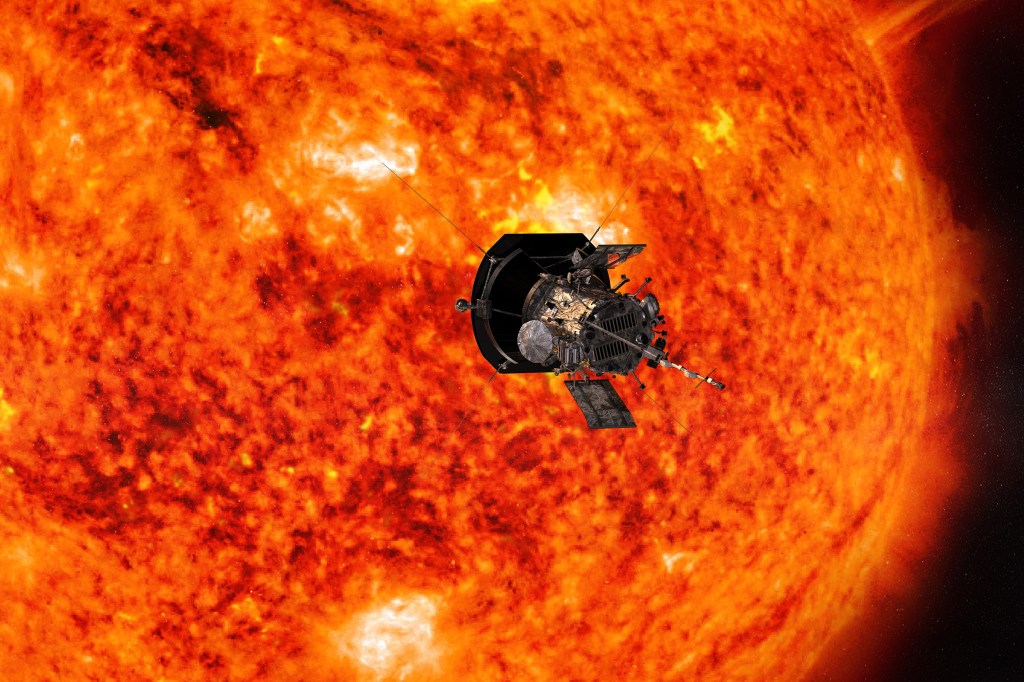
Touching the sun
An instrument made by scientists and engineers at the Center for Astrophysics has helped verify that — for the first time in history — a spacecraft has entered the corona of the sun.

-
University seen as well-equipped to meet goals of ambitious institute
Scholars across University say Harvard is well-suited to the challenge owing to breadth, size of intellectual resources, experience.

-
New University-wide institute to integrate natural, artificial intelligence
University-wide initiative made possible by gift from Priscilla Chan and Mark Zuckerberg.

-
Negotiating the irrational with Daniel Kahneman
Nobel-winning behavioral economist and author of “Thinking Fast and Slow” shares advice on negotiation at Harvard event.

-
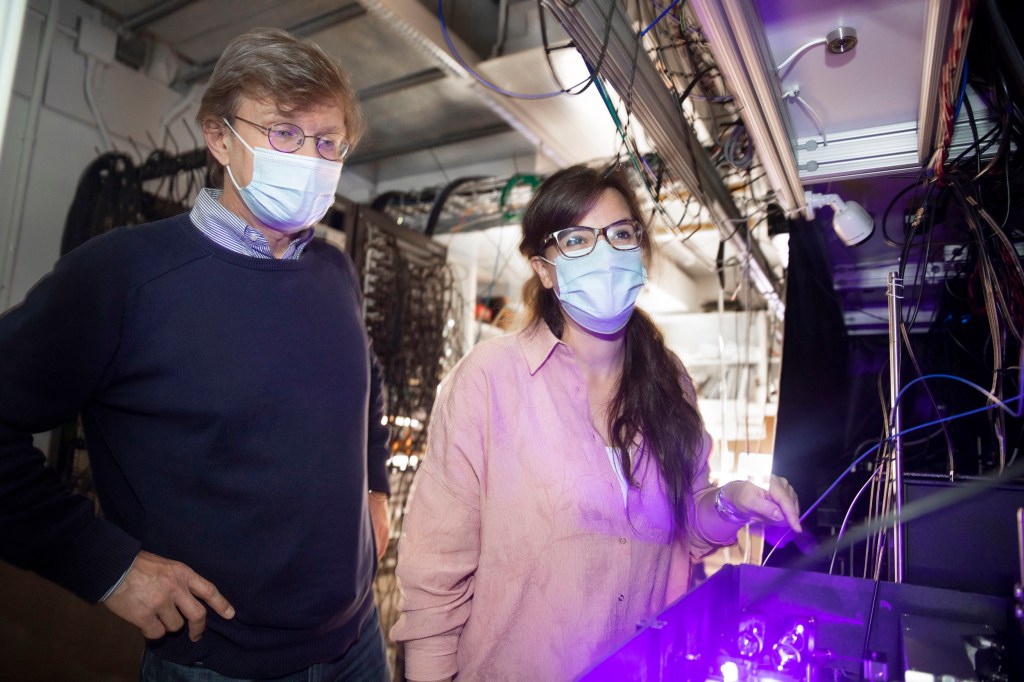
Step in quest for quantum computing
Harvard researchers observe a state of matter predicted and hunted for 50 years, but never previously observed.

-
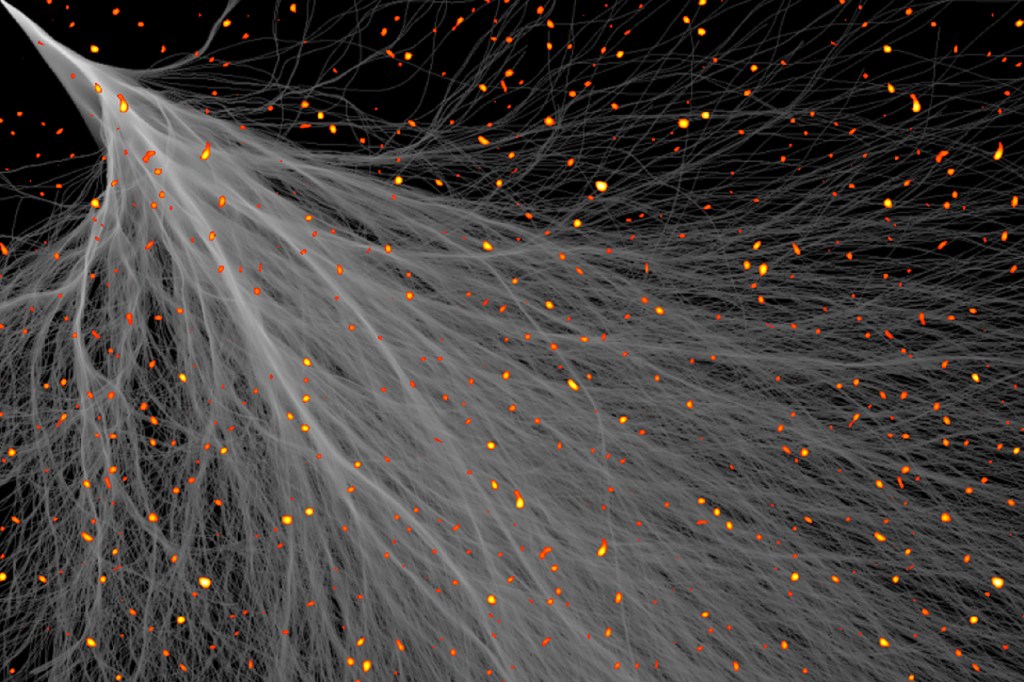
Potential step toward new superconductors
Never-before-seen electron behavior could help scientists create superwires for supercharged technology.
-
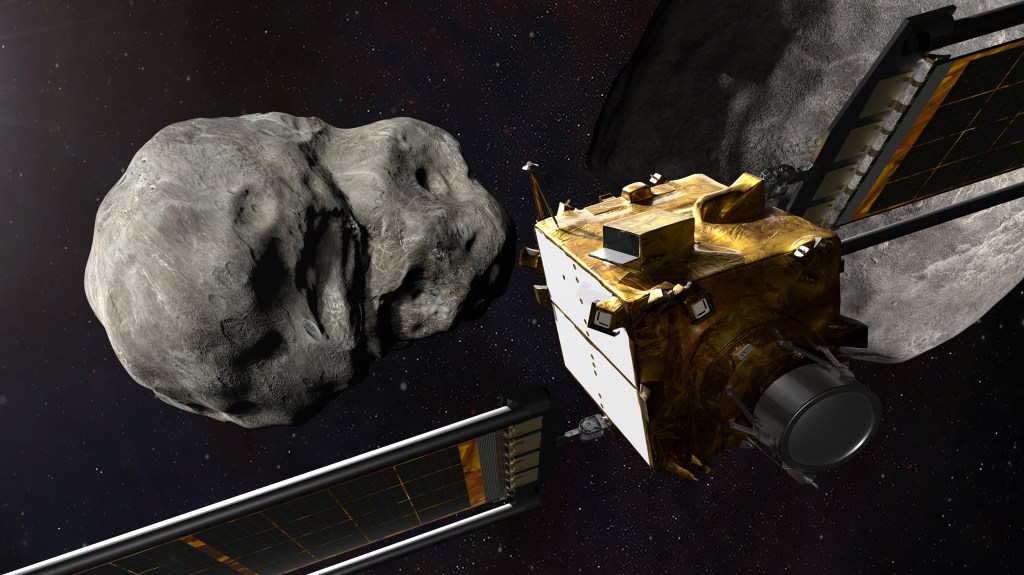
Getting the asteroid before it gets us
Jonathan McDowell of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics explains the science and objectives guiding the agency’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test.

-
Elizabeth Kolbert sees a world depleted, and possibly defeated, by climate change
New Yorker writer Elizabeth Kolbert and Planetary Health Alliance Director Samuel Myers discussed whether humans can save the Earth during a “Weather Reports” panel hosted by the Harvard Divinity School.

-
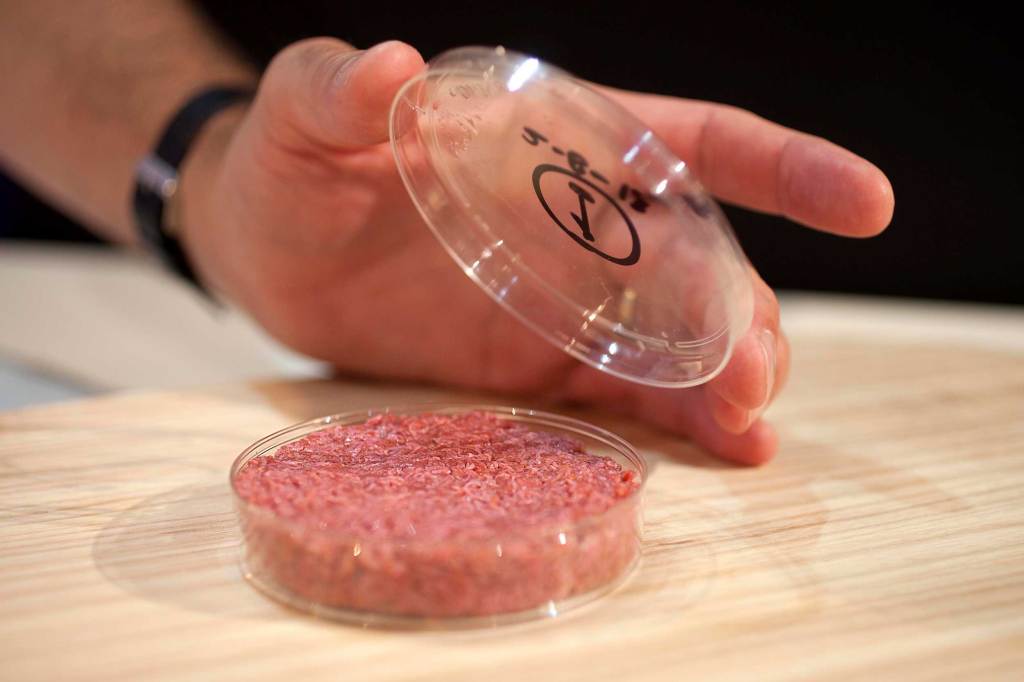
Meat and muscles, sure. But the human eye is a stretch, for now.
The author and MIT professor Ritu Raman discussed the promise and ethical challenges of a lab-shaped future.

-
When will a robot write a novel?
In considering whether a robot could write a work of fiction, the computer science Krzysztof Gajos says it depends—trashy novel or a good one?

-
A Rosetta Stone of biology
Harvard researcher develops program to read any genome sequence and decipher its genetic code.

-
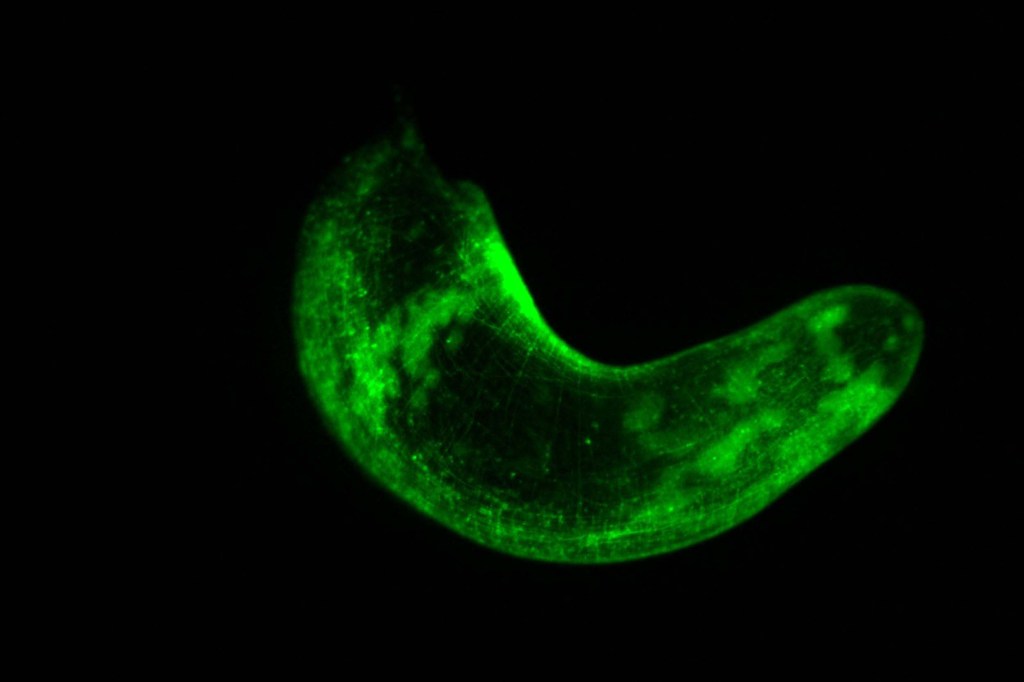
Lessons in regeneration by light of glowing worms
Harvard-led team is learning secrets of regeneration through a method for manipulating genome, which allows a better view of workings of cells.
-
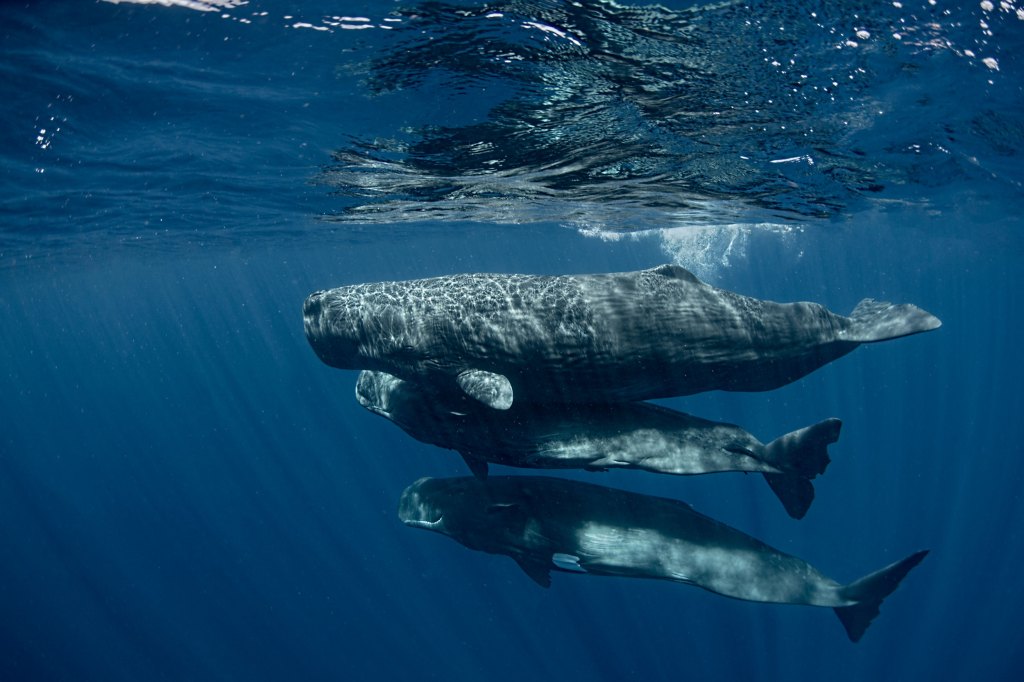
If we could talk to the animals … whales, specifically
A group of scholars who met at Radcliffe in 2017 have formed a nonprofit aimed at deciphering whale communication.

-
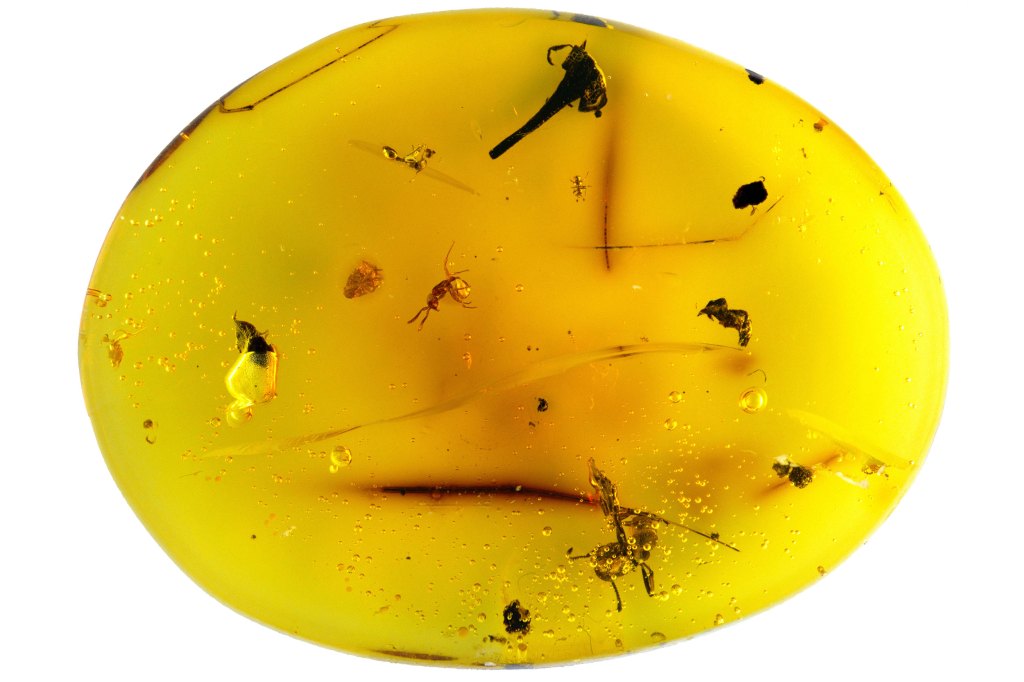
A big discovery of a tiny critter
Discovery in 16-million-year-old amber is the third species of water bear ever found.

-
Mathematician’s life advice: Subtract the boring parts
Marcus du Sautoy discussed his latest work “Thinking Better: The Art of the Shortcut in Math and Life,” with Melissa Franklin, Mallinckrodt Professor of Physics.

-
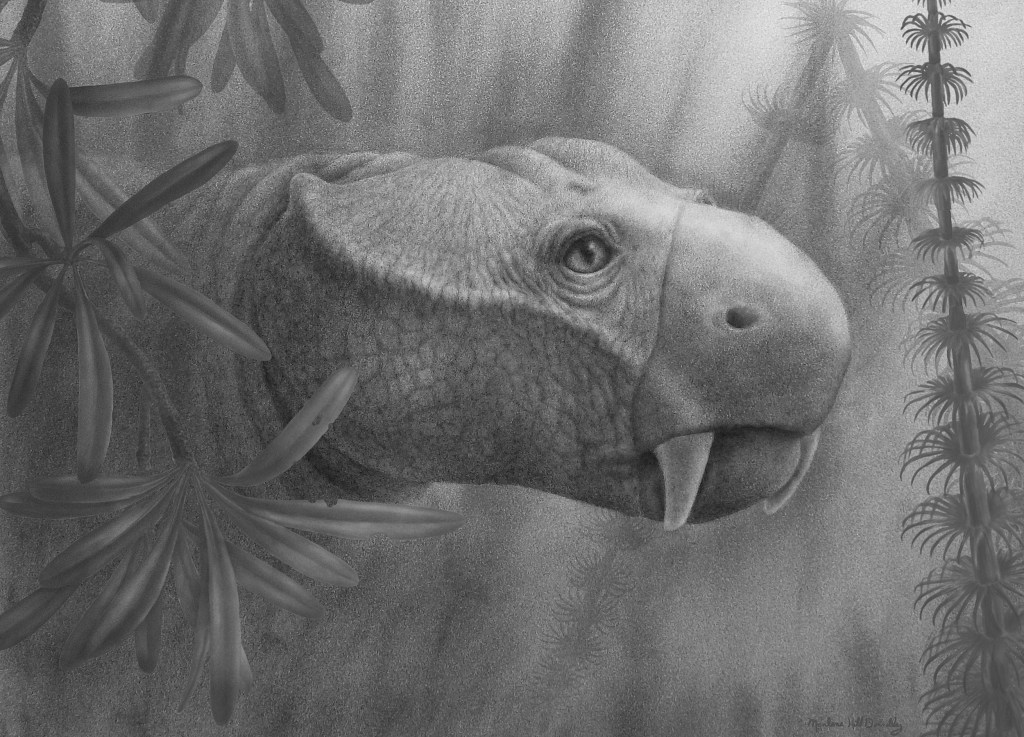
Why did some mammals develop tusks?
New study defines and traces the evolution of tusks from the first animals to sport them.

-
Coming to grips with planetary existential threat
Environmental Science and Public Policy takes multidisciplinary approach to complex existential threat.

-
People weren’t so lazy back then
Research comparing 19th- and 21st-century Americans finds a half-hour decline in physical activity. Blame it on planes, trains, and automobiles.

-
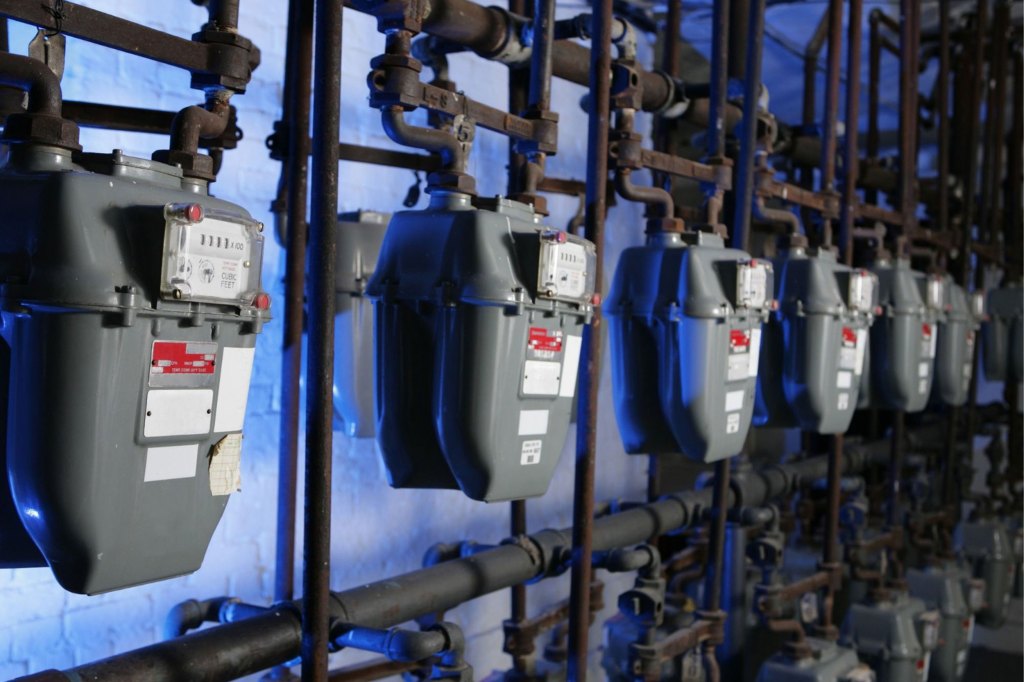
Leaky natural gas pipelines are tip of the iceberg
Methane emissions from the distribution and use of natural gas across U.S. cities are 2 to 10 times higher than recent estimates from the EPA.

-
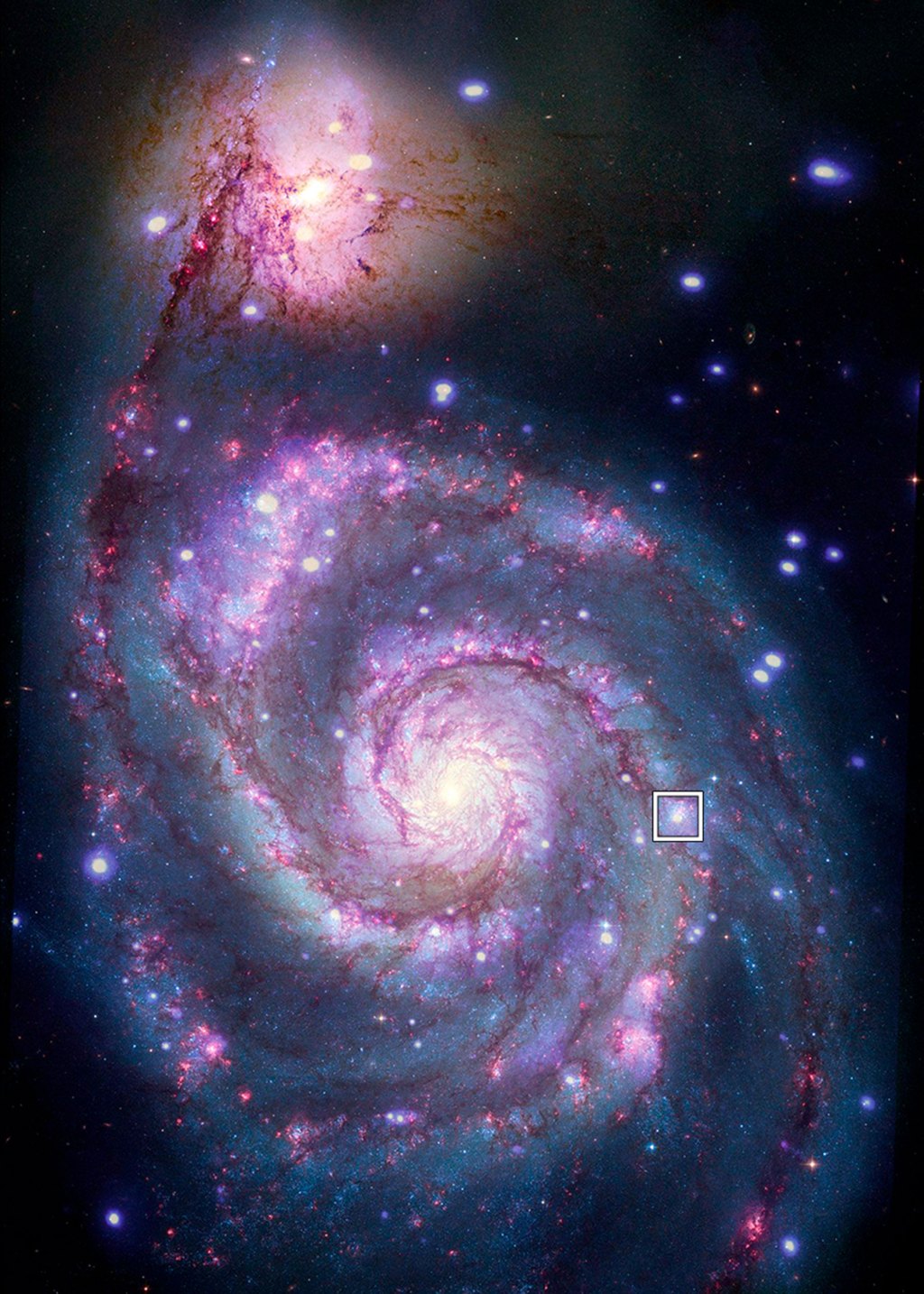
Tantalizing transit
Signs of a planet transiting a star outside of the Milky Way galaxy may have been detected for the first time.

-
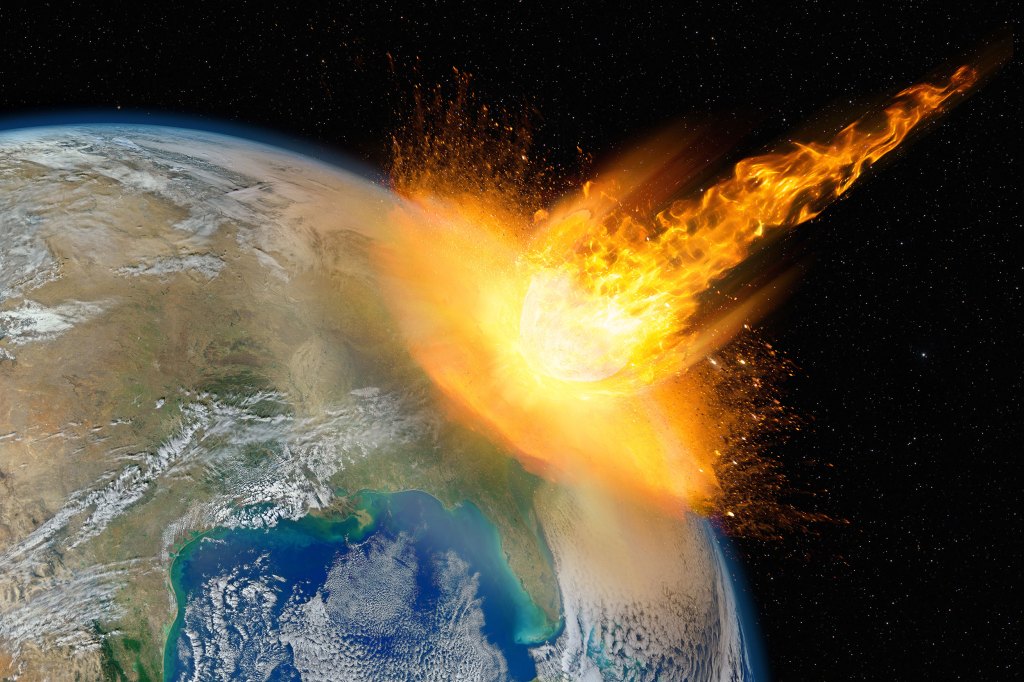
How asteroid, comet strikes may have delayed evolution of atmosphere
Collisions more common than thought and hampered growth of oxygen on planet, Harvard professor’s team finds.

-
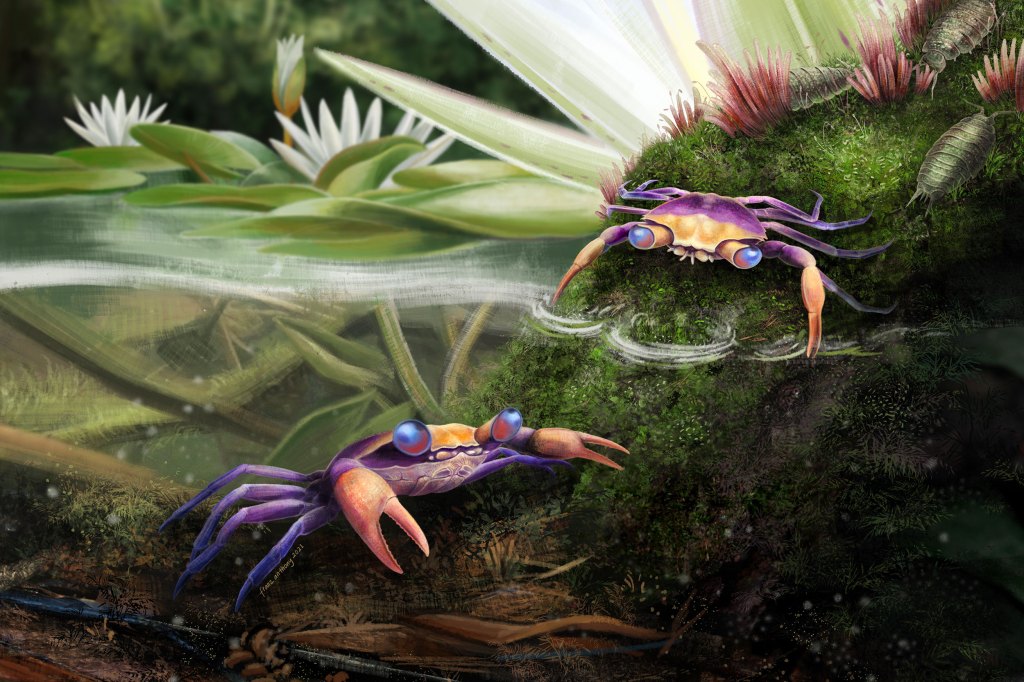
Bad for 100-million-year-old crab, but good for scientists
Javier Luque’s first thought while looking at the 100-million-year-old piece of amber wasn’t whether the crustacean trapped inside could help fill a crucial gap in crab evolution. He just kind…



