Science & Tech
-
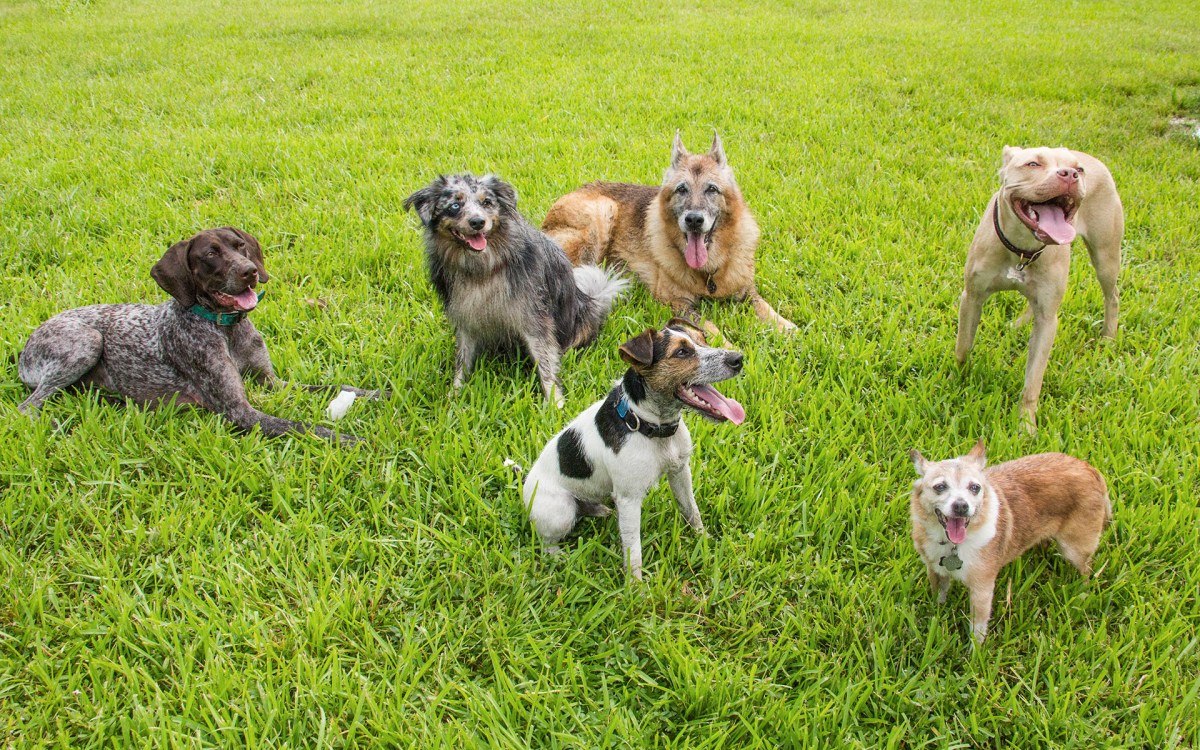

Harsh past might bare its teeth
Early adversity leads to higher aggression and fearfulness in adult canines, study says

-

What will AI mean for humanity?
Scholars from range of disciplines see red flags, possibilities ahead
-
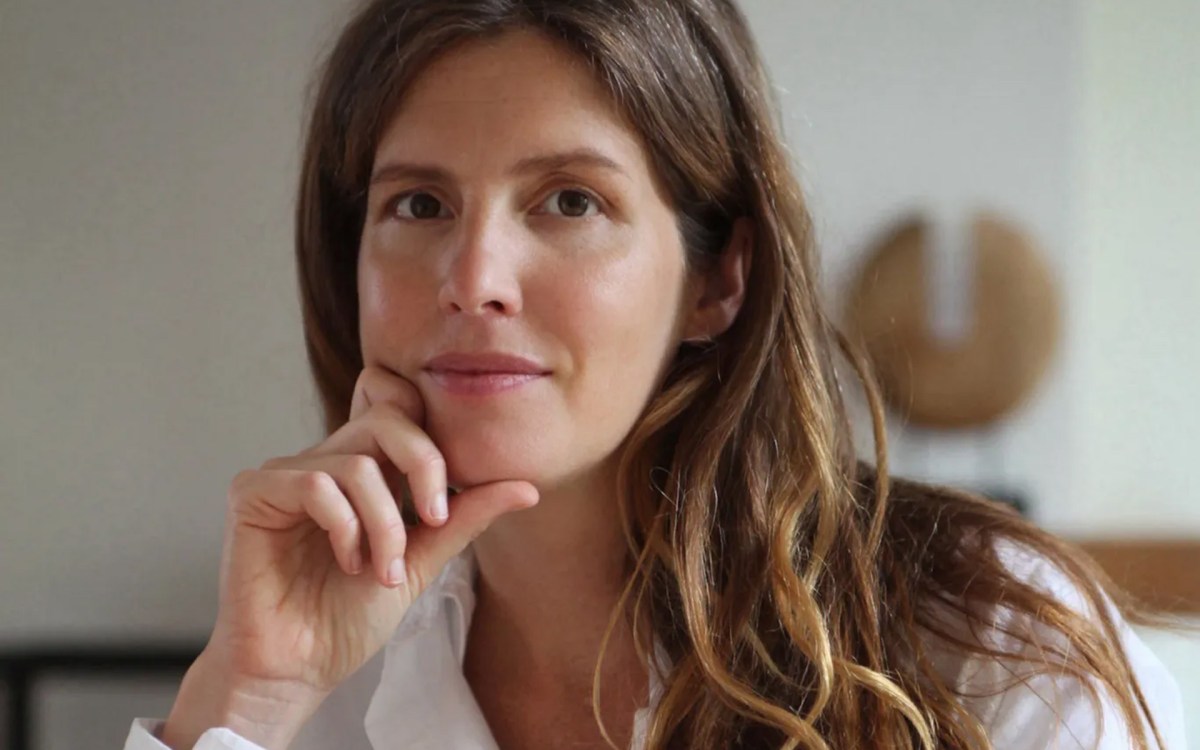

‘Human exceptionalism is at the root of the ecological crisis’
Saving the planet requires getting over ourselves, argues author of ‘The Arrogant Ape’
-
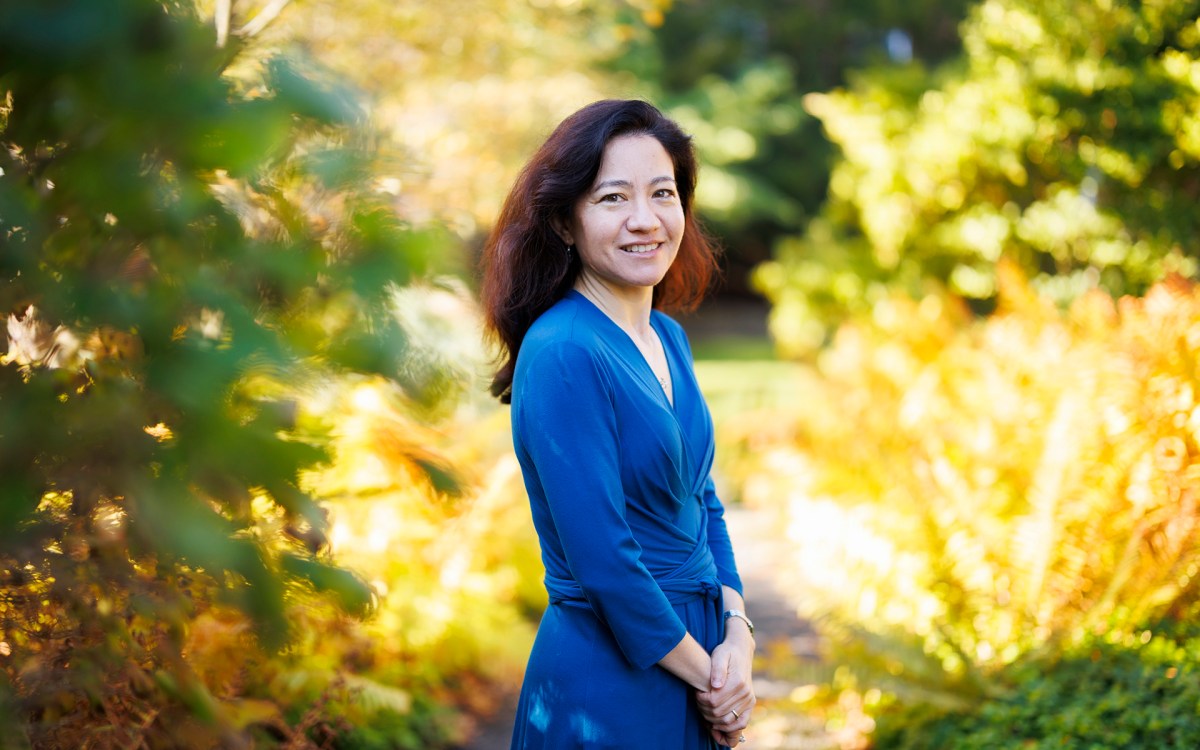

Lauren Williams awarded MacArthur ‘genius grant’
Math professor honored for theoretical breakthroughs with sometimes surprising applications across phenomena such as tsunamis, traffic
-

-
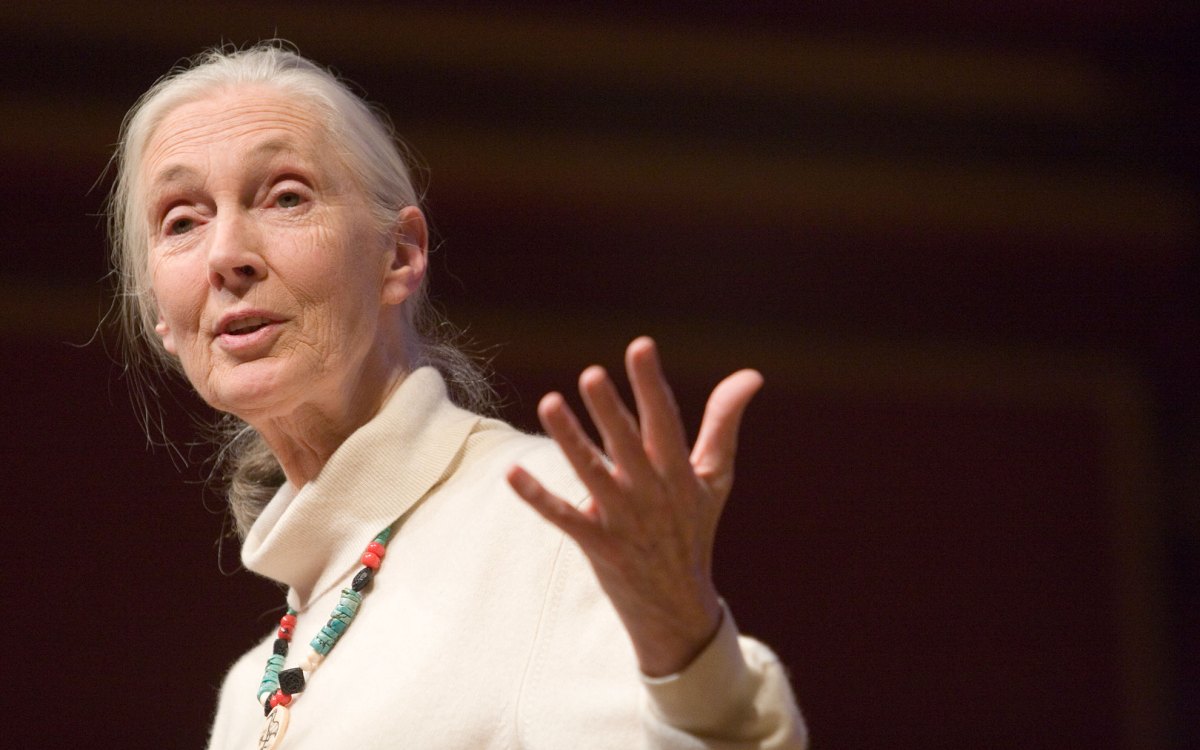

‘She had a sense of caring for everybody that she encountered.’
Richard Wrangham remembers his teacher and colleague Jane Goodall as a force of science, empathy, and hope
-
A silly-sounding prize for some serious science
Harvard-trained researchers win Golden Goose Awards from the American Association for the Advancement of Science.

-
An umbrella to combat warming
Harvard’s Keutsch Research Group is working on a controversial idea that might someday be our best hope against climate change: stratospheric aerosol injection.
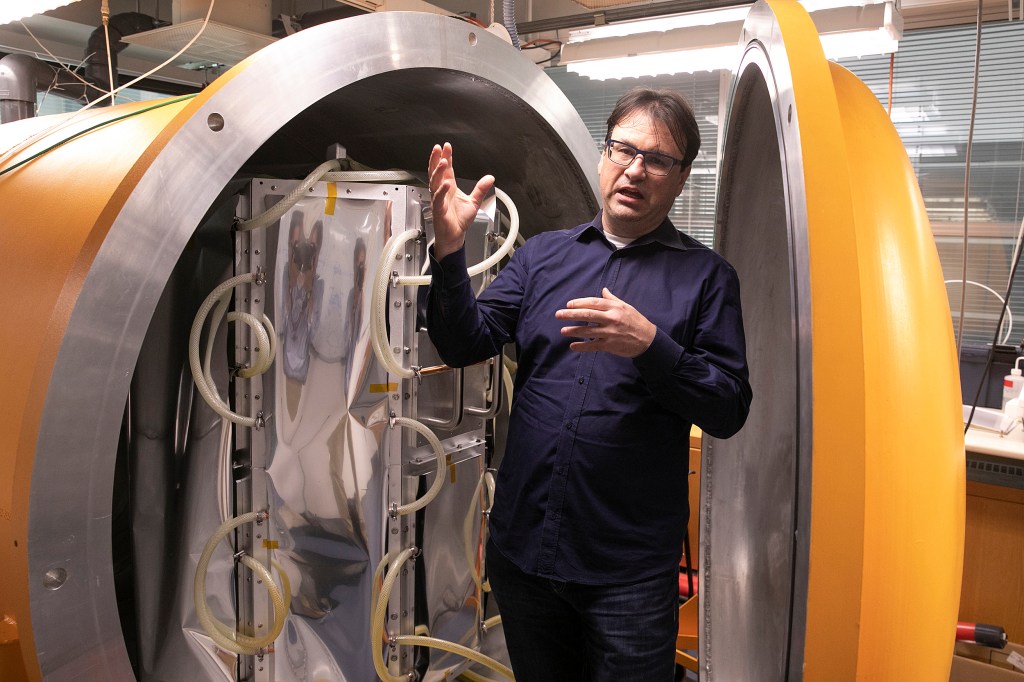

-
Life on the ice
Harvard researchers describe life in the South Pole.
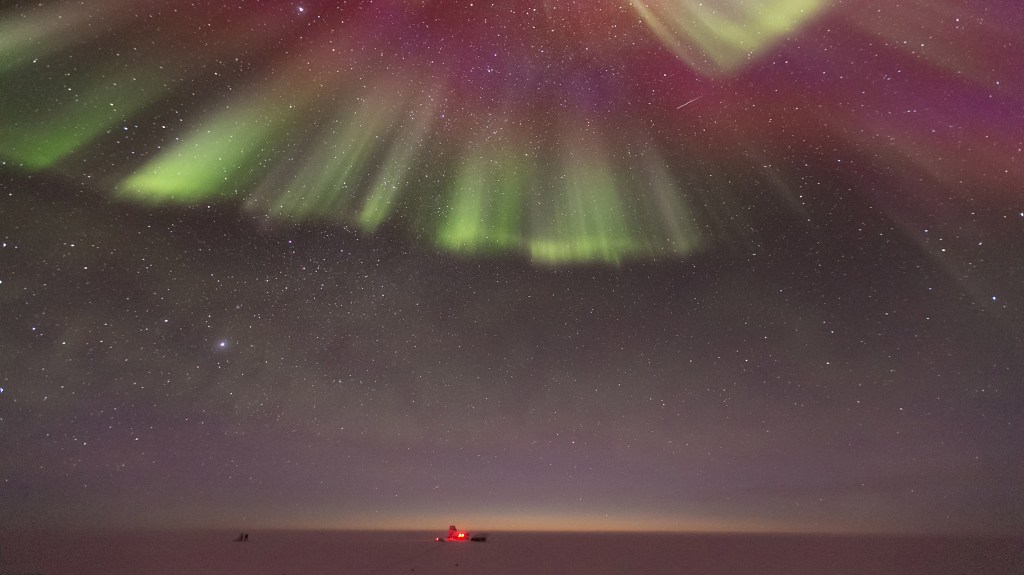

-
A ‘Goldilocks zone’ for planet size
Researchers have redefined the lower size limit for planets to maintain surface liquid water for long periods of time, extending the so-called habitable zone for small, low-gravity planets.
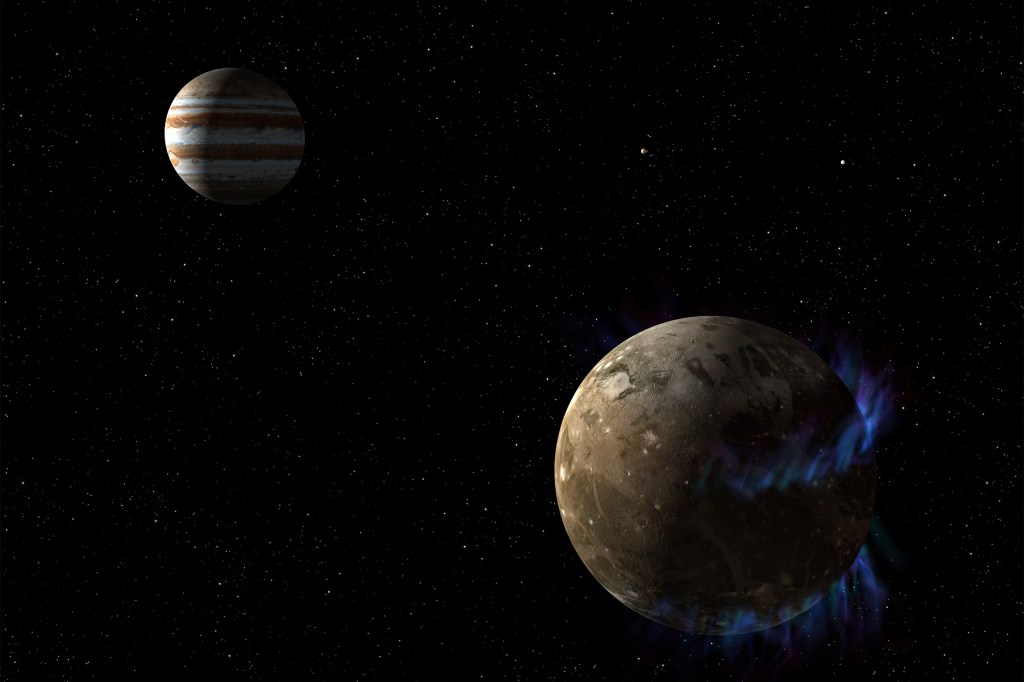

-
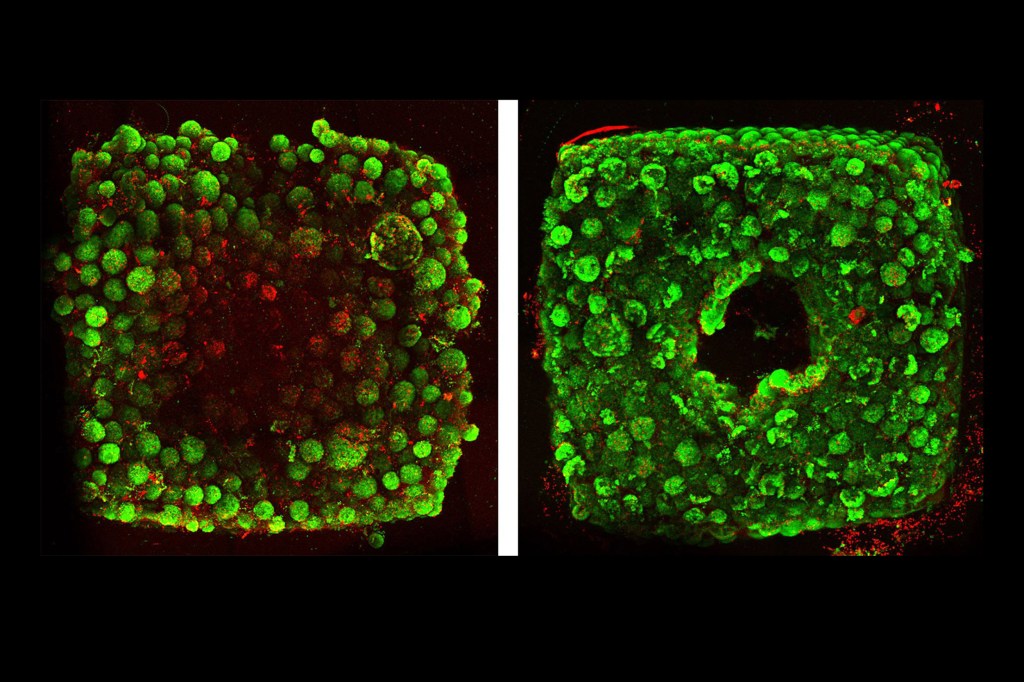
A SWIFTer way to build organs
A new technique called SWIFT (sacrificial writing into functional tissue) ultimately may be used therapeutically to repair and replace human organs with lab-grown versions containing patients’ own cells.
-
Lessons in learning
Study shows students in ‘active learning’ classrooms learn more than they think

-
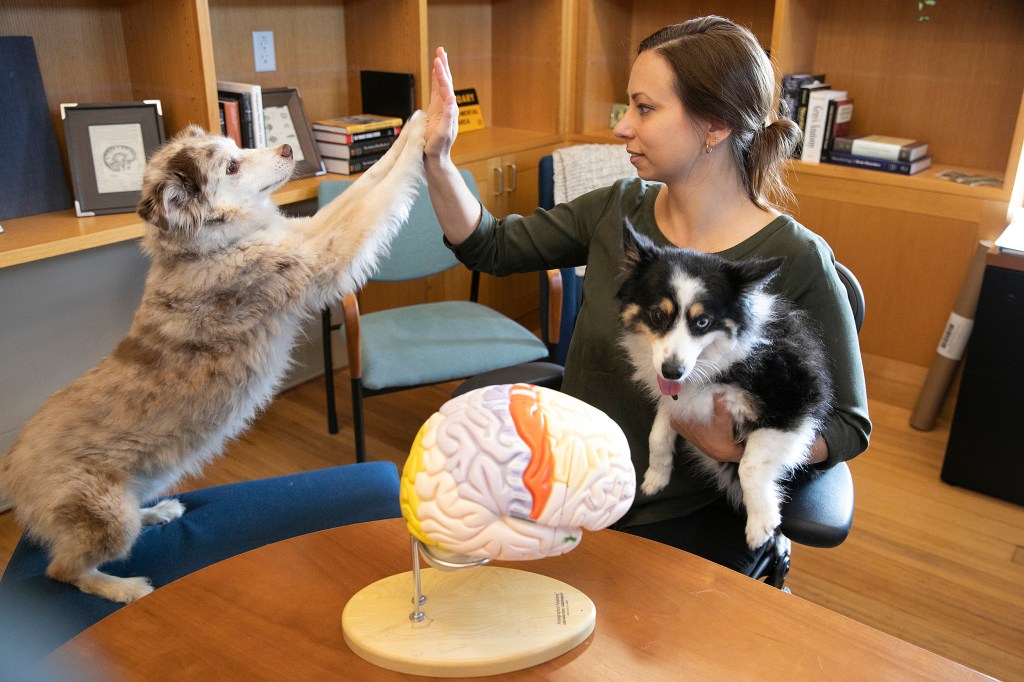
Hunters, herders, companions: Breeding dogs has reordered their brains
Erin Hecht, who joined the faculty in January, has published her first paper on our canine comrades in the Journal of Neuroscience, finding that different breeds have different brain organizations owing to human cultivation of specific traits.

-
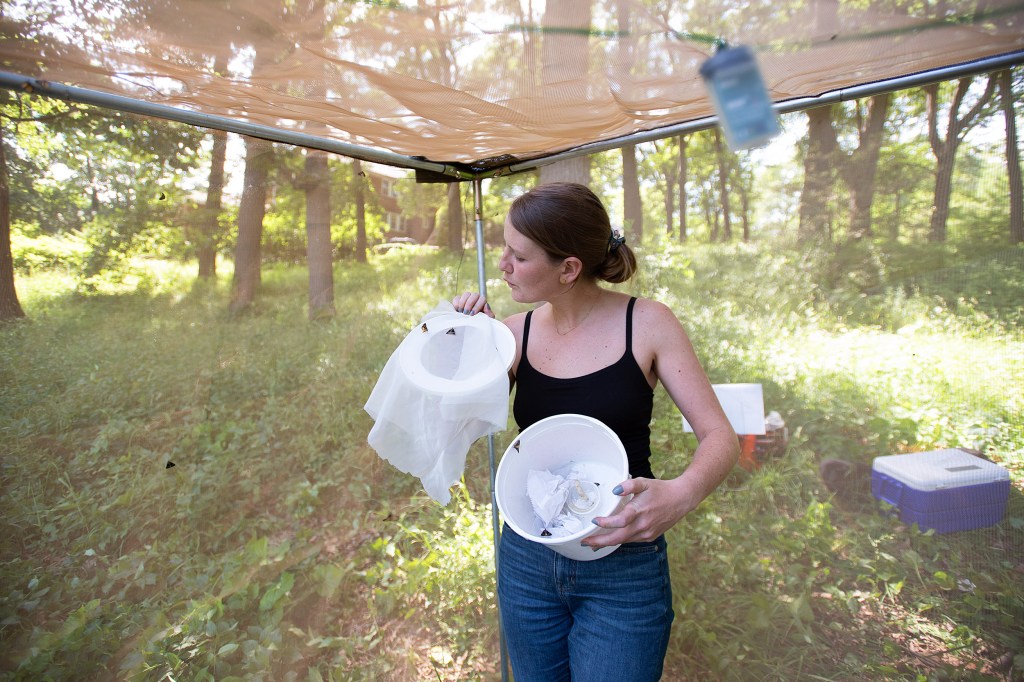
Fighting flora with fauna
Scientists at the Arnold Arboretum are employing a species of predator moth to fight the invasive swallow-wort vine.

-
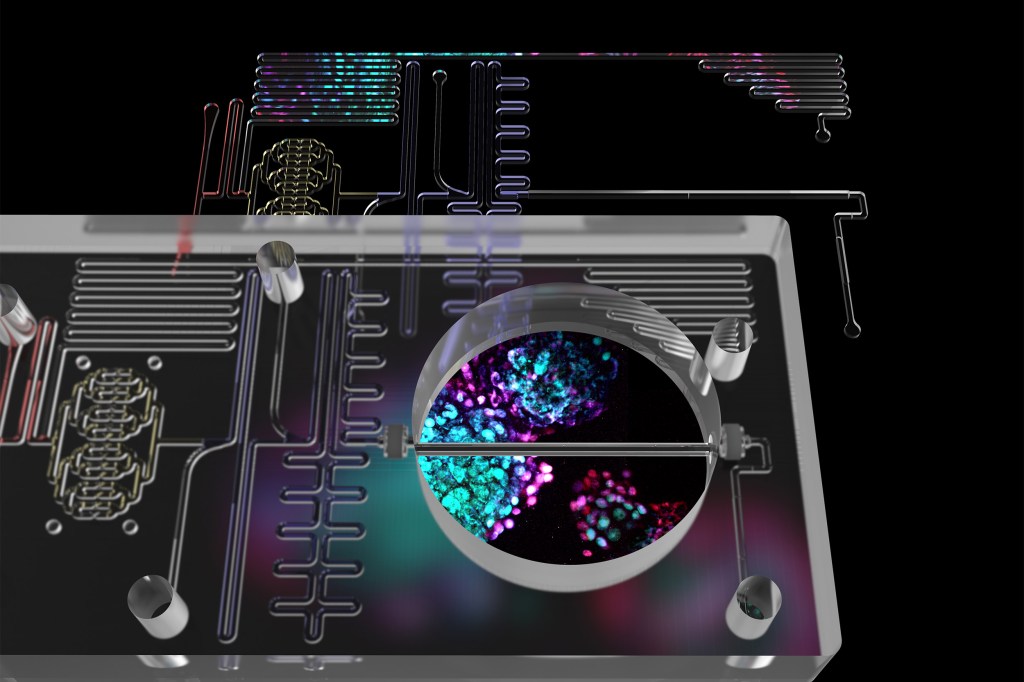
Pancreas on a chip
Islet-on-a-chip technology allows clinicians to easily determine the therapeutic value of beta cells for any given patient.
-
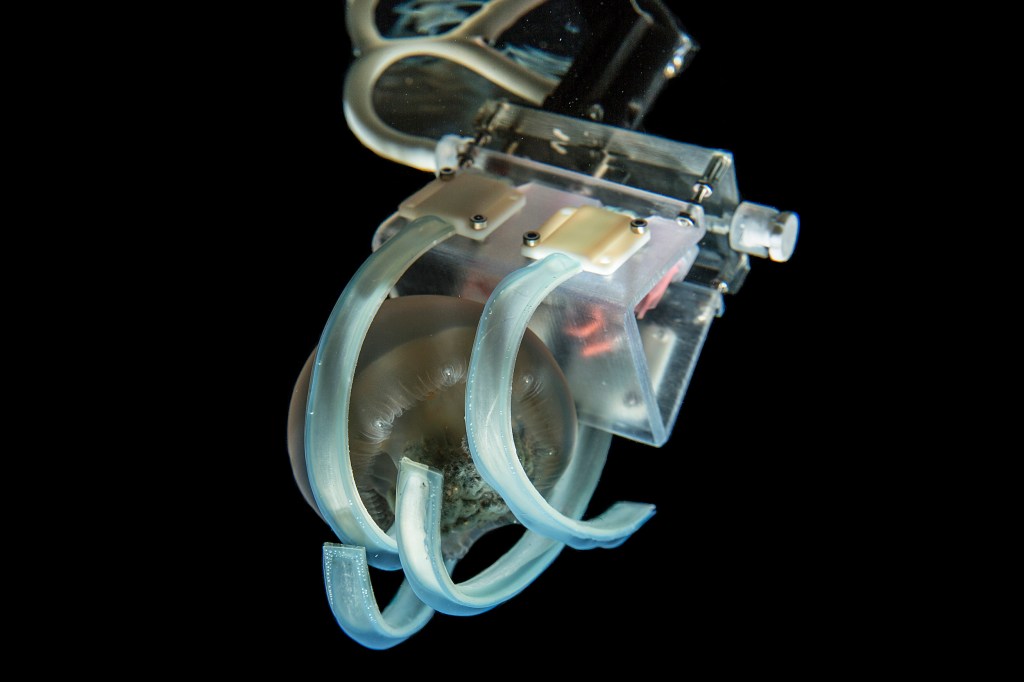
A gentle grip on gelatinous creatures
To study jellyfish and other fragile marine life without damaging them, researchers developed ultra-soft underwater grippers that catch and release jellyfish without harm.
-
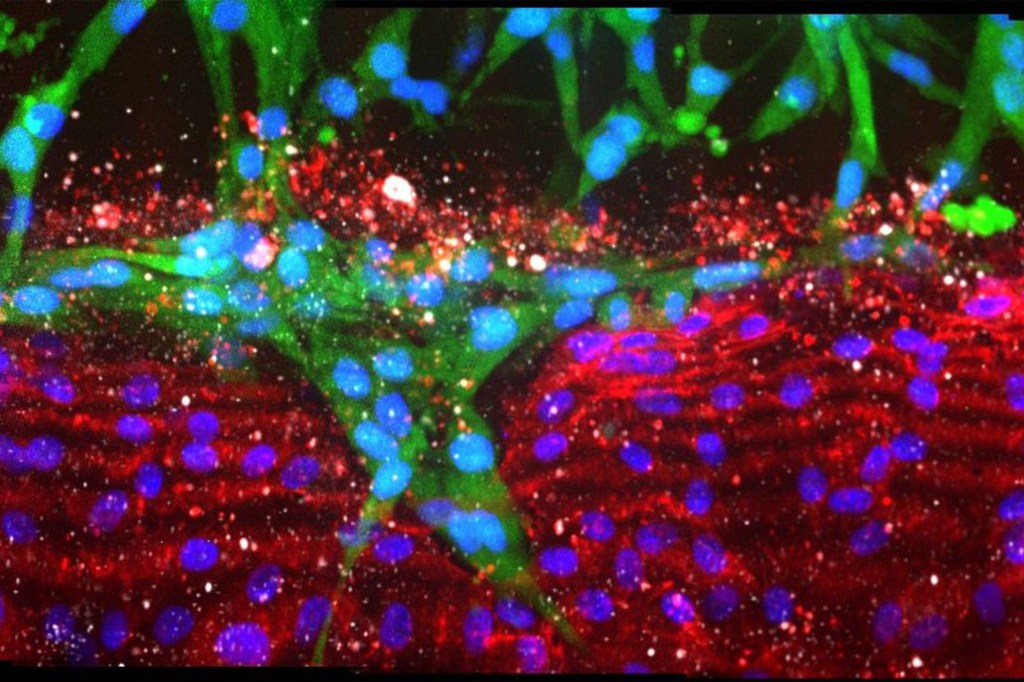
Exposing how pancreatic cancer does its dirty work
New research has found that pancreatic cancer actively destroys nearby blood vessels and replaces them with cancerous cells, blocking chemotherapy from reaching tumors. This insight could lead to new treatments that act by preventing cancer’s colonization of blood vessels.
-
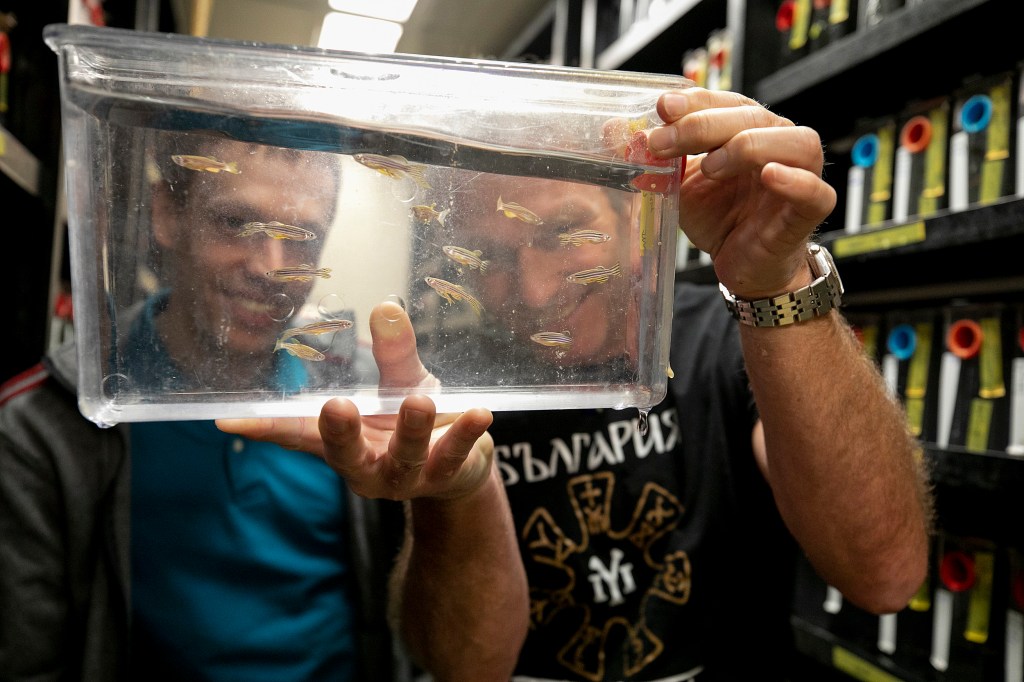
How a zebrafish model may hold a key to biology
Martin Haesemeyer set out to build an artificial neural network that worked differently than fish’s brains, but what he got was a system that almost perfectly mimicked the zebrafish — and that could be a powerful tool for understanding biology.

-
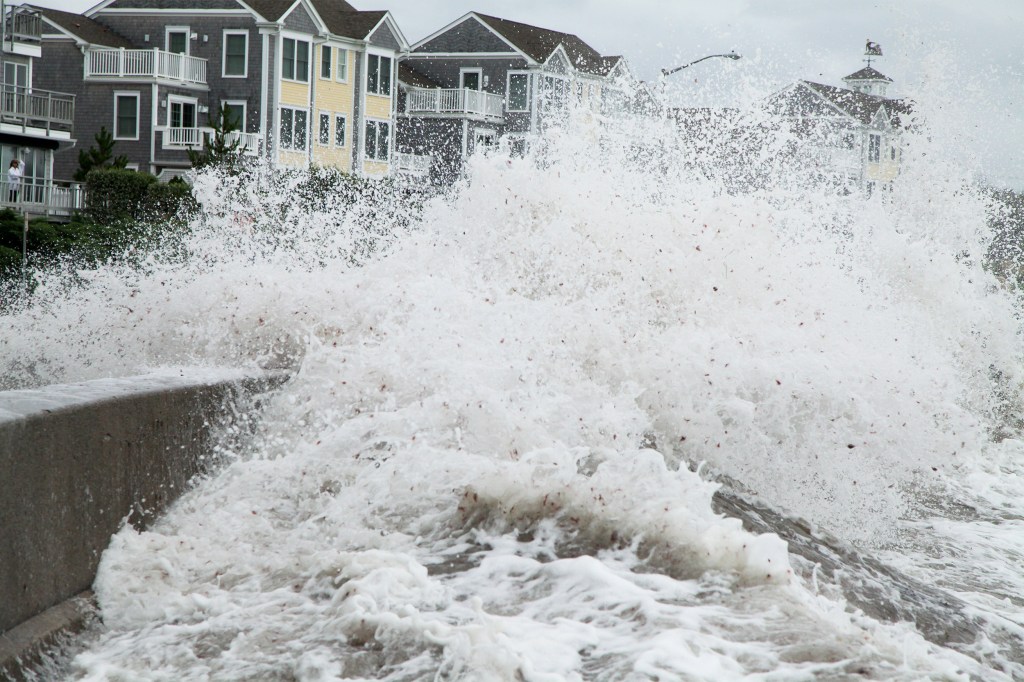
Want to avoid climate-related disasters? Try moving
For decades, the response to flooding and hurricanes was a vow to rebuild. A.R. Siders believes the time has come to consider managed retreat, or the practice of moving communities away from disaster-prone areas to safer lands.

-
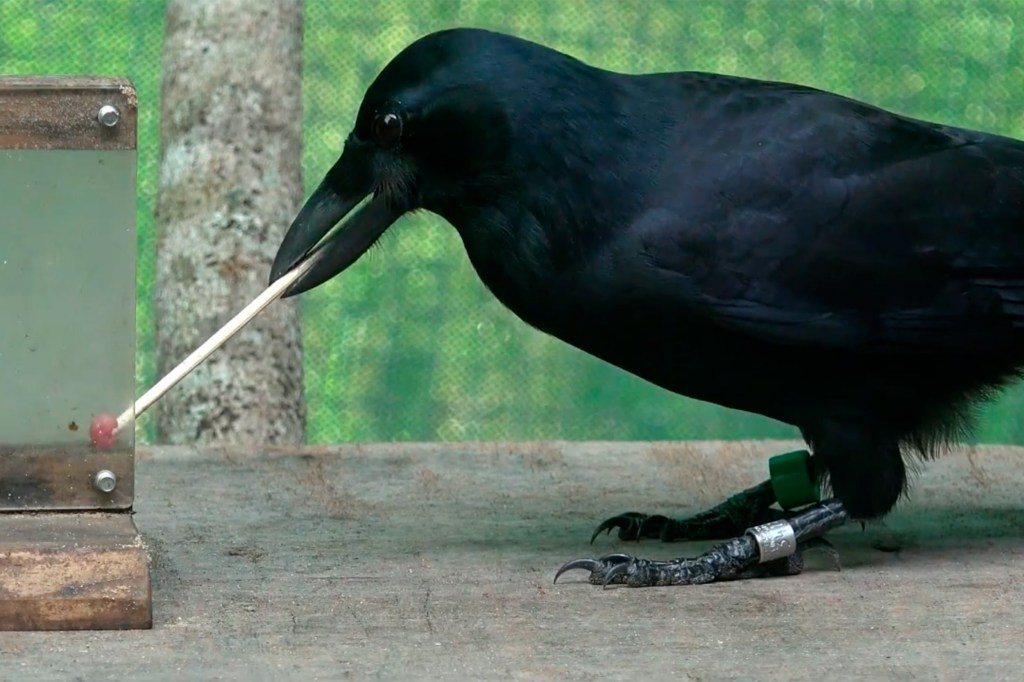
Clever crows
A new paper, co-authored by Dakota McCoy, a graduate student working in the lab of George Putnam Professor of Biology David Haig, suggests that, after using tools, crows were more optimistic.

-
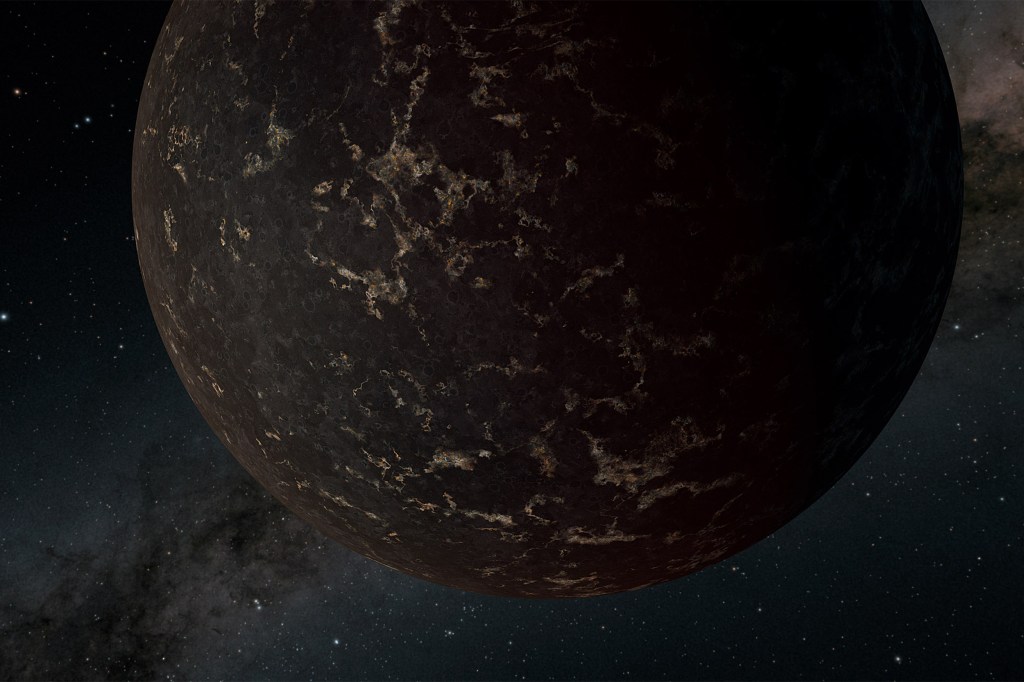
Prospects clouded for finding life on the largest class of planets
Led by Laura Kreidberg, a Clay Fellow at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, a new study shows that LHS 3844b, a terrestrial exoplanet orbiting a small sun 48.6 light-years away, has no detectable atmosphere

-
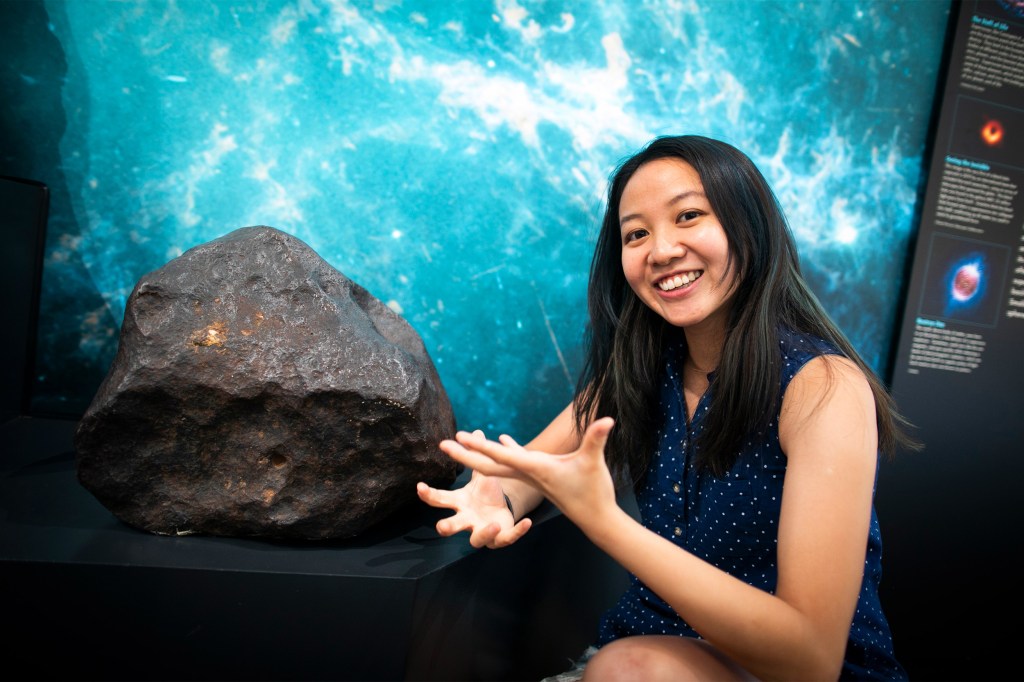
How the moon came to be
A fourth-year graduate student in the lab of Professor of Geochemistry Stein Jacobsen, Yaray Ku is working on a project aimed at understanding how the moon formed, and to do it, she’s working with actual lunar samples.

-
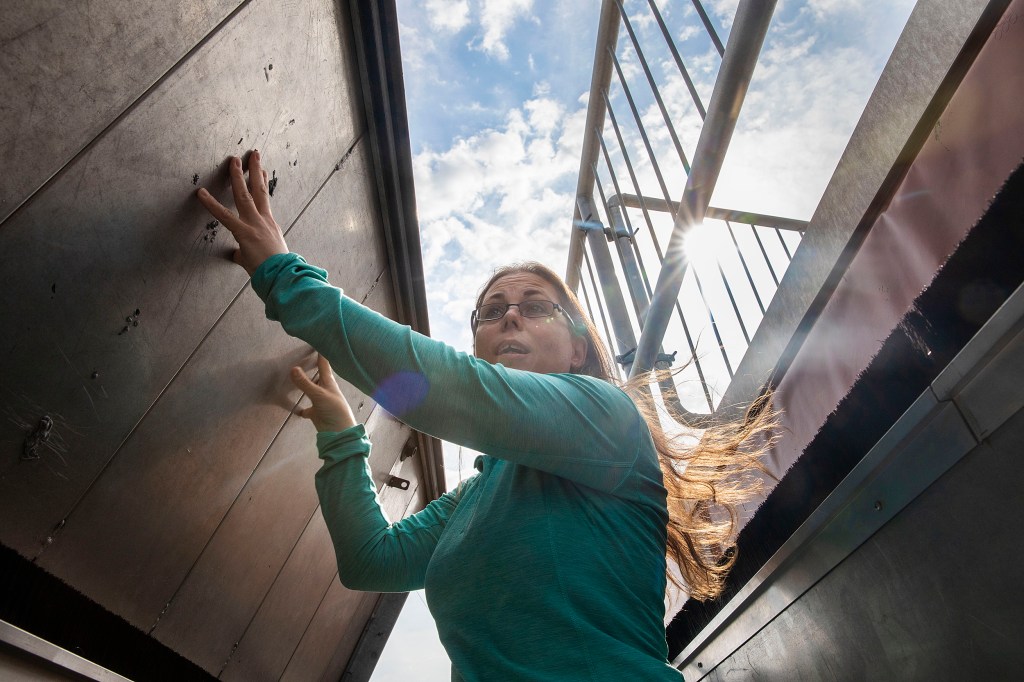
Astronomy Lab sees the light — and wants everyone else to, too
Accessibility devices at the lab use sound to allow the visually impaired to envision the stars

-
Uncovering how cells become organs
Tiny sensors are embedded into stretchable, integrated mesh that grows with the developing tissue, allowing scientists to track how cells grow into organs.

-
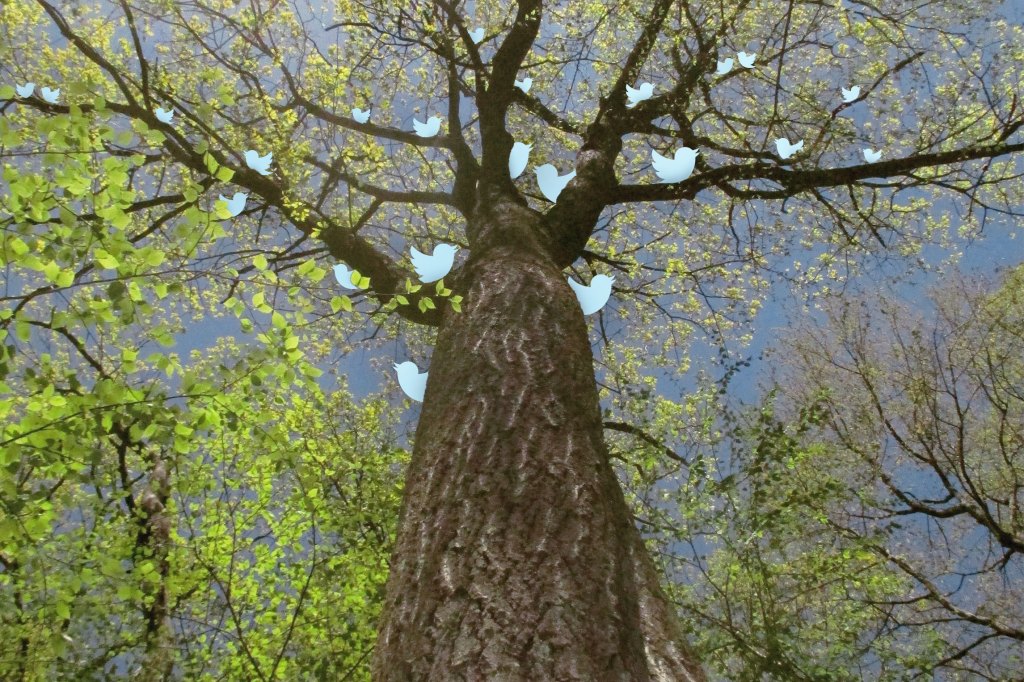
A red oak live tweets climate change
Tree in Harvard Forest outfitted with sensors, cameras, and other digital equipment sends out on-the-ground coverage.

-
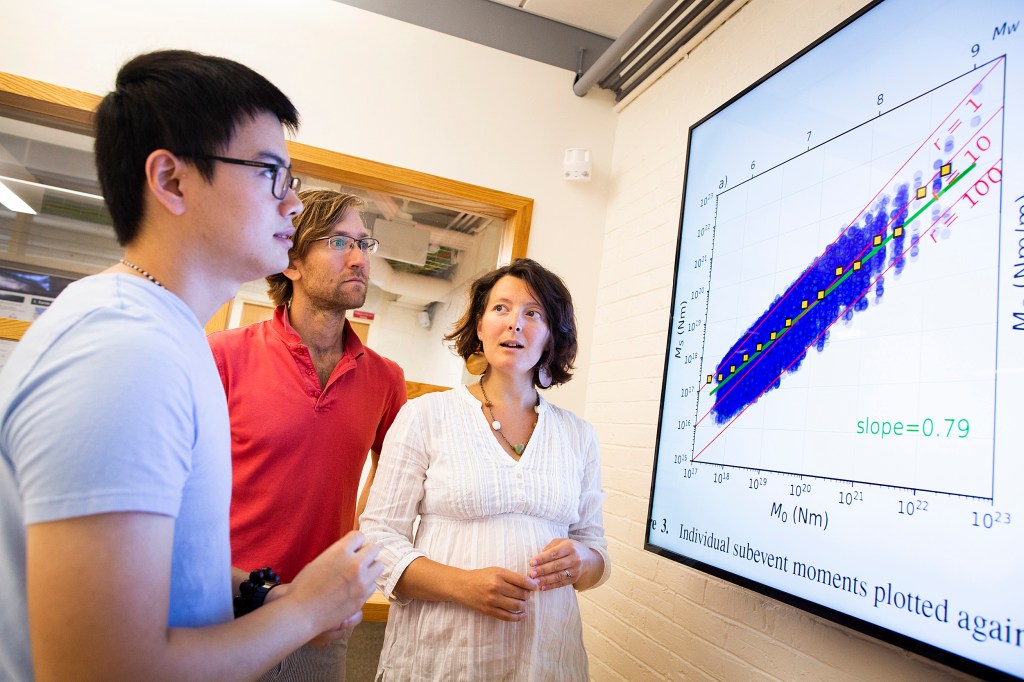
Predicting the strength of earthquakes
Scientists will be able to predict earthquake magnitudes earlier thanks to new research by Marine Denolle, assistant professor in the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences at Harvard.
-
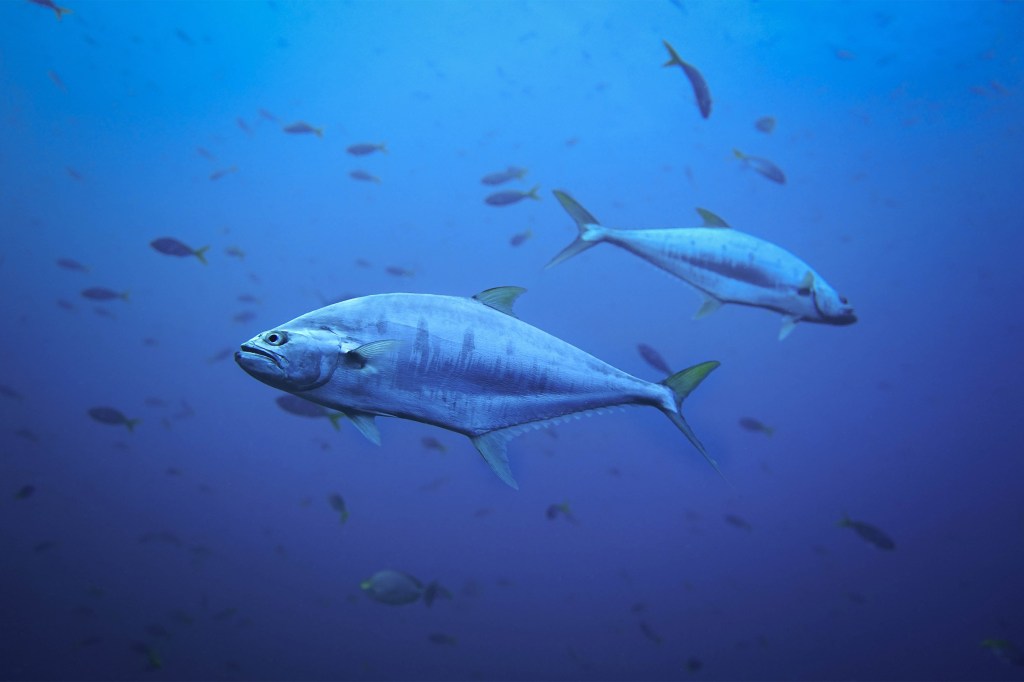
Mercury levels in fish are on the rise
A new study concludes that while the regulation of mercury emissions have successfully reduced methylmercury levels in fish, spiking temperatures are driving those levels back up and will play a major role in the methylmercury levels of marine life in the future.

-
Giving teachers a DNA refresher
Mansi Srivastava’s lab worked with middle school teachers in an education workshop on DNA and evolution.

-
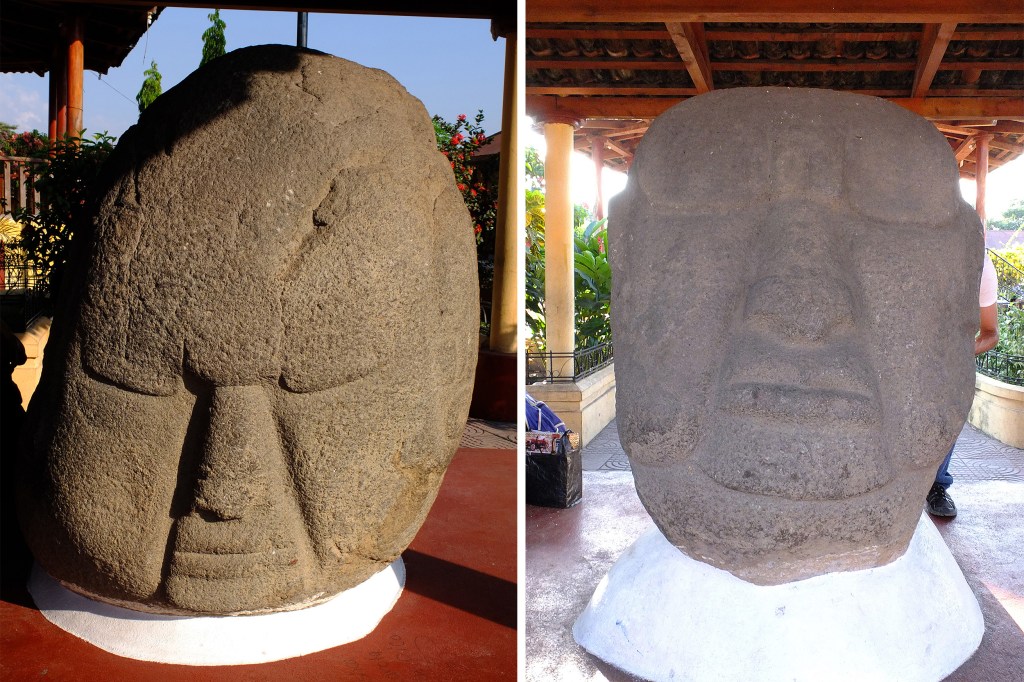
The Mesoamerican attraction to magnetism
Led by Assistant Professor of Earth and Planetary Sciences Roger Fu, a team of researchers has shown that the makers of ancient Mesoamerican statues found in Guatemala intentionally carved the figures to place the magnetic areas over the navel or right temple — suggesting not only that they were familiar with the concept of magnetism, but had some way of detecting the magnetic anomalies.

-
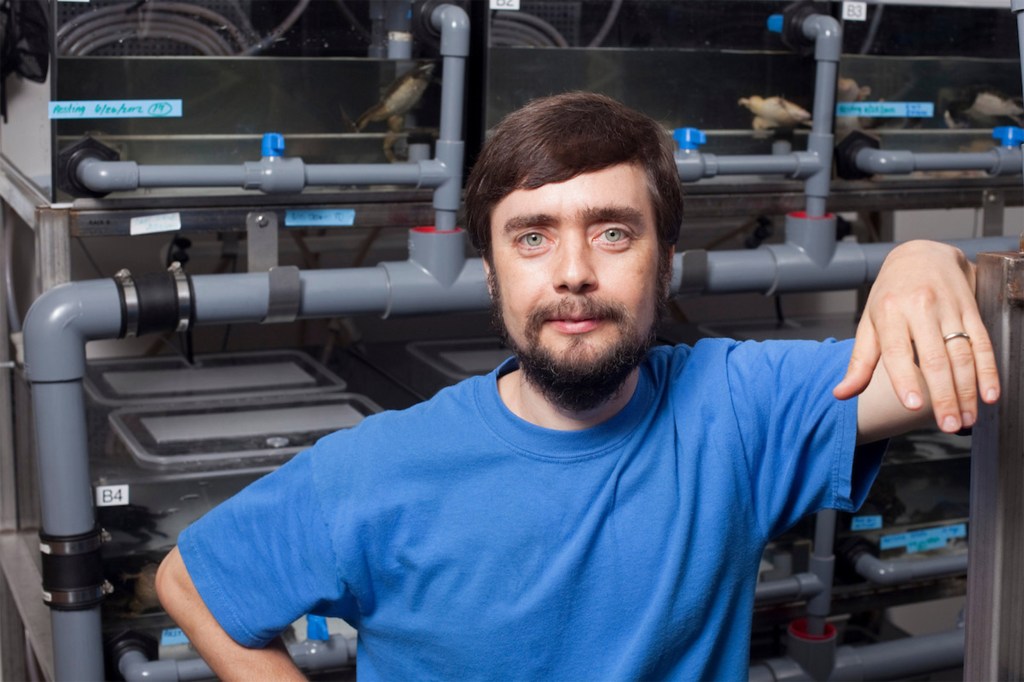
Electrifying insights into how bodies form
A researcher is reviving the study of bioelectricity to learn how cells communicate with each other to form tissues and organs, and how harnessing those signals could one day lead to truly regenerative medicine, in which amputees could simply regrow limbs.
-
Visual forensics that can detect fake text
Researchers at the SEAS and IBM Research developed a better way to help people detect AI-generated text.

-
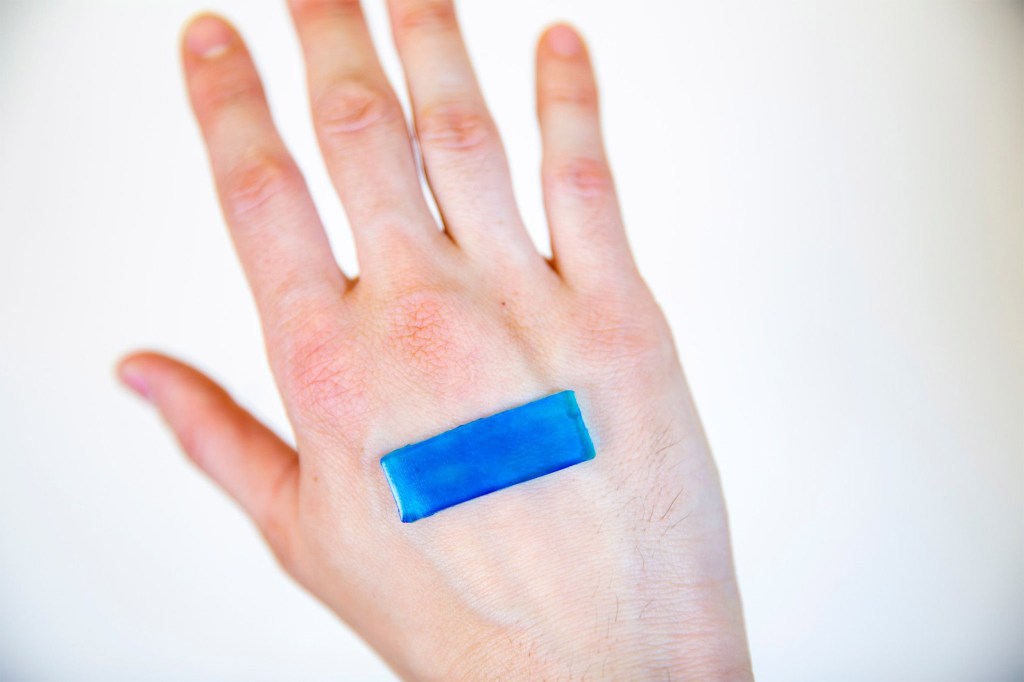
Using body heat to speed healing
To speeding up wound healing, researchers have developed active adhesive dressings based on heat-responsive hydrogels that are mechanically active, stretchy, tough, highly adhesive, and antimicrobial.
-
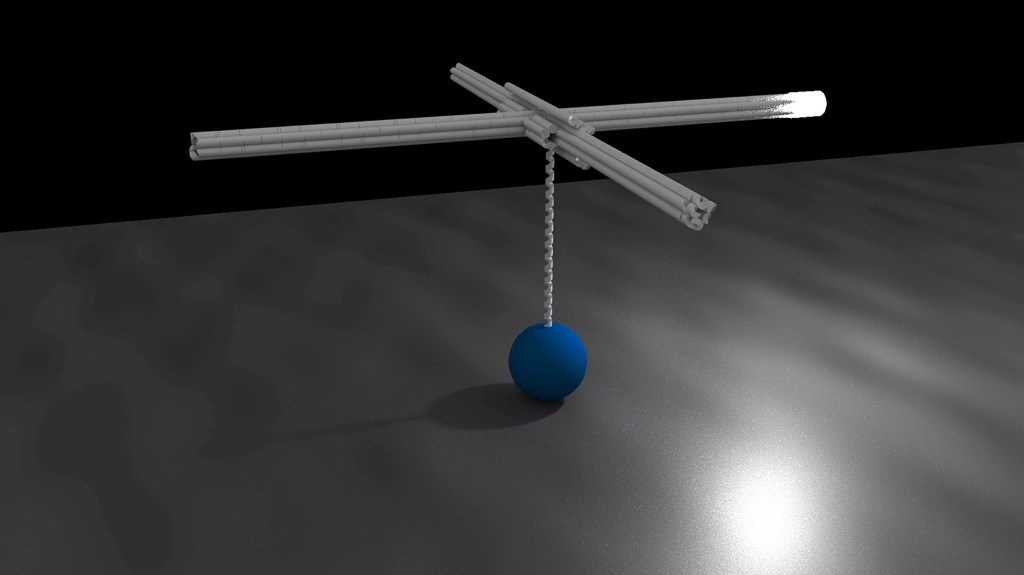
A new spin on an old question
Understanding how DNA and proteins interact — or fail to — could help answer fundamental biological questions about human health and disease.
-
A way to make Mars habitable
Researchers from Harvard University, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab, and the University of Edinburgh suggest that regions of the Martian surface could be made habitable with a material — silica aerogel — that would mimic Earth’s atmospheric greenhouse effect.

-
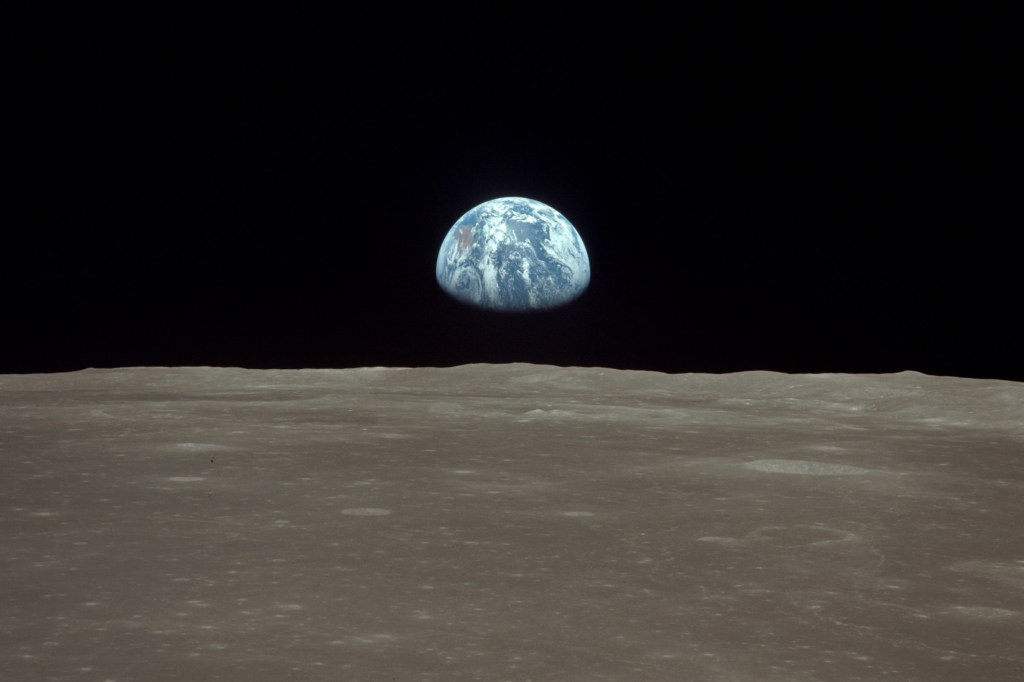
Harvard reflects on Apollo 11 and Neil Armstrong’s moon walk
A trio of Harvard astronomers reflect on the impact of Neil Armstrong’s first steps on the moon, then and now.

-
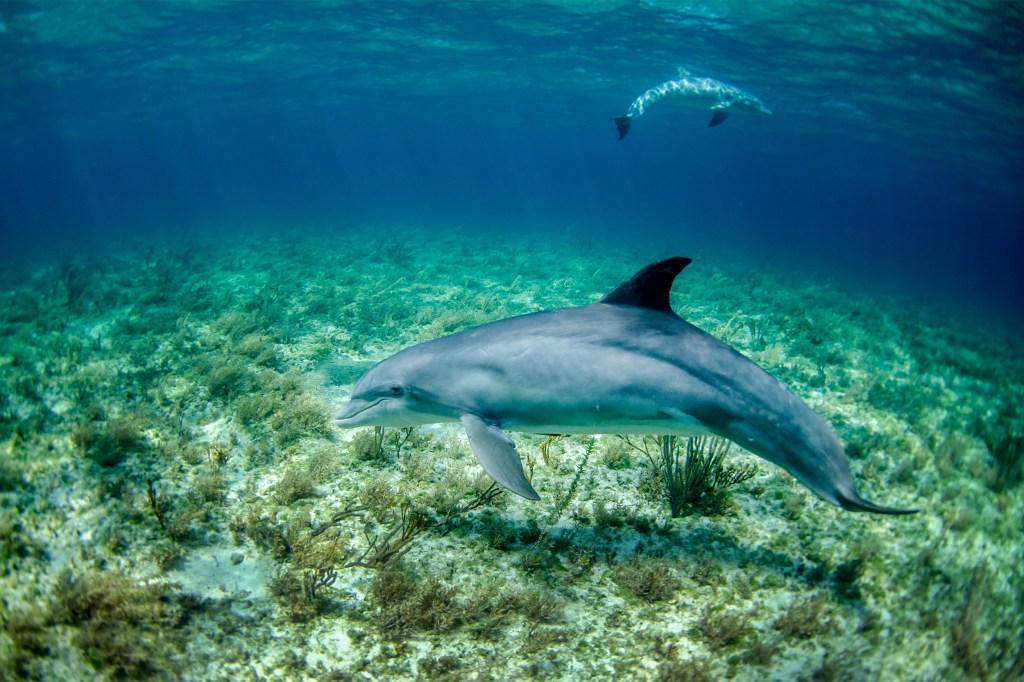
Beneath the surface
New study debunks long-held theory that dolphins had ridged skin, which helped them swim faster.



