Science & Tech
-

Harsh past might bare its teeth
Early adversity leads to higher aggression and fearfulness in adult canines, study says

-

What will AI mean for humanity?
Scholars from range of disciplines see red flags, possibilities ahead
-

‘Human exceptionalism is at the root of the ecological crisis’
Saving the planet requires getting over ourselves, argues author of ‘The Arrogant Ape’
-

Lauren Williams awarded MacArthur ‘genius grant’
Math professor honored for theoretical breakthroughs with sometimes surprising applications across phenomena such as tsunamis, traffic
-

-

‘She had a sense of caring for everybody that she encountered.’
Richard Wrangham remembers his teacher and colleague Jane Goodall as a force of science, empathy, and hope
-
Here comes the sun
Seasonal changes in UV may alter the spread of COVID but not as much as social distancing.
-
Helping your child make the best use of time online
Urs Gasser and John Palfrey are authors of the newly released book “The Connected Parent: An Expert Guide to Parenting in a Digital World.”

-
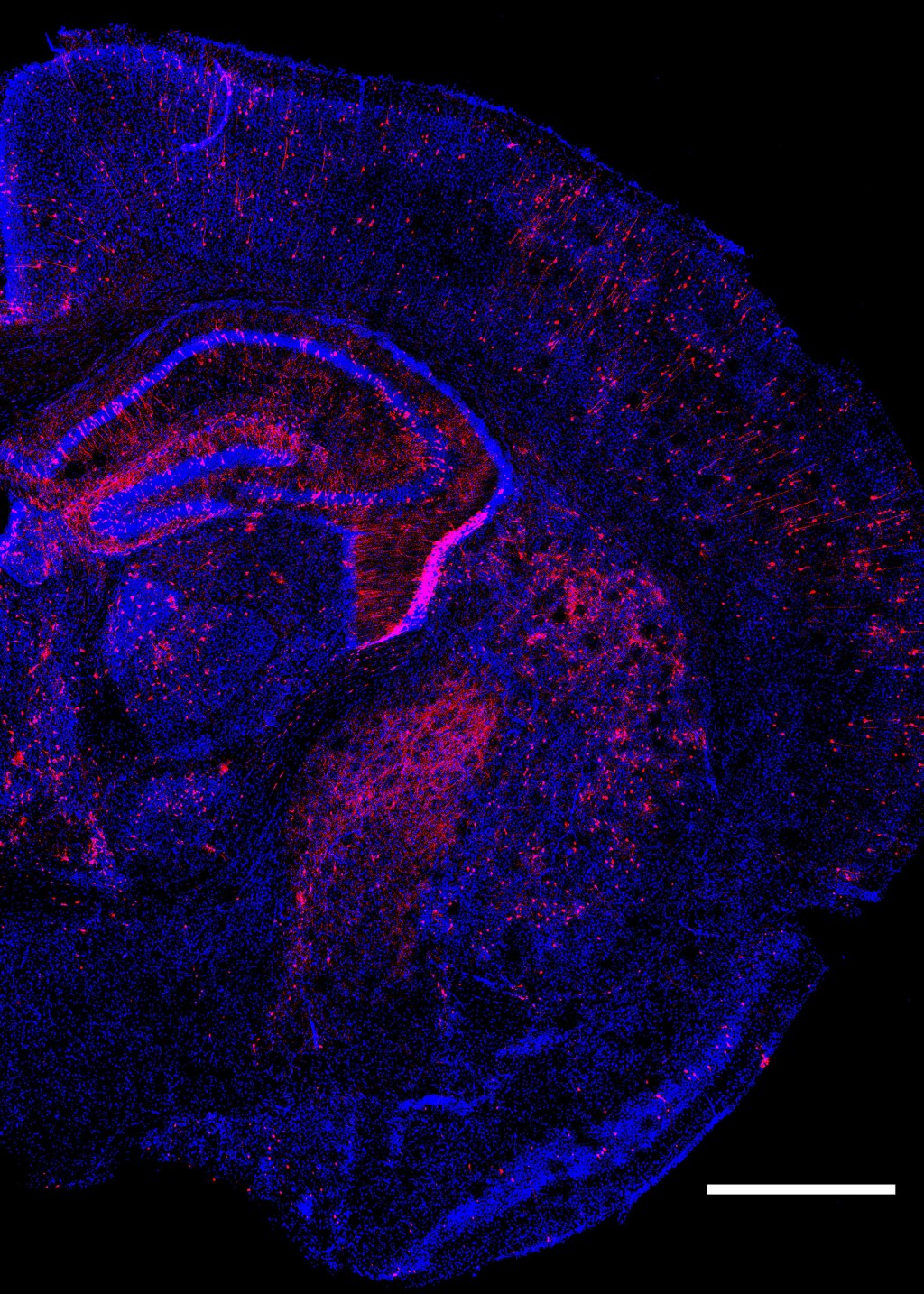
Making memories
A Harvard Medical School study in mice reveals how memory neurons reorganize after new experiences.
-
‘Climate Conversations’ series aims to build community, spur action
‘Climate Conversations’ series engages researchers, leaders, practitioners, and organizers to seek paths to collaboration, solutions.

-
Imagine a world in which AI is in your home, at work, everywhere
Harvard’s AI+Art project aims to get people thinking about how artificial intelligence may impact our lives in the future.

-
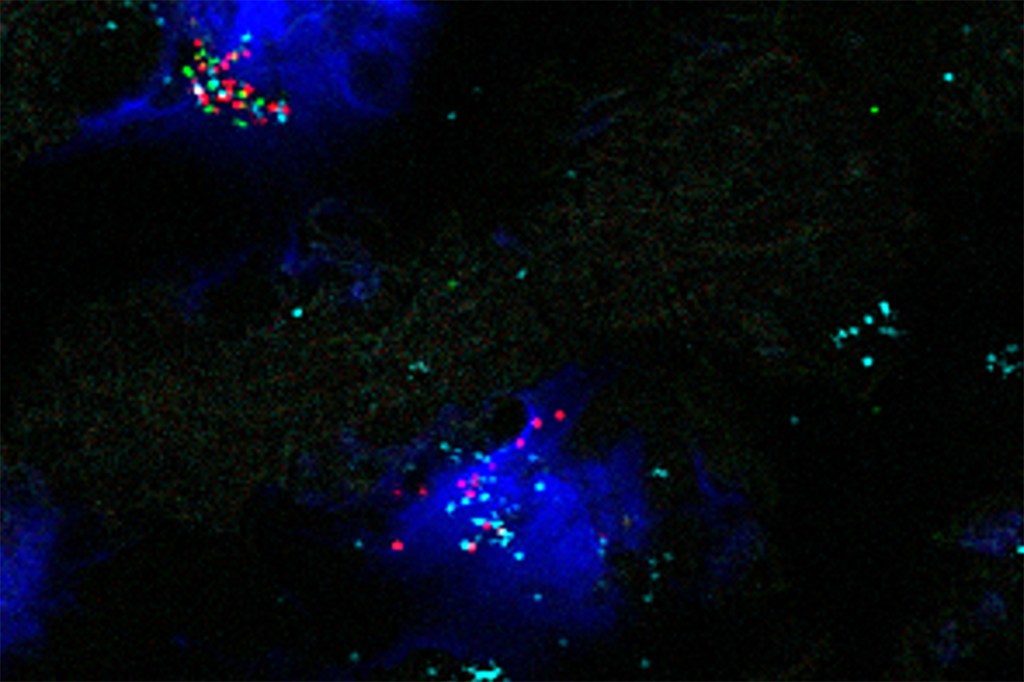
New technology to investigate autism spectrum disorder
Scientists applied the “Perturb-Seq” method to study dozens of genes that are associated with autism spectrum disorder, identifying how specific cell types in the developing mouse brain are impacted by mutations.
-
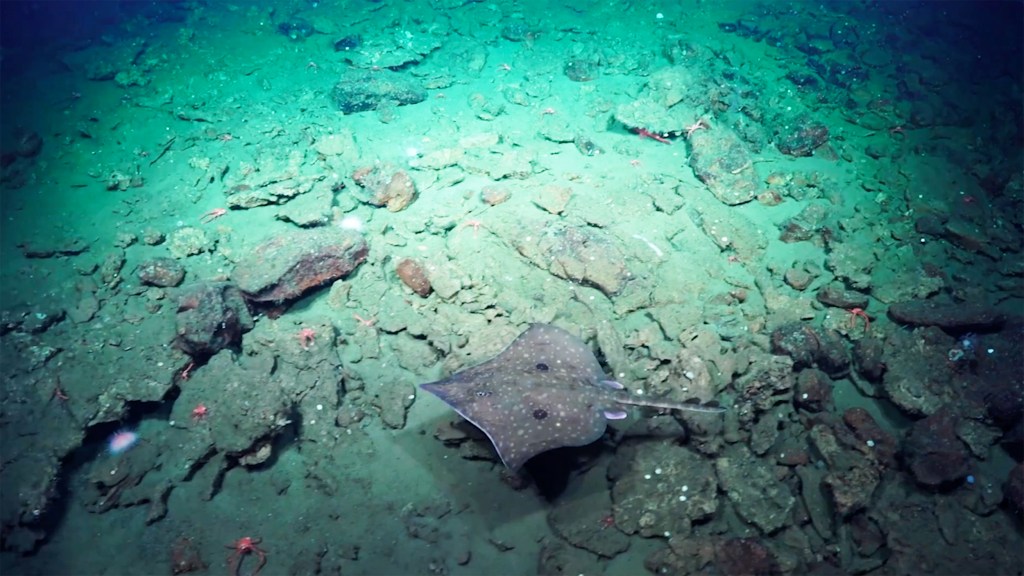
Zooming to the ocean floor
OEB 119 students are patched in via livestream and a satellite call to a team of researchers leading an exploration on the seafloor.

-
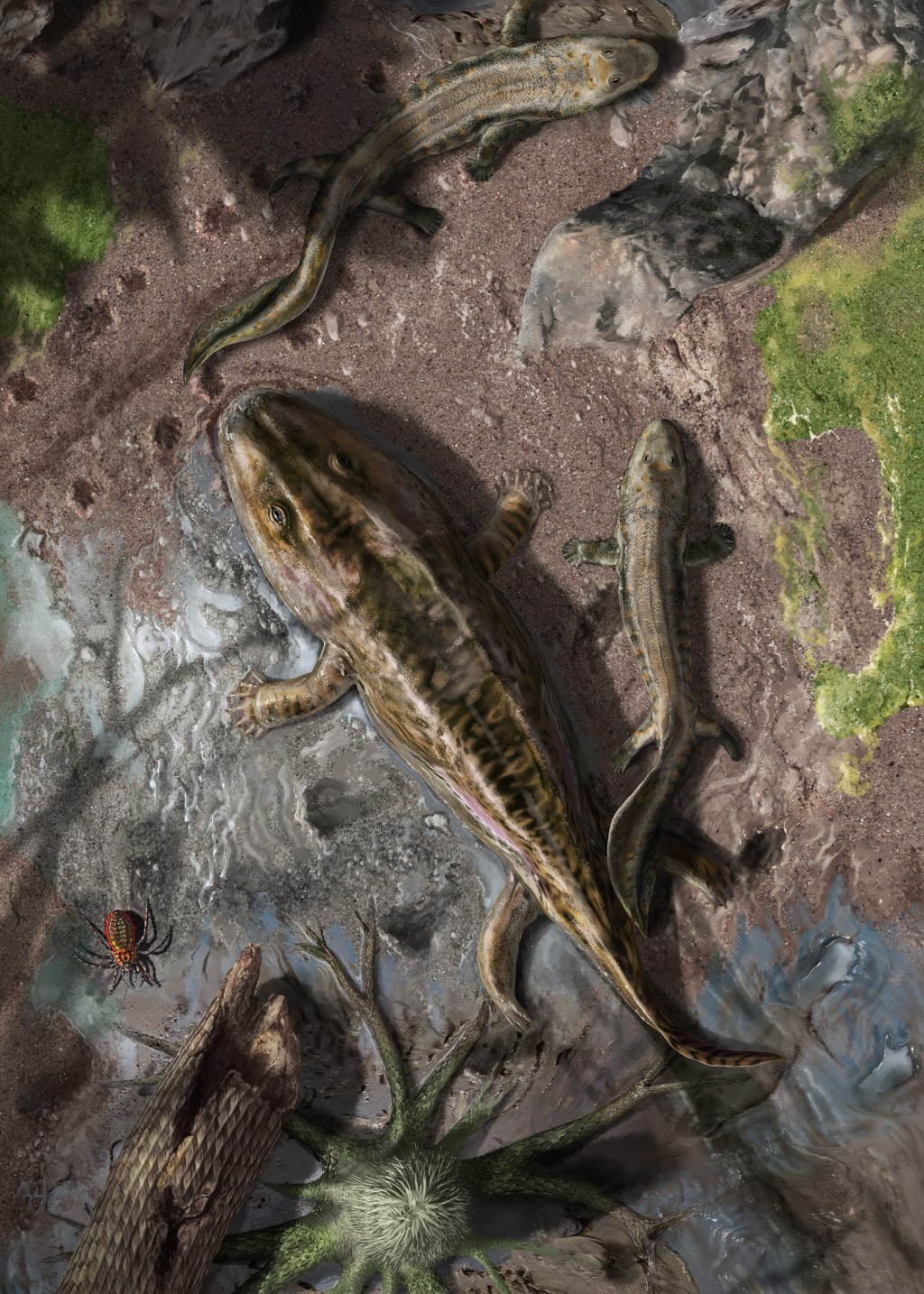
From fins to limbs and water to land
Harvard scientists reconstruct evolution of limb-based motion in early tetrapods.

-
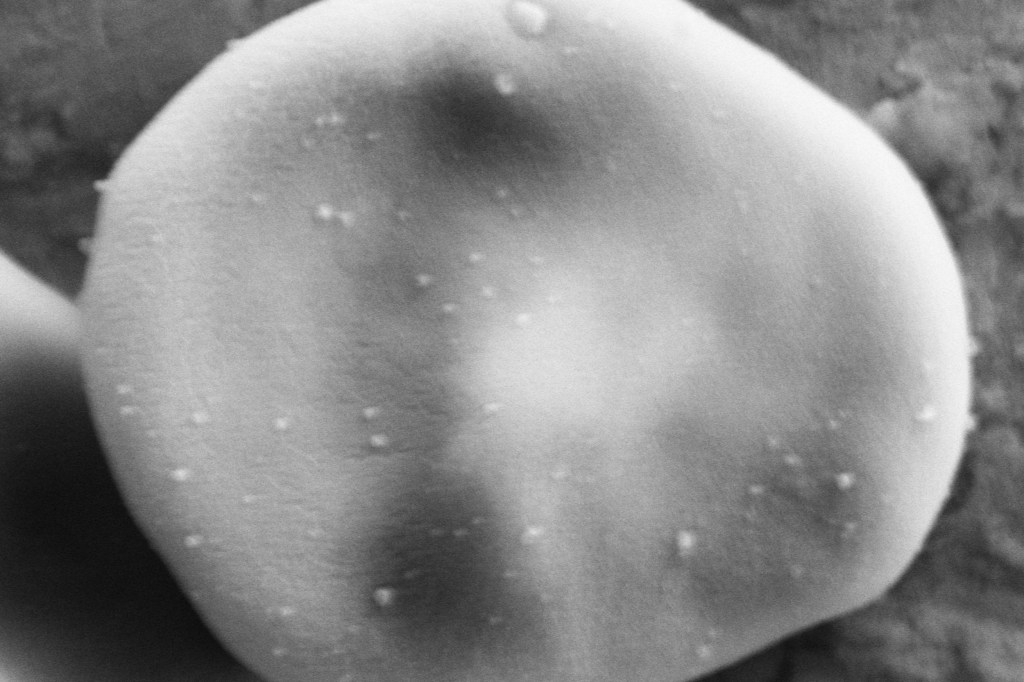
An ionic forcefield for nanoparticles
For the first time in mice, researchers have coated nanoparticles with an ionic liquid that allows the nanoparticles to survive the immune system and deliver drugs to their targeted spot.
-
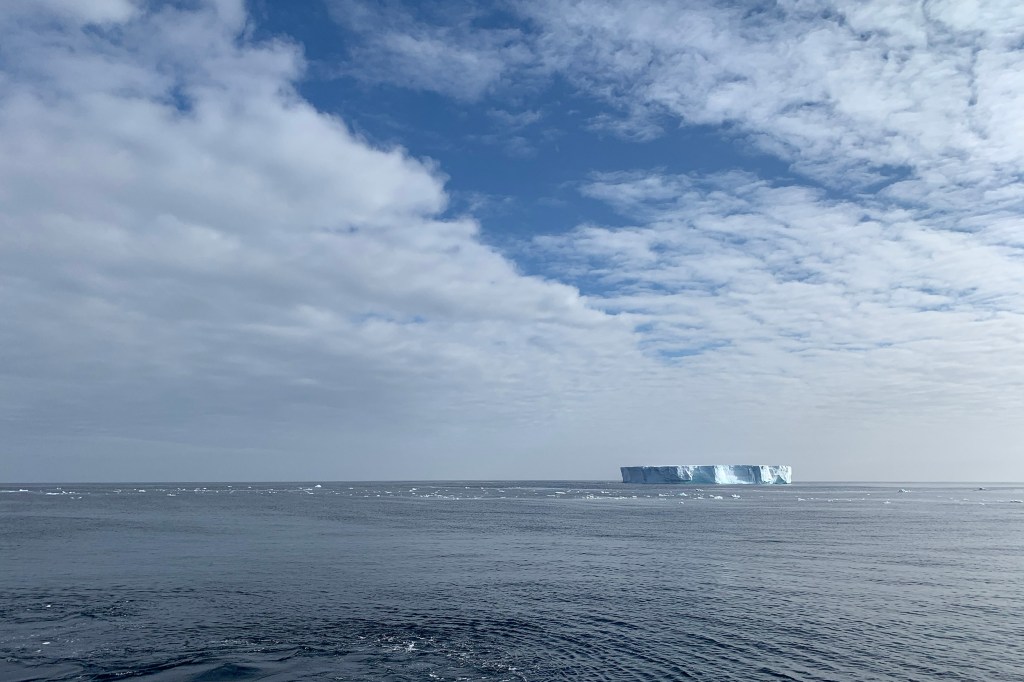
Evidence of the interconnectedness of global climate
Ice sheets thousands of kilometers apart influence each other through sea level changes.

-
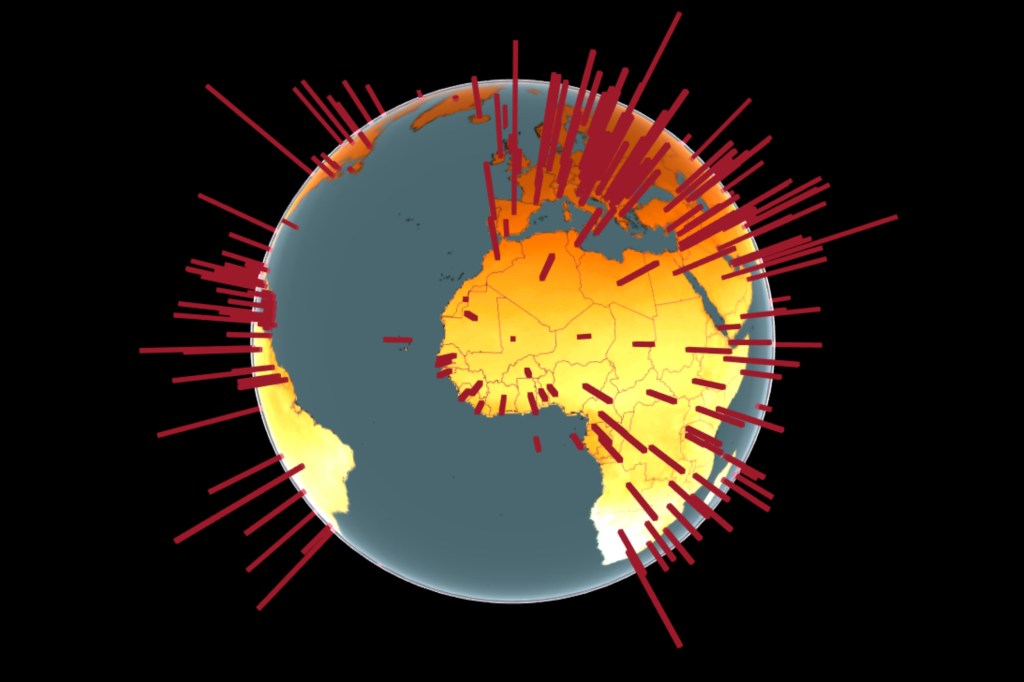
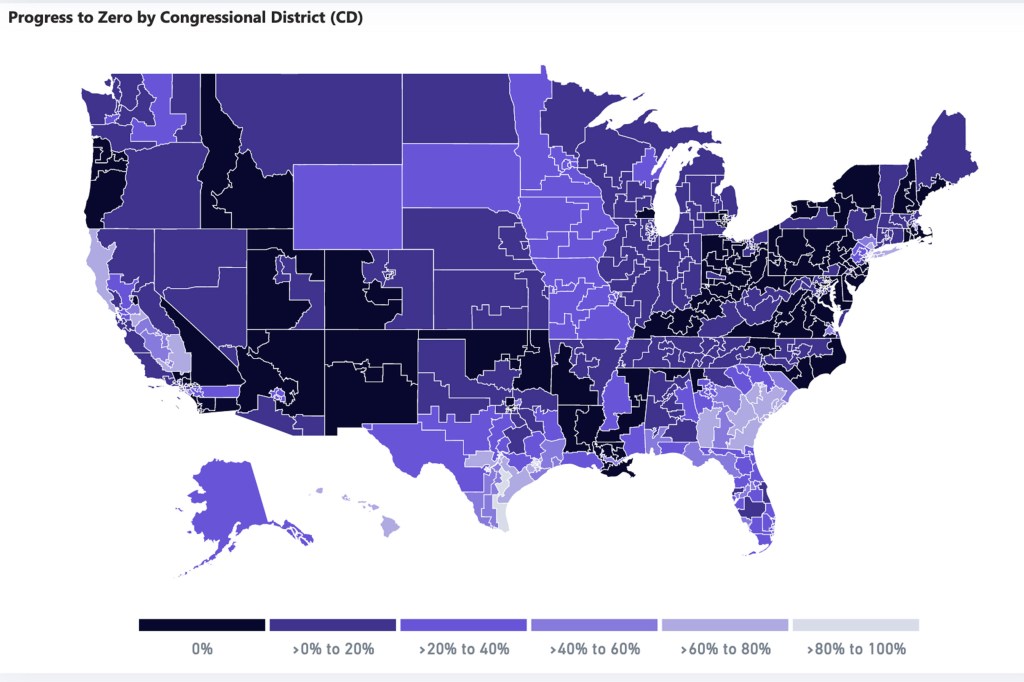
Live tracker notes COVID cases, deaths by congressional districts
The Harvard Center for Population and Development Studies and Center for Geographic Analysis worked with Microsoft to create a live tracker that monitors the status of COVID cases, broken down by congressional district, to help officials develop testing and vaccine deployment strategies in their areas.
-
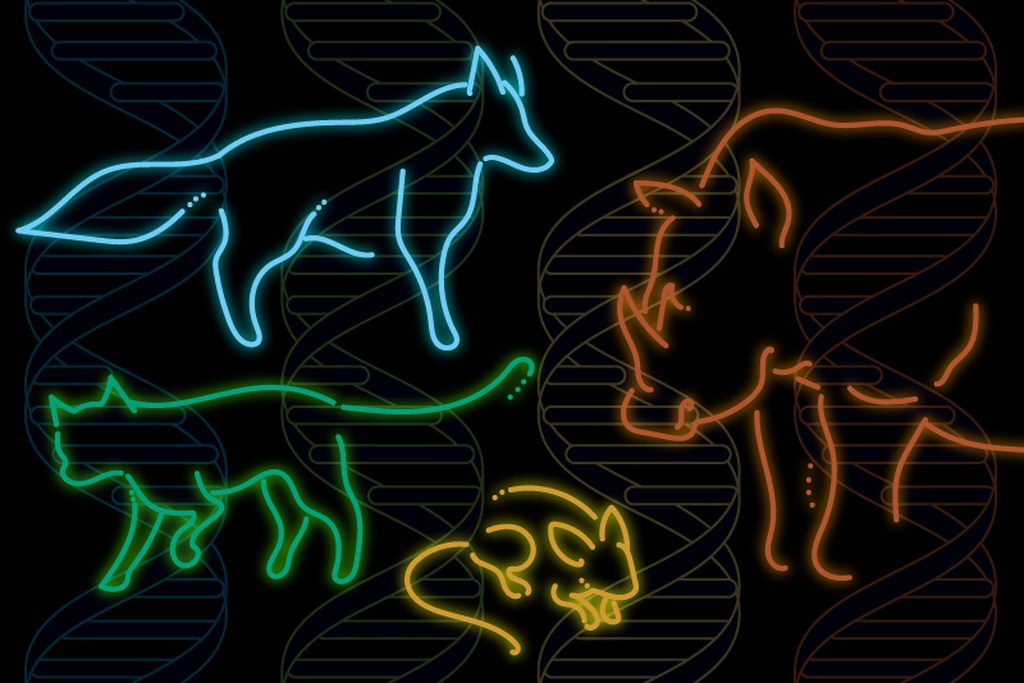
Largest set of mammalian genomes reveals species at risk of extinction
A team of researchers analyzed and compared the genomes of more than 80 percent of all mammalian families, which captures mammalian diversity at an unprecedented scale.

-
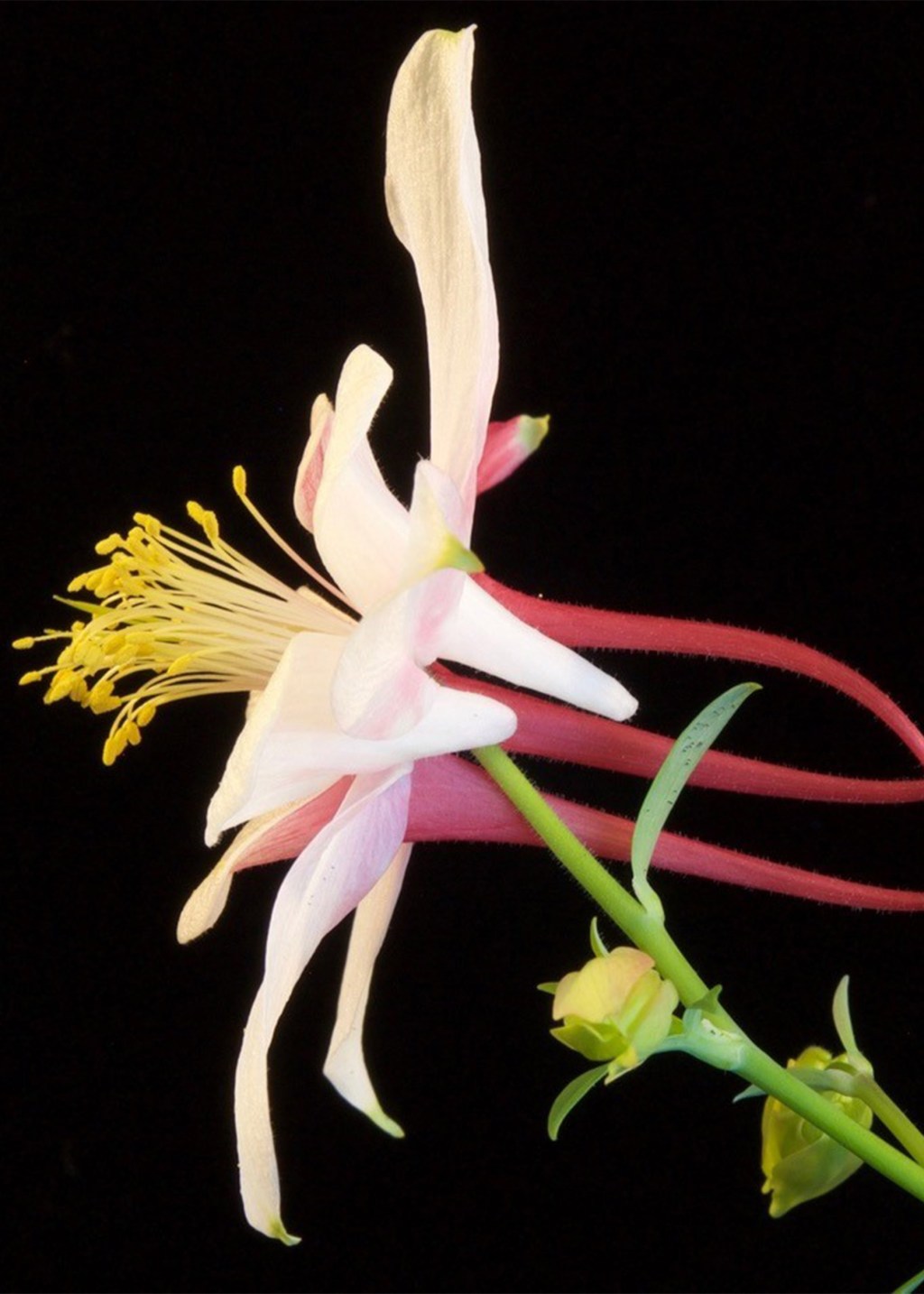
The Popovich of floral nectar spurs
Researchers discover gene controlling nectar spur development, opening door for insights into evolution.

-
Digging into the history of the cosmos
The main goal of Cora Dvorkin’s lab is trying to understand the nature of one of the universe’s most important and puzzling features: dark matter.

-
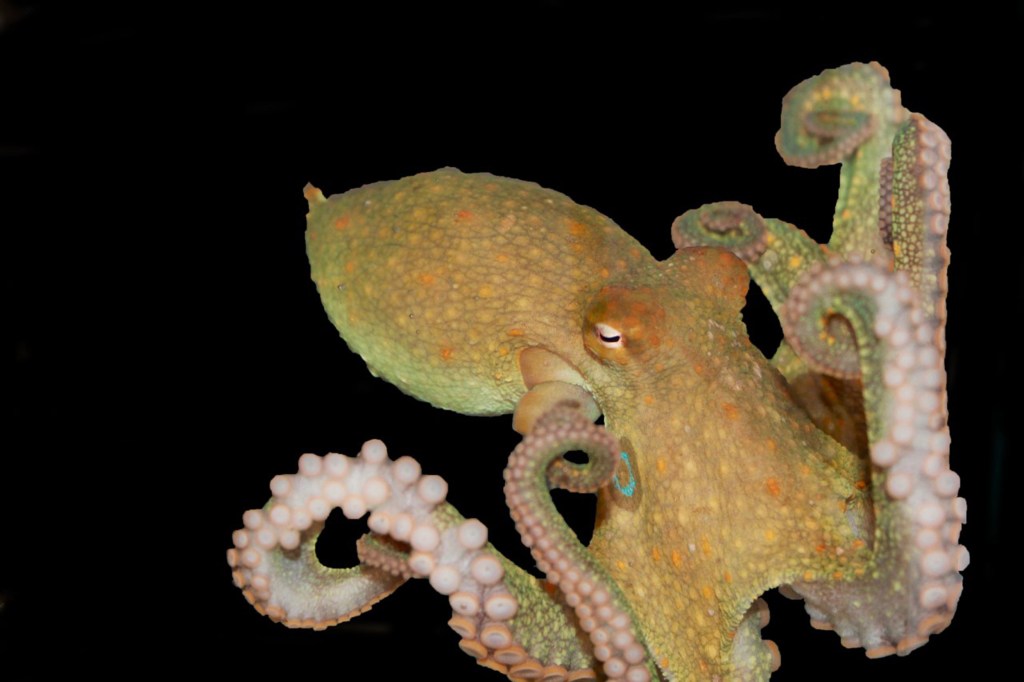
Touch and taste? It’s all in the suckers
Harvard researchers uncover novel family of sensors in octopuses.

-
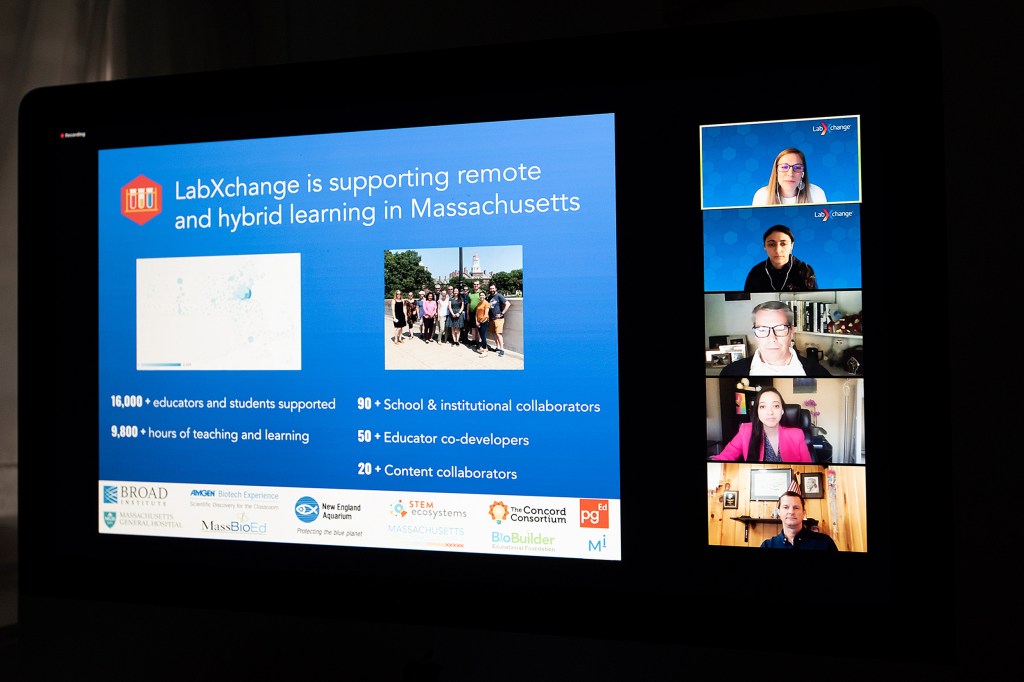
LabXchange meets and beats challenges of remote learning
LabXchange, a free digital-learning platform for science education, allows students, educators, scientists, and researchers to collaborate globally in an online community.
-
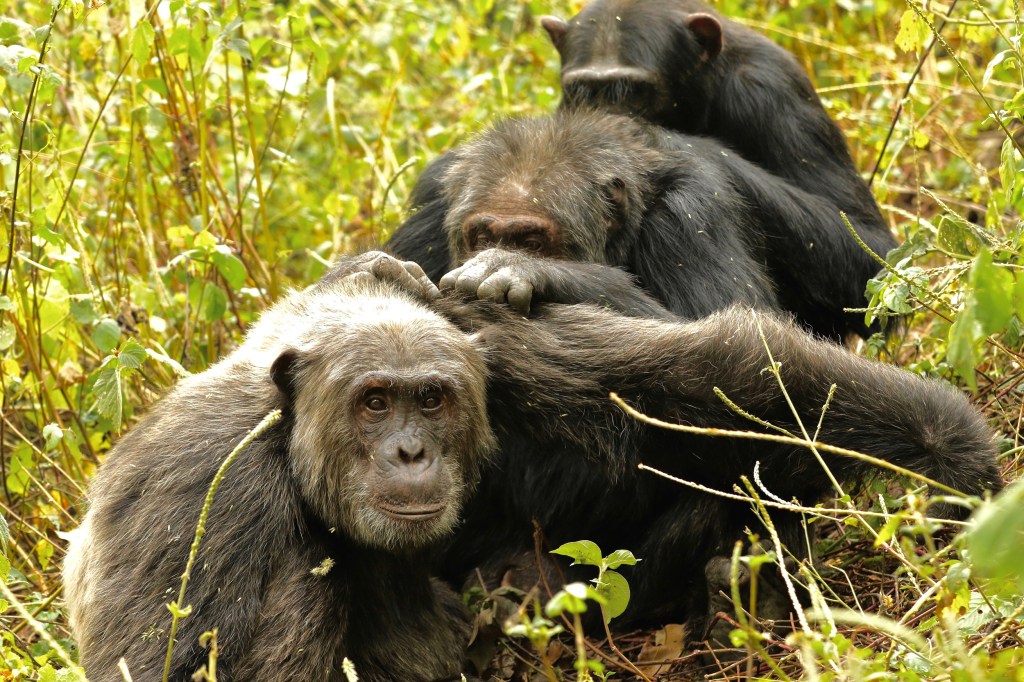
Why do we get so picky about friendship late in life? Ask the chimps
Understanding why older chimps tend to favor small circles of meaningful, established friendships rather than seek new ones may help scientists gain a better picture of what healthy human aging should look like and what triggers this social change.

-
Enzymatic DNA synthesis sees the light
Controlling a DNA-synthesizing enzyme with photolithographic methods from the computer chip industry facilitates multiplexed writing and storage of digital data in DNA.

-
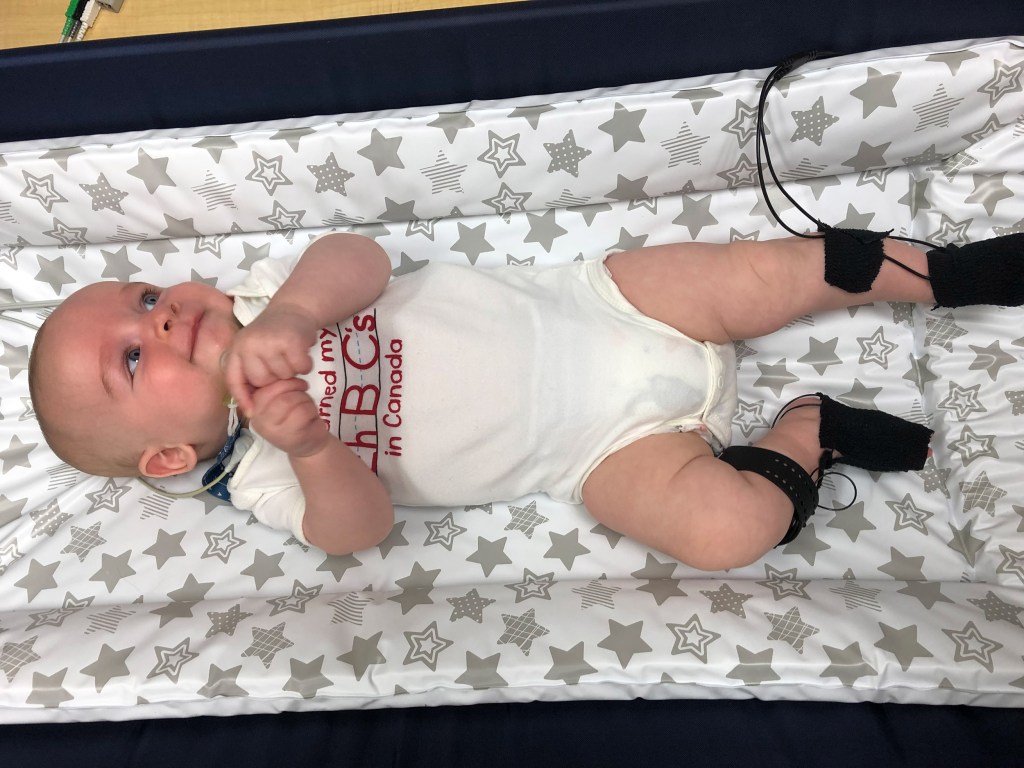
Frère Jacques, are you sleeping?
Researchers at Harvard’s Music Lab have determined that American infants relaxed when played lullabies that were unfamiliar and in a foreign language.
-
Trailblazing initiative marries ethics, tech
Faculty from the Computer Science and Philosophy departments join forces in a successful new undergraduate initiative, Embedded EthiCS, to change the way computer scientists think about the ethical implications of new technology.
-
Pandemic academics
A new Harvard course challenges students to use science to evaluate COVID-19 policies.

-
Deep learning takes on synthetic biology
Computational algorithms enable identification and optimization of RNA-based tools for myriad applications.
-
A timeline on the evolution of reptiles
A new study by a team of Harvard-led researchers contradicts a widely held theory that major transitions in evolution always happened in big, quick (geologically speaking) bursts, triggered by major environmental shifts.

-
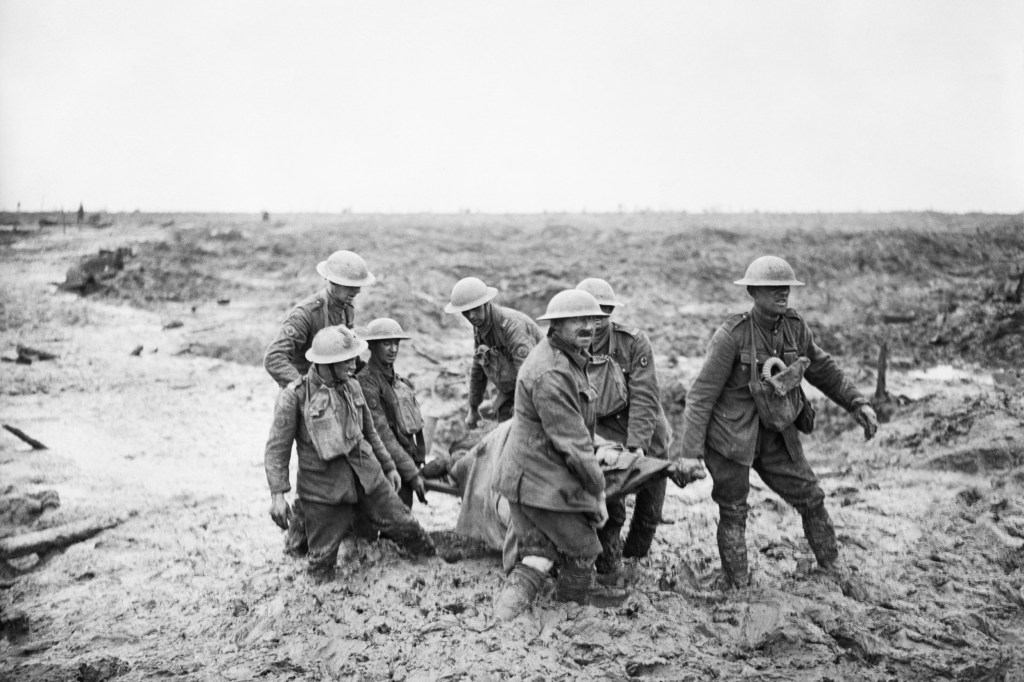
Six-year deluge linked to Spanish flu, World War I deaths
A new study of ice-core data shows that an unusual, six-year period of cold temperatures and heavy rainfall coincided with European deaths during the 1918 Spanish flu.

-
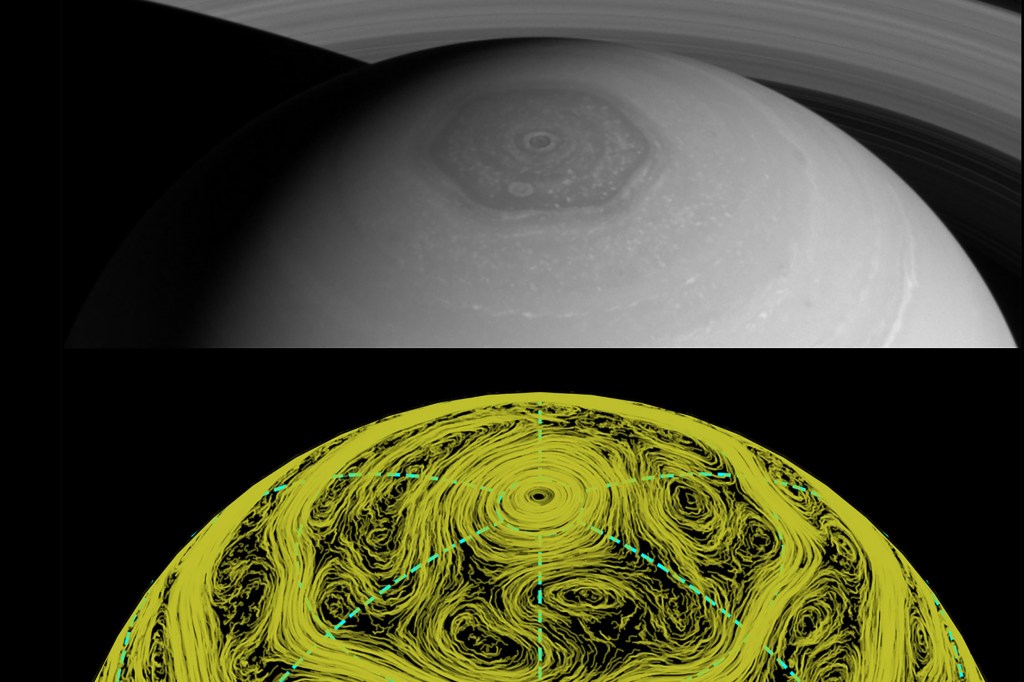
Interplanetary storm chasing
Harvard researchers use a 3D model to figure out how a hexagon-shaped mega-storm on Saturn was formed.
-
How cells sort themselves
Researchers have discovered a key control mechanism that cells use to self-organize in early embryonic development.
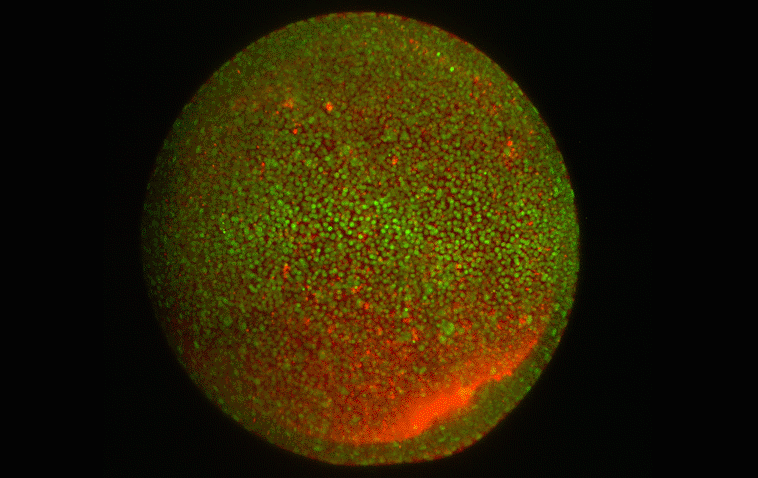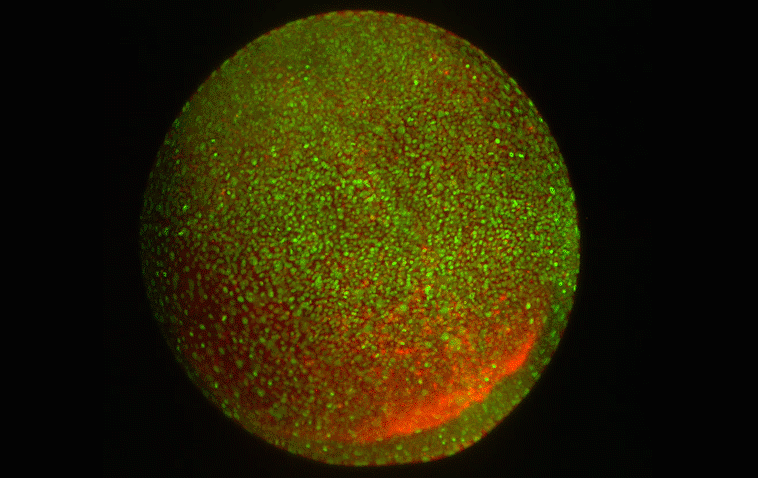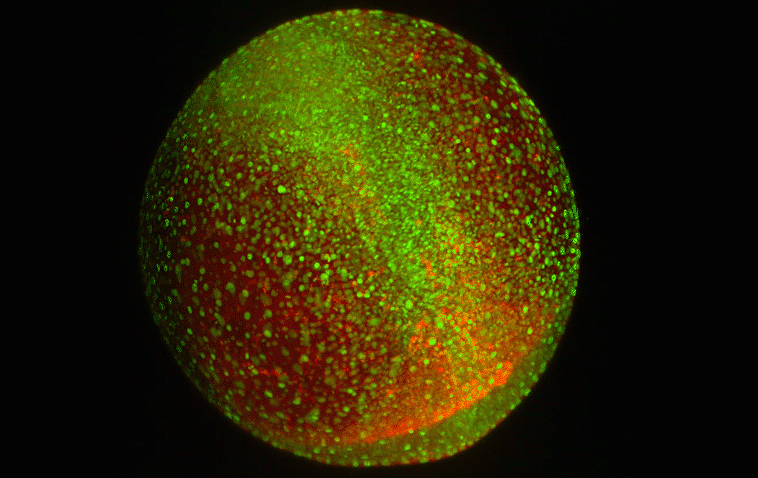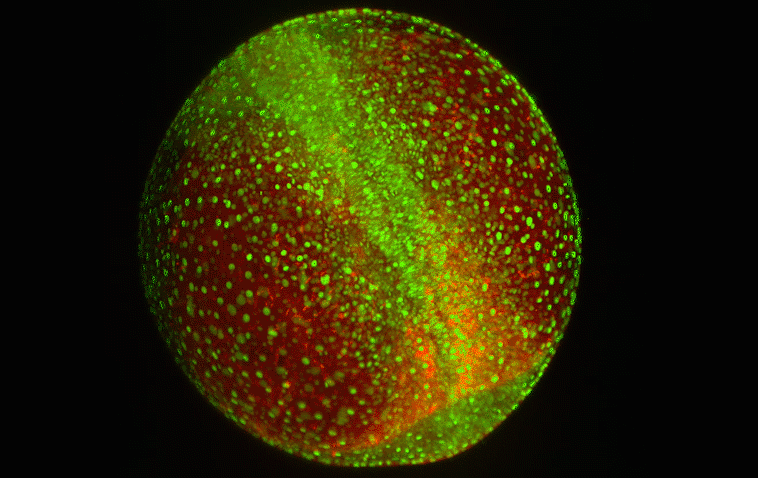
-
When it hits 100 degrees in Siberia …
With the threat of extreme heat rising, from California to Siberia, we ask climate scientist Peter Huybers what to expect in the future.

-
Infection detection
“Viral history” tool VirScan offers new insights into antibody response to SARS-CoV-2.
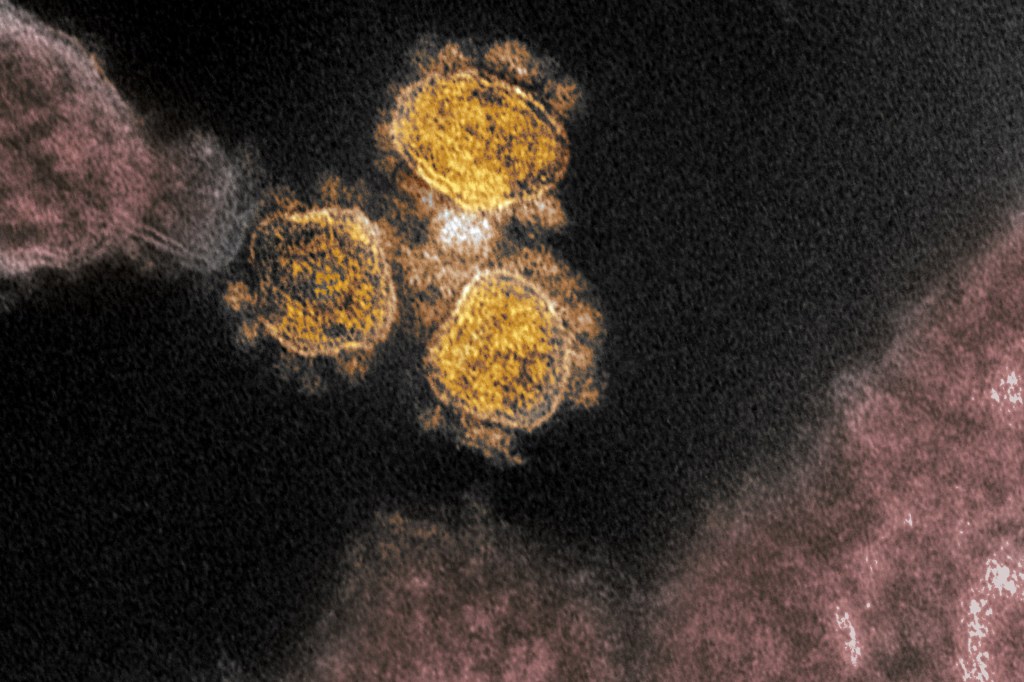
-
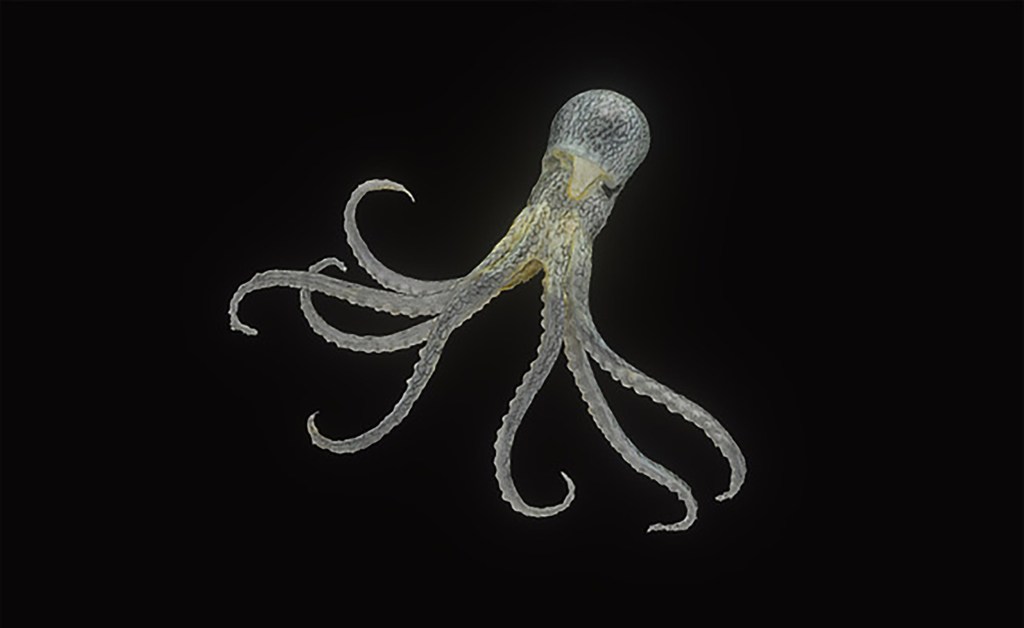
A model of how museums can share their collections more widely
Harvard has digitized 19th-century glass models of 15 marine invertebrates made by Rudolf and Leopold Blaschka. The 3D models are the result of between 250 to 700 images that had to be taken per glass piece.

-
A map of the human heart
Highly detailed map of the human heart could guide personalized heart treatments.