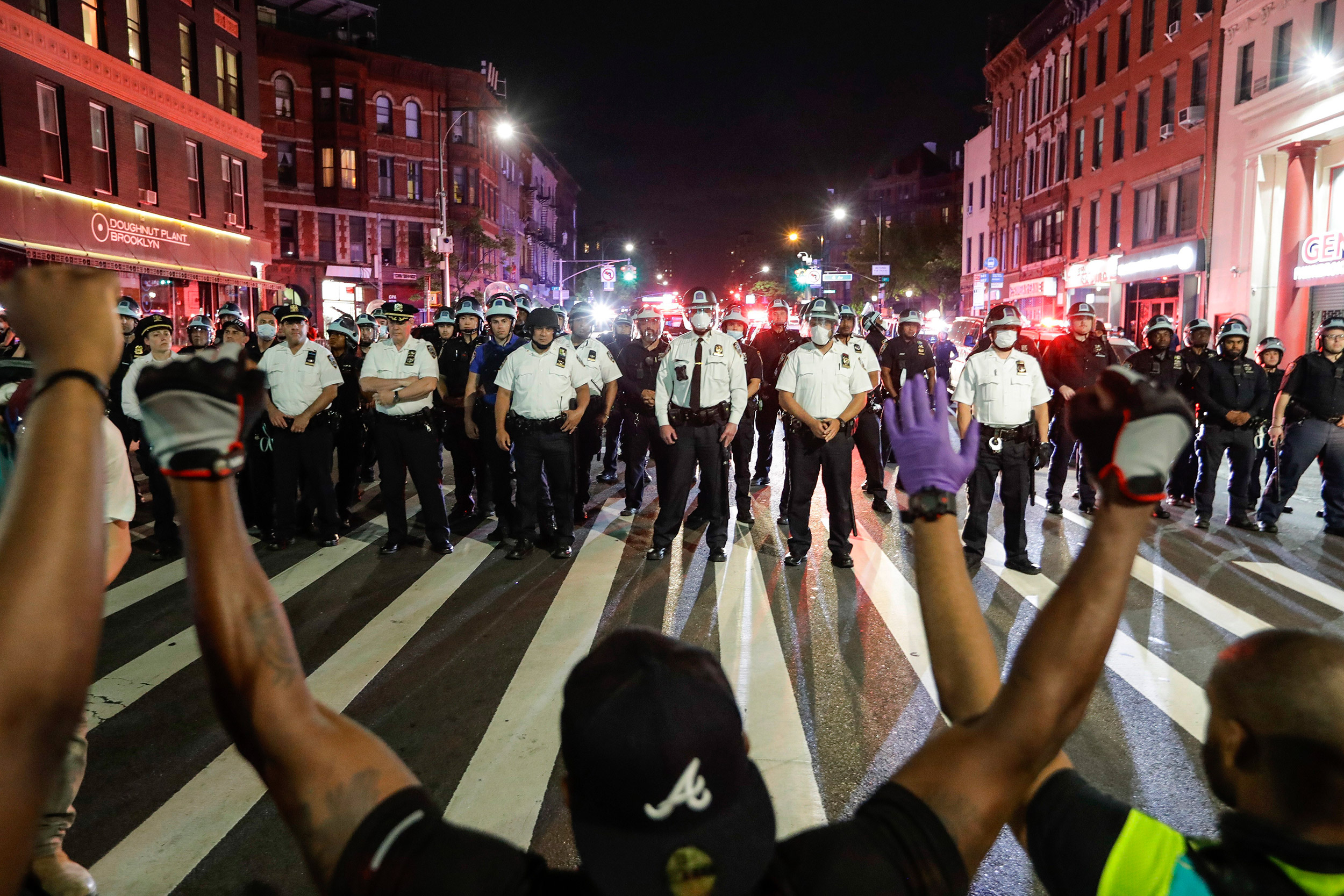
Protesters take a knee in front of New York City police officers during a solidarity rally for George Floyd, June 4, 2020.
AP Photo/Frank Franklin II
Solving racial disparities in policing
Experts say approach must be comprehensive as roots are embedded in culture
“Unequal” is a multipart series highlighting the work of Harvard faculty, staff, students, alumni, and researchers on issues of race and inequality across the U.S. The first part explores the experience of people of color with the criminal justice legal system in America.
It seems there’s no end to them. They are the recent videos and reports of Black and brown people beaten or killed by law enforcement officers, and they have fueled a national outcry over the disproportionate use of excessive, and often lethal, force against people of color, and galvanized demands for police reform.
This is not the first time in recent decades that high-profile police violence — from the 1991 beating of Rodney King to the fatal shooting of Michael Brown in 2014 — ignited calls for change. But this time appears different. The police killings of Breonna Taylor in March, George Floyd in May, and a string of others triggered historic, widespread marches and rallies across the nation, from small towns to major cities, drawing protesters of unprecedented diversity in race, gender, and age.
According to historians and other scholars, the problem is embedded in the story of the nation and its culture. Rooted in slavery, racial disparities in policing and police violence, they say, are sustained by systemic exclusion and discrimination, and fueled by implicit and explicit bias. Any solution clearly will require myriad new approaches to law enforcement, courts, and community involvement, and comprehensive social change driven from the bottom up and the top down.
While police reform has become a major focus, the current moment of national reckoning has widened the lens on systemic racism for many Americans. The range of issues, though less familiar to some, is well known to scholars and activists. Across Harvard, for instance, faculty members have long explored the ways inequality permeates every aspect of American life. Their research and scholarship sits at the heart of a new Gazette series starting today aimed at finding ways forward in the areas of democracy; wealth and opportunity; environment and health; and education. It begins with this first on policing.
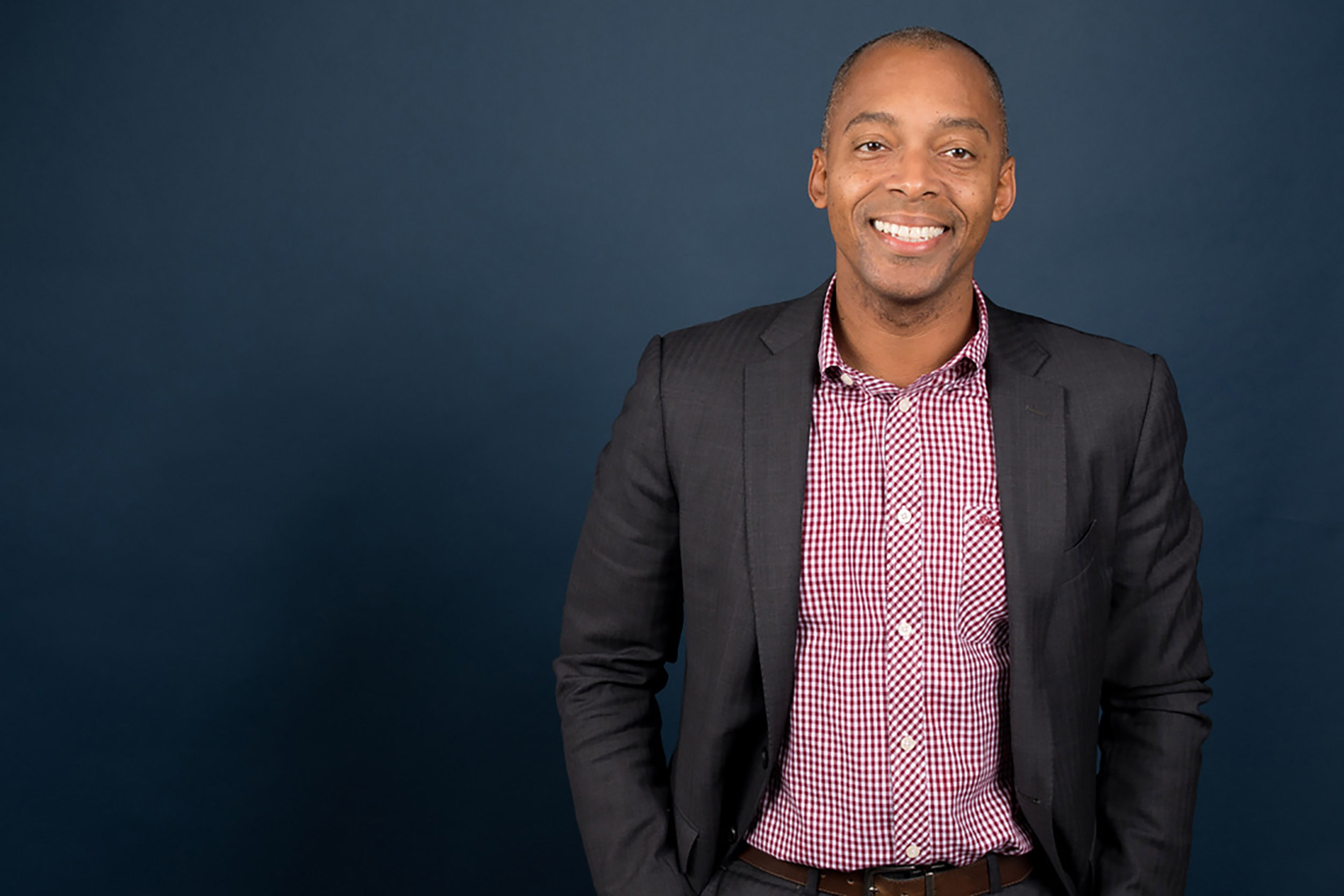

Harvard Kennedy School Professor Khalil Gibran Muhammad traces the history of policing in America to “slave patrols” in the antebellum South, in which white citizens were expected to help supervise the movements of enslaved Black people.
Photo by Martha Stewart
The history of racialized policing
Like many scholars, Khalil Gibran Muhammad, professor of history, race, and public policy at the Harvard Kennedy School, traces the history of policing in America to “slave patrols” in the antebellum South, in which white citizens were expected to help supervise the movements of enslaved Black people. This legacy, he believes, can still be seen in policing today. “The surveillance, the deputization essentially of all white men to be police officers or, in this case, slave patrollers, and then to dispense corporal punishment on the scene are all baked in from the very beginning,” he told NPR last year.
Slave patrols, and the slave codes they enforced, ended after the Civil War and the passage of the 13th amendment, which formally ended slavery “except as a punishment for crime.” But Muhammad notes that former Confederate states quickly used that exception to justify new restrictions. Known as the Black codes, the various rules limited the kinds of jobs African Americans could hold, their rights to buy and own property, and even their movements.
“The genius of the former Confederate states was to say, ‘Oh, well, if all we need to do is make them criminals and they can be put back in slavery, well, then that’s what we’ll do.’ And that’s exactly what the Black codes set out to do. The Black codes, for all intents and purposes, criminalized every form of African American freedom and mobility, political power, economic power, except the one thing it didn’t criminalize was the right to work for a white man on a white man’s terms.” In particular, he said the Ku Klux Klan “took about the business of terrorizing, policing, surveilling, and controlling Black people. … The Klan totally dominates the machinery of justice in the South.”
When, during what became known as the Great Migration, millions of African Americans fled the still largely agrarian South for opportunities in the thriving manufacturing centers of the North, they discovered that metropolitan police departments tended to enforce the law along racial and ethnic lines, with newcomers overseen by those who came before. “There was an early emphasis on people whose status was just a tiny notch better than the folks whom they were focused on policing,” Muhammad said. “And so the Anglo-Saxons are policing the Irish or the Germans are policing the Irish. The Irish are policing the Poles.” And then arrived a wave of Black Southerners looking for a better life.
In his groundbreaking work, “The Condemnation of Blackness: Race, Crime, and the Making of Modern Urban America,” Muhammad argues that an essential turning point came in the early 1900s amid efforts to professionalize police forces across the nation, in part by using crime statistics to guide law enforcement efforts. For the first time, Americans with European roots were grouped into one broad category, white, and set apart from the other category, Black.
Citing Muhammad’s research, Harvard historian Jill Lepore has summarized the consequences this way: “Police patrolled Black neighborhoods and arrested Black people disproportionately; prosecutors indicted Black people disproportionately; juries found Black people guilty disproportionately; judges gave Black people disproportionately long sentences; and, then, after all this, social scientists, observing the number of Black people in jail, decided that, as a matter of biology, Black people were disproportionately inclined to criminality.”
“History shows that crime data was never objective in any meaningful sense,” Muhammad wrote. Instead, crime statistics were “weaponized” to justify racial profiling, police brutality, and ever more policing of Black people.
This phenomenon, he believes, has continued well into this century and is exemplified by William J. Bratton, one of the most famous police leaders in recent America history. Known as “America’s Top Cop,” Bratton led police departments in his native Boston, Los Angeles, and twice in New York, finally retiring in 2016.
Bratton rejected notions that crime was a result of social and economic forces, such as poverty, unemployment, police practices, and racism. Instead, he said in a 2017 speech, “It is about behavior.” Through most of his career, he was a proponent of statistically-based “predictive” policing — essentially placing forces in areas where crime numbers were highest, focused on the groups found there.
Bratton argued that the technology eliminated the problem of prejudice in policing, without ever questioning potential bias in the data or algorithms themselves — a significant issue given the fact that Black Americans are arrested and convicted of crimes at disproportionately higher rates than whites. This approach has led to widely discredited practices such as racial profiling and “stop-and-frisk.” And, Muhammad notes, “There is no research consensus on whether or how much violence dropped in cities due to policing.”
Gathering numbers
In 2015 The Washington Post began tracking every fatal shooting by an on-duty officer, using news stories, social media posts, and police reports in the wake of the fatal police shooting of Brown, a Black teenager in Ferguson, Mo. According to the newspaper, Black Americans are killed by police at twice the rate of white Americans, and Hispanic Americans are also killed by police at a disproportionate rate.
Such efforts have proved useful for researchers such as economist Rajiv Sethi.
A Joy Foundation Fellow at the Harvard Radcliffe Institute, Sethi is investigating the use of lethal force by law enforcement officers, a difficult task given that data from such encounters is largely unavailable from police departments. Instead, Sethi and his team of researchers have turned to information collected by websites and news organizations including The Washington Post and The Guardian, merged with data from other sources such as the Bureau of Justice Statistics, the Census, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
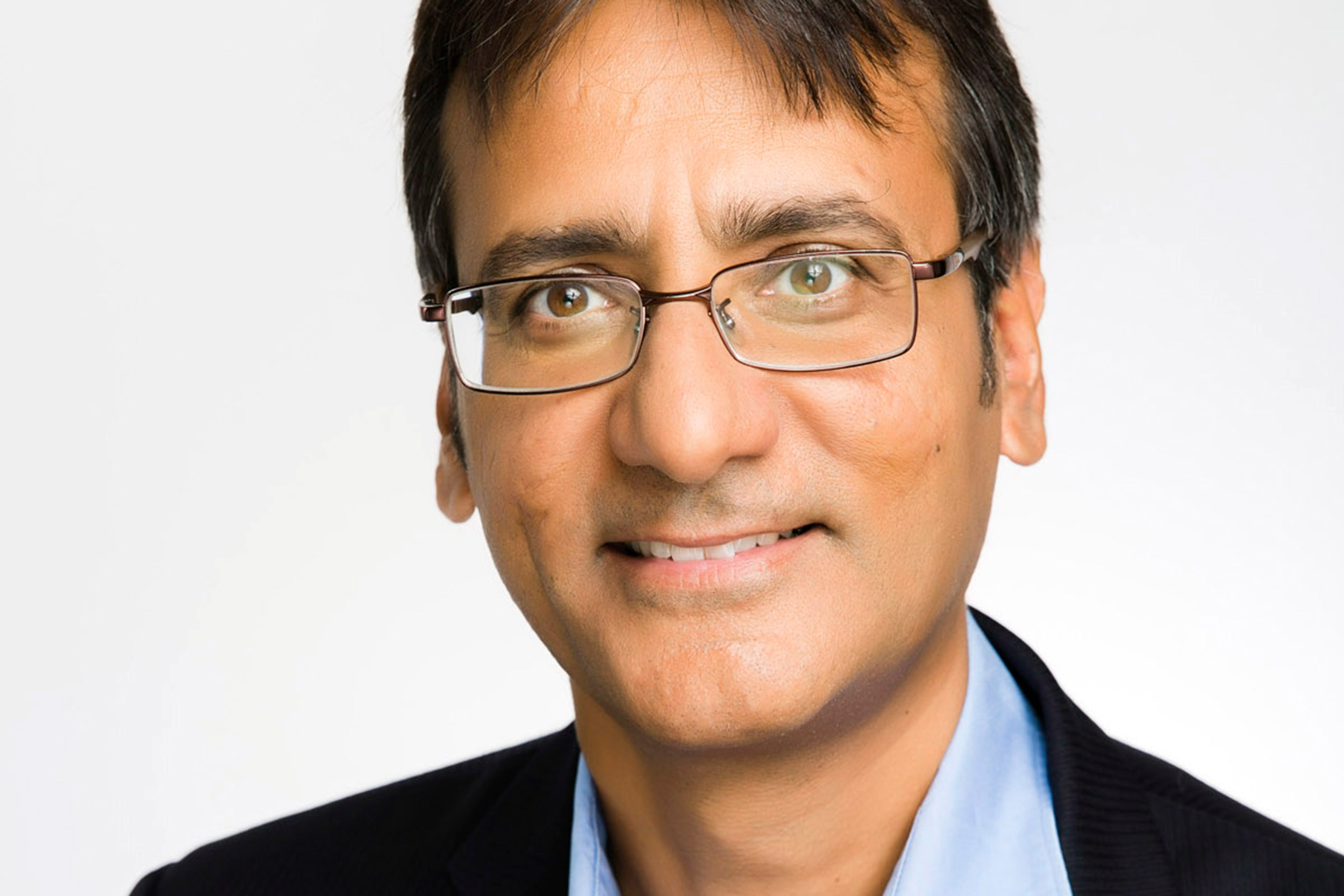

A Joy Foundation Fellow at the Harvard Radcliffe Institute, Rajiv Sethi is investigating the use of lethal force by law enforcement officers,
Courtesy photo
They have found that exposure to deadly force is highest in the Mountain West and Pacific regions relative to the mid-Atlantic and northeastern states, and that racial disparities in relation to deadly force are even greater than the national numbers imply. “In the country as a whole, you’re about two to three times more likely to face deadly force if you’re Black than if you are white” said Sethi. “But if you look at individual cities separately, disparities in exposure are much higher.”
Examining the characteristics associated with police departments that experience high numbers of lethal encounters is one way to better understand and address racial disparities in policing and the use of violence, Sethi said, but it’s a massive undertaking given the decentralized nature of policing in America. There are roughly 18,000 police departments in the country, and more than 3,000 sheriff’s offices, each with its own approaches to training and selection.
“They behave in very different ways, and what we’re finding in our current research is that they are very different in the degree to which they use deadly force,” said Sethi. To make real change, “You really need to focus on the agency level where organizational culture lies, where selection and training protocols have an effect, and where leadership can make a difference.”
Sethi pointed to the example of Camden, N.J., which disbanded and replaced its police force in 2013, initially in response to a budget crisis, but eventually resulting in an effort to fundamentally change the way the police engaged with the community. While there have been improvements, including greater witness cooperation, lower crime, and fewer abuse complaints, the Camden case doesn’t fit any particular narrative, said Sethi, noting that the number of officers actually increased as part of the reform. While the city is still faced with its share of problems, Sethi called its efforts to rethink policing “important models from which we can learn.”
Fighting vs. preventing crime
For many analysts, the real problem with policing in America is the fact that there is simply too much of it. “We’ve seen since the mid-1970s a dramatic increase in expenditures that are associated with expanding the criminal legal system, including personnel and the tasks we ask police to do,” said Sandra Susan Smith, Daniel and Florence Guggenheim Professor of Criminal Justice at HKS, and the Carol K. Pforzheimer Professor at the Radcliffe Institute. “And at the same time we see dramatic declines in resources devoted to social welfare programs.”
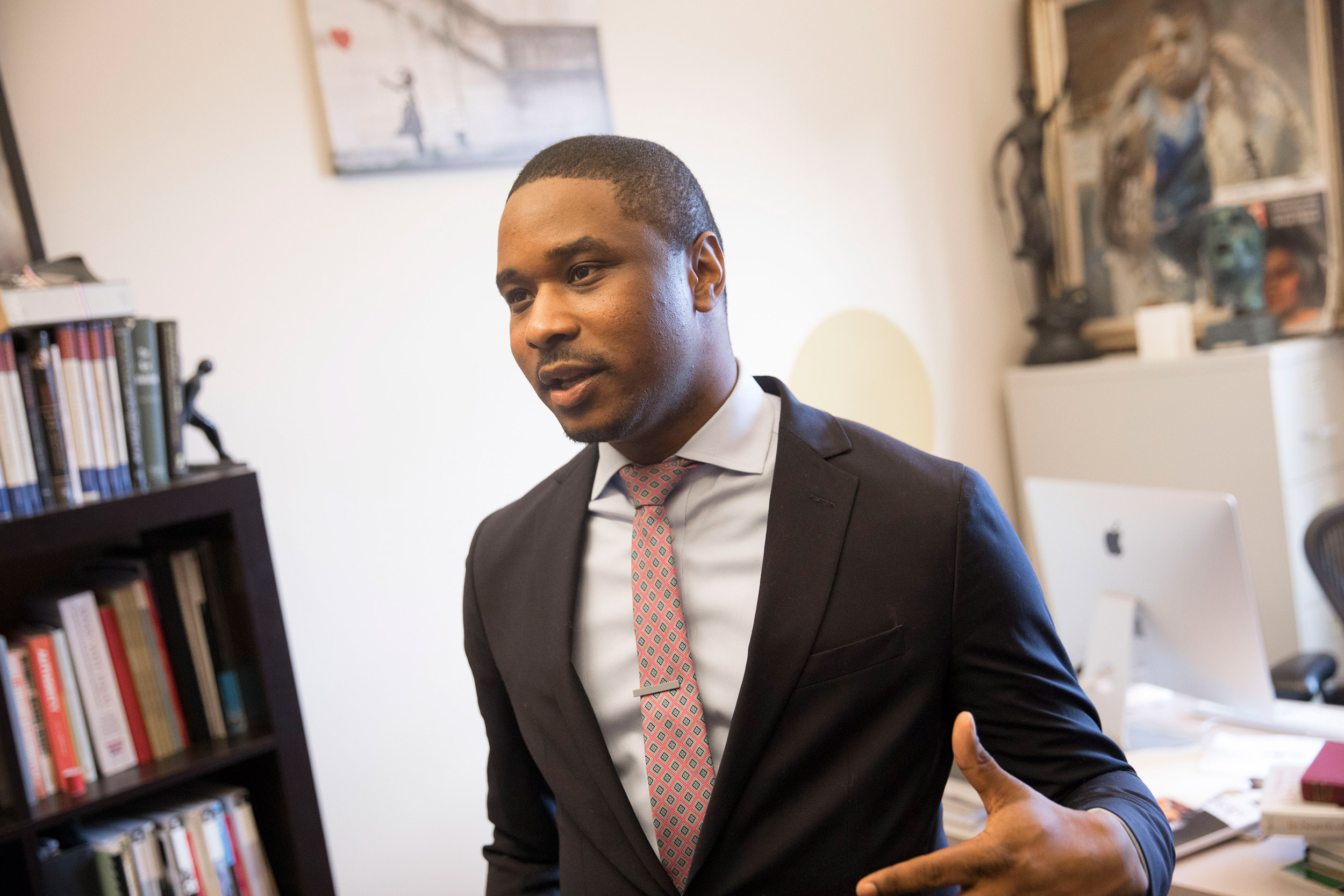

“You can have all the armored personnel carriers you want in Ferguson, but public safety is more likely to come from redressing environmental pollution, poor education, and unfair work,” said Brandon Terry, assistant professor of African and African American Studies and social studies.
Kris Snibble/Harvard file photo
Smith’s comment highlights a key argument embraced by many activists and experts calling for dramatic police reform: diverting resources from the police to better support community services including health care, housing, and education, and stronger economic and job opportunities. They argue that broader support for such measures will decrease the need for policing, and in turn reduce violent confrontations, particularly in over-policed, economically disadvantaged communities, and communities of color.
For Brandon Terry, that tension took the form of an ice container during his Baltimore high school chemistry final. The frozen cubes were placed in the middle of the classroom to help keep the students cool as a heat wave sent temperatures soaring. “That was their solution to the building’s lack of air conditioning,” said Terry, a Harvard assistant professor of African and African American Studies and social studies. “Just grab an ice cube.”
Terry’s story is the kind many researchers cite to show the negative impact of underinvesting in children who will make up the future population, and instead devoting resources toward policing tactics that embrace armored vehicles, automatic weapons, and spy planes. Terry’s is also the kind of tale promoted by activists eager to defund the police, a movement begun in the late 1960s that has again gained momentum as the death toll from violent encounters mounts. A scholar of Martin Luther King Jr., Terry said the Civil Rights leader’s views on the Vietnam War are echoed in the calls of activists today who are pressing to redistribute police resources.
“King thought that the idea of spending many orders of magnitude more for an unjust war than we did for the abolition of poverty and the abolition of ghettoization was a moral travesty, and it reflected a kind of sickness at the core of our society,” said Terry. “And part of what the defund model is based upon is a similar moral criticism, that these budgets reflect priorities that we have, and our priorities are broken.”
Terry also thinks the policing debate needs to be expanded to embrace a fuller understanding of what it means for people to feel truly safe in their communities. He highlights the work of sociologist Chris Muller and Harvard’s Robert Sampson, who have studied racial disparities in exposures to lead and the connections between a child’s early exposure to the toxic metal and antisocial behavior. Various studies have shown that lead exposure in children can contribute to cognitive impairment and behavioral problems, including heightened aggression.
“You can have all the armored personnel carriers you want in Ferguson,” said Terry, “but public safety is more likely to come from redressing environmental pollution, poor education, and unfair work.”
Policing and criminal justice system
Alexandra Natapoff, Lee S. Kreindler Professor of Law, sees policing as inexorably linked to the country’s criminal justice system and its long ties to racism.
“Policing does not stand alone or apart from how we charge people with crimes, or how we convict them, or how we treat them once they’ve been convicted,” she said. “That entire bundle of official practices is a central part of how we govern, and in particular, how we have historically governed Black people and other people of color, and economically and socially disadvantaged populations.”
Unpacking such a complicated issue requires voices from a variety of different backgrounds, experiences, and fields of expertise who can shine light on the problem and possible solutions, said Natapoff, who co-founded a new lecture series with HLS Professor Andrew Crespo titled “Policing in America.”
In recent weeks the pair have hosted Zoom discussions on topics ranging from qualified immunity to the Black Lives Matter movement to police unions to the broad contours of the American penal system. The series reflects the important work being done around the country, said Natapoff, and offers people the chance to further “engage in dialogue over these over these rich, complicated, controversial issues around race and policing, and governance and democracy.”
Courts and mass incarceration
Much of Natapoff’s recent work emphasizes the hidden dangers of the nation’s misdemeanor system. In her book “Punishment Without Crime: How Our Massive Misdemeanor System Traps the Innocent and Makes America More Unequal,” Natapoff shows how the practice of stopping, arresting, and charging people with low-level offenses often sends them down a devastating path.
“This is how most people encounter the criminal apparatus, and it’s the first step of mass incarceration, the initial net that sweeps people of color disproportionately into the criminal system,” said Natapoff. “It is also the locus that overexposes Black people to police violence. The implications of this enormous net of police and prosecutorial authority around minor conduct is central to understanding many of the worst dysfunctions of our criminal system.”
One consequence is that Black and brown people are incarcerated at much higher rates than white people. America has approximately 2.3 million people in federal, state, and local prisons and jails, according to a 2020 report from the nonprofit the Prison Policy Initiative. According to a 2018 report from the Sentencing Project, Black men are 5.9 times as likely to be incarcerated as white men and Hispanic men are 3.1 times as likely.
Reducing mass incarceration requires shrinking the misdemeanor net “along all of its axes” said Natapoff, who supports a range of reforms including training police officers to both confront and arrest people less for low-level offenses, and the policies of forward-thinking prosecutors willing to “charge fewer of those offenses when police do make arrests.”
She praises the efforts of Suffolk County District Attorney Rachael Rollins in Massachusetts and George Gascón, the district attorney in Los Angeles County, Calif., who have pledged to stop prosecuting a range of misdemeanor crimes such as resisting arrest, loitering, trespassing, and drug possession. “If cities and towns across the country committed to that kind of reform, that would be a profoundly meaningful change,” said Natapoff, “and it would be a big step toward shrinking our entire criminal apparatus.”
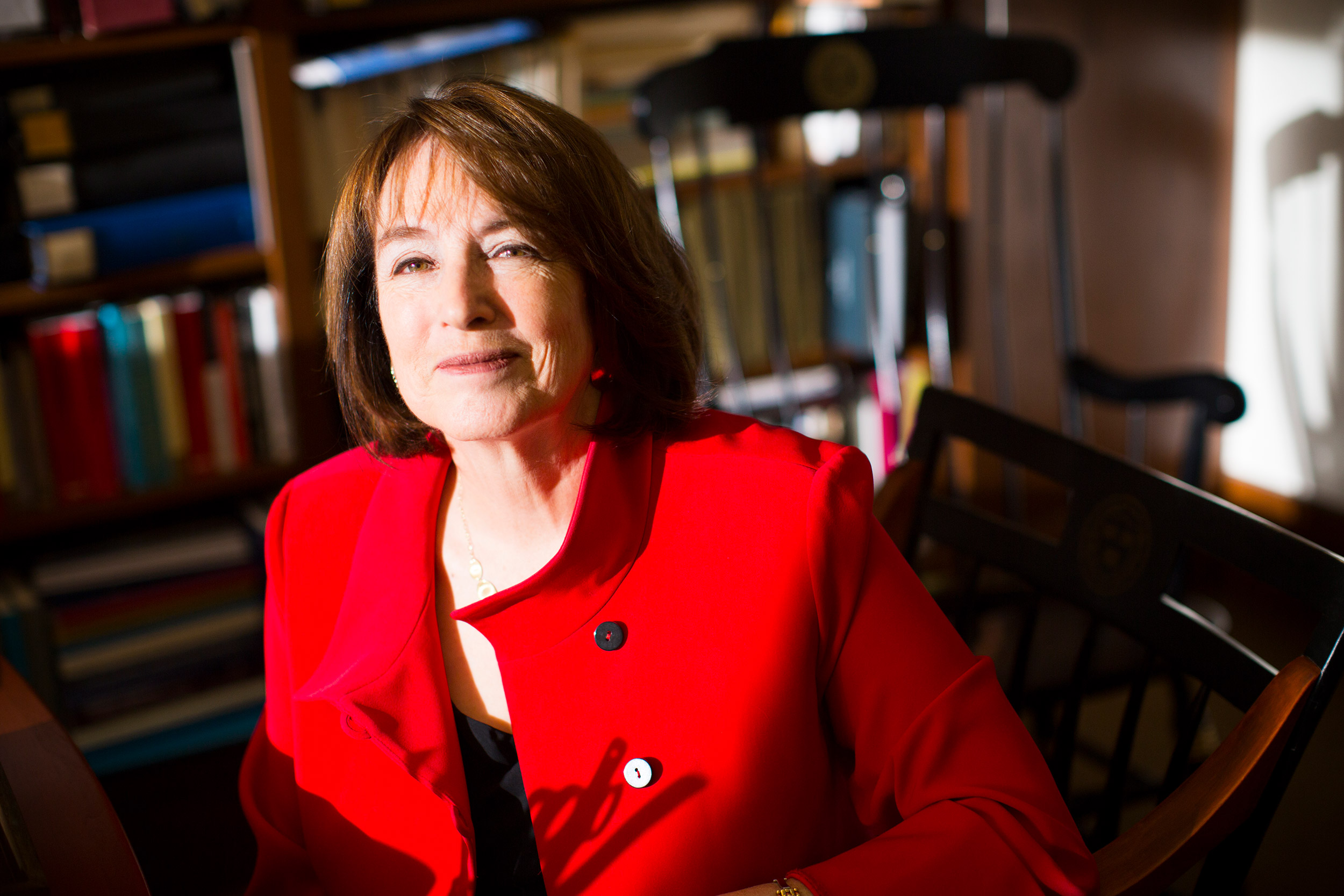

Retired U.S. Judge Nancy Gertner cites the need to reform federal sentencing guidelines, arguing that all too often they have been proven to be biased and to result in packing the nation’s jails and prisons.
Stephanie Mitchell/Harvard file photo
Sentencing reform
Another contributing factor in mass incarceration is sentencing disparities.
A recent Harvard Law School study found that, as is true nationally, people of color are “drastically overrepresented in Massachusetts state prisons.” But the report also noted that Black and Latinx people were less likely to have their cases resolved through pretrial probation — a way to dismiss charges if the accused meet certain conditions — and receive much longer sentences than their white counterparts.
Retired U.S. Judge Nancy Gertner also notes the need to reform federal sentencing guidelines, arguing that all too often they have been proven to be biased and to result in packing the nation’s jails and prisons. She points to the way the 1994 Crime Bill (legislation sponsored by then-Sen. Joe Biden of Delaware) ushered in much harsher drug penalties for crack than for powder cocaine. This tied the hands of judges issuing sentences and disproportionately punished people of color in the process. “The disparity in the treatment of crack and cocaine really was backed up by anecdote and stereotype, not by data,” said Gertner, a lecturer at HLS. “There was no data suggesting that crack was infinitely more dangerous than cocaine. It was the young Black predator narrative.”
The First Step Act, a bipartisan prison reform bill aimed at reducing racial disparities in drug sentencing and signed into law by President Donald Trump in 2018, is just what its name implies, said Gertner.
“It reduces sentences to the merely inhumane rather than the grotesque. We still throw people in jail more than anybody else. We still resort to imprisonment, rather than thinking of other alternatives. We still resort to punishment rather than other models. None of that has really changed. I don’t deny the significance of somebody getting out of prison a year or two early, but no one should think that that’s reform.”
Not just bad apples
Reform has long been a goal for federal leaders. Many heralded Obama-era changes aimed at eliminating racial disparities in policing and outlined in the report by The President’s Task Force on 21st Century policing. But HKS’s Smith saw them as largely symbolic. “It’s a nod to reform. But most of the reforms that are implemented in this country tend to be reforms that nibble around the edges and don’t really make much of a difference.”
Efforts such as diversifying police forces and implicit bias training do little to change behaviors and reduce violent conduct against people of color, said Smith, who cites studies suggesting a majority of Americans hold negative biases against Black and brown people, and that unconscious prejudices and stereotypes are difficult to erase.
“Experiments show that you can, in the context of a day, get people to think about race differently, and maybe even behave differently. But if you follow up, say, a week, or two weeks later, those effects are gone. We don’t know how to produce effects that are long-lasting. We invest huge amounts to implement such police reforms, but most often there’s no empirical evidence to support their efficacy.”
Even the early studies around the effectiveness of body cameras suggest the devices do little to change “officers’ patterns of behavior,” said Smith, though she cautions that researchers are still in the early stages of collecting and analyzing the data.
And though police body cameras have caught officers in unjust violence, much of the general public views the problem as anomalous.
“Despite what many people in low-income communities of color think about police officers, the broader society has a lot of respect for police and thinks if you just get rid of the bad apples, everything will be fine,” Smith added. “The problem, of course, is this is not just an issue of bad apples.”
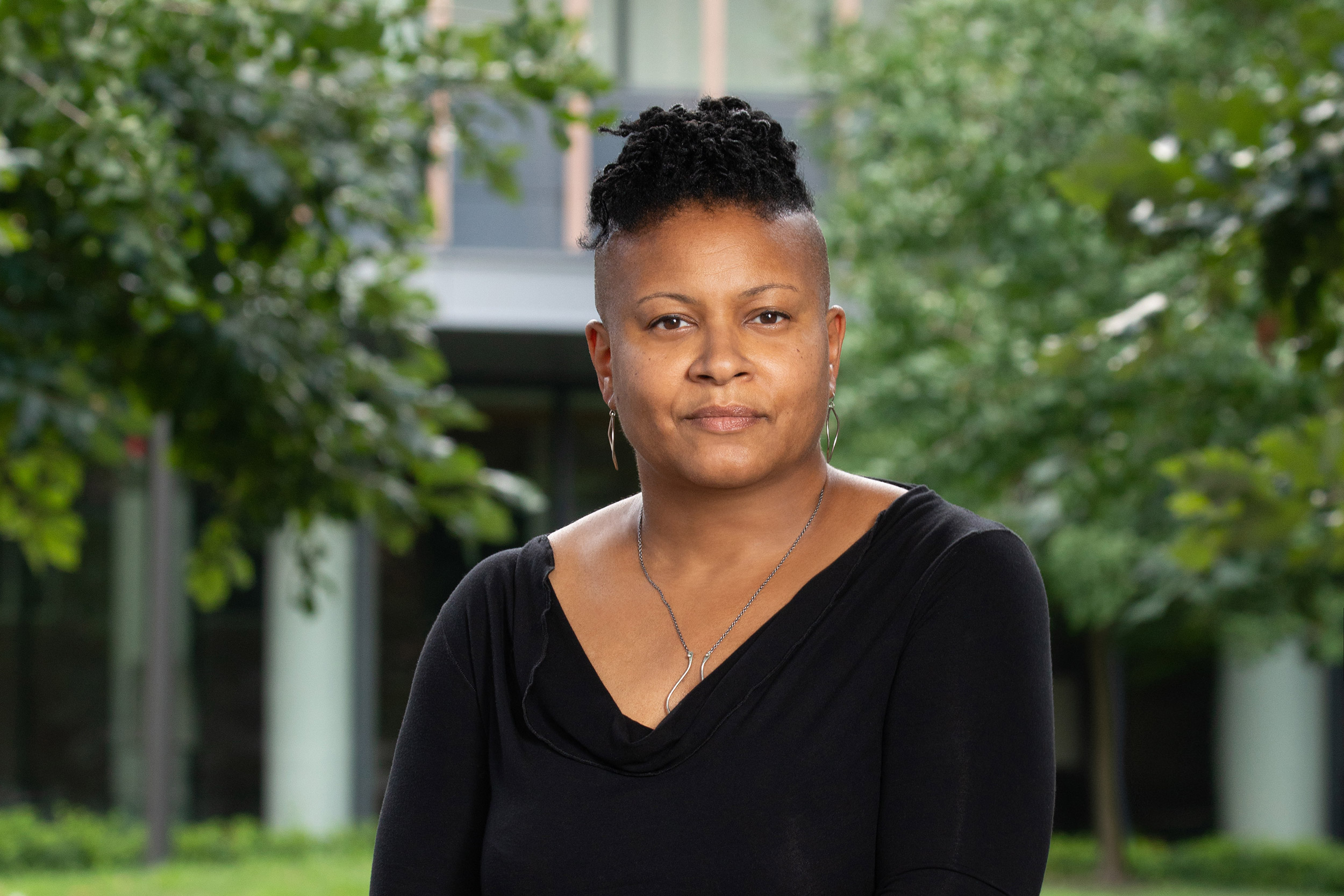

Efforts such as diversifying police forces and implicit bias training do little to change behaviors and reduce violent conduct against people of color, said Sandra Susan Smith, a professor of criminal justice Harvard Kennedy School.
Courtesy photo
Community-based ways forward
Still Smith sees reason for hope and possible ways forward involving a range of community-based approaches. As part of the effort to explore meaningful change, Smith, along with Christopher Winship, Diker-Tishman Professor of Sociology at Harvard University and a member of the senior faculty at HKS, have organized “Reimagining Community Safety: A Program in Criminal Justice Speaker Series” to better understand the perspectives of practitioners, policymakers, community leaders, activists, and academics engaged in public safety reform.
Some community-based safety models have yielded important results. Smith singles out the Crisis Assistance Helping Out on the Streets program (known as CAHOOTS) in Eugene, Ore., which supplements police with a community-based public safety program. When callers dial 911 they are often diverted to teams of workers trained in crisis resolution, mental health, and emergency medicine, who are better equipped to handle non-life-threatening situations. The numbers support her case. In 2017 the program received 25,000 calls, only 250 of which required police assistance. Training similar teams of specialists who don’t carry weapons to handle all traffic stops could go a long way toward ending violent police encounters, she said.
“Imagine you have those kinds of services in play,” said Smith, paired with community-based anti-violence program such as Cure Violence, which aims to stop violence in targeted neighborhoods by using approaches health experts take to control disease, such as identifying and treating individuals and changing social norms. Together, she said, these programs “could make a huge difference.”
At Harvard Law School, students have been studying how an alternate 911-response team might function in Boston. “We were trying to move from thinking about a 911-response system as an opportunity to intervene in an acute moment, to thinking about what it would look like to have a system that is trying to help reweave some of the threads of community, a system that is more focused on healing than just on stopping harm” said HLS Professor Rachel Viscomi, who directs the Harvard Negotiation and Mediation Clinical Program and oversaw the research.
The forthcoming report, compiled by two students in the HLS clinic, Billy Roberts and Anna Vande Velde, will offer officials a range of ideas for how to think about community safety that builds on existing efforts in Boston and other cities, said Viscomi.
But Smith, like others, knows community-based interventions are only part of the solution. She applauds the Justice Department’s investigation into the Ferguson Police Department after the shooting of Brown. The 102-page report shed light on the department’s discriminatory policing practices, including the ways police disproportionately targeted Black residents for tickets and fines to help balance the city’s budget. To fix such entrenched problems, state governments need to rethink their spending priorities and tax systems so they can provide cities and towns the financial support they need to remain debt-free, said Smith.
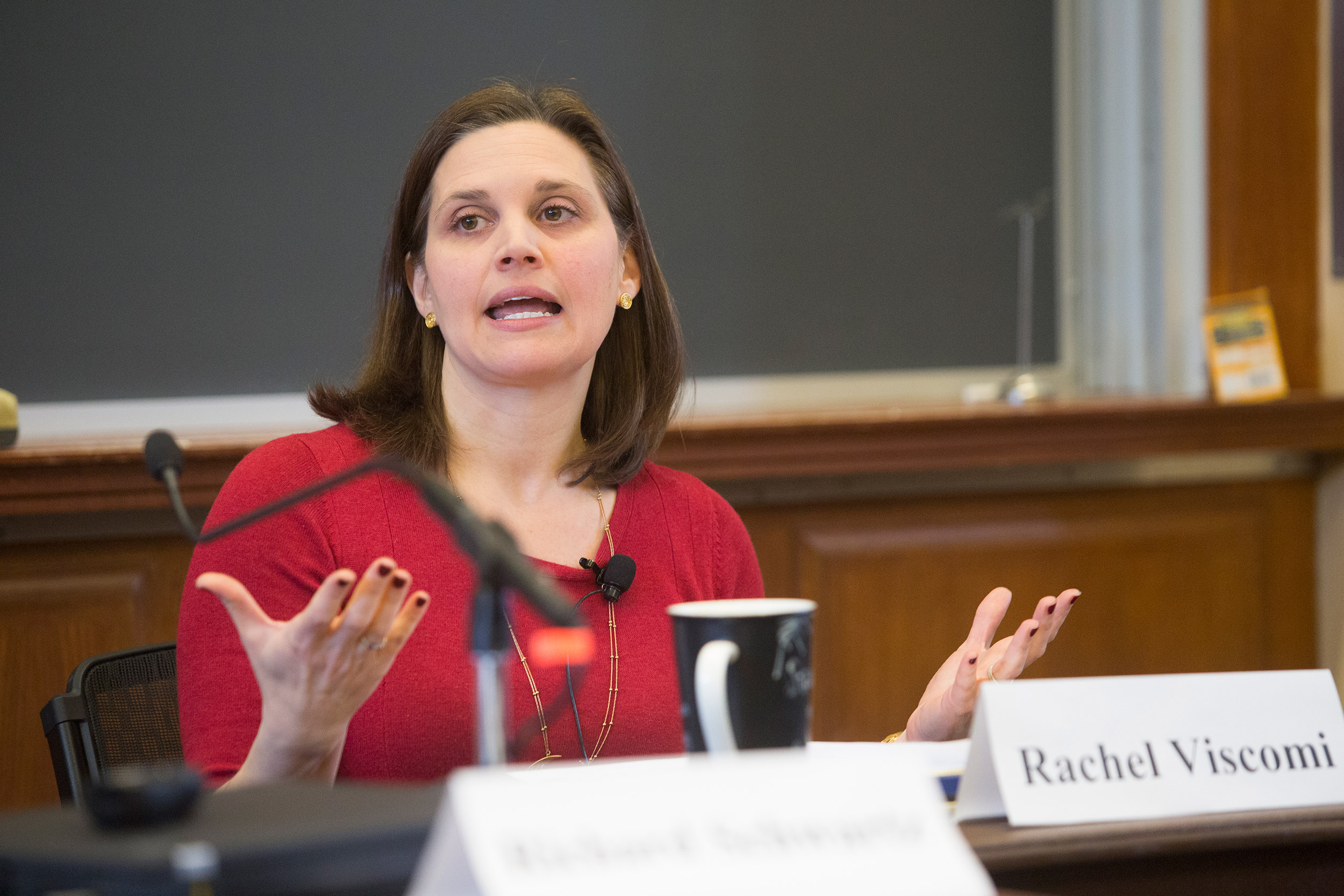

Rethinking the 911-response system to being one that is “more focused on healing than just on stopping harm” is part of the student-led research under the direction of Law School Professor Rachel Viscomi, who heads up the Harvard Negotiation and Mediation Clinical Program.
Jon Chase/Harvard file photo
“Part of the solution has to be a discussion about how government is funded and how a city like Ferguson got to a place where government had so few resources that they resorted to extortion of their residents, in particular residents of color, in order to make ends meet,” she said. “We’ve learned since that Ferguson is hardly the only municipality that has struggled with funding issues and sought to address them through the oppression and repression of their politically, socially, and economically marginalized Black and Latino residents.”
Police contracts, she said, also need to be reexamined. The daughter of a “union man,” Smith said she firmly supports officers’ rights to union representation to secure fair wages, health care, and safe working conditions. But the power unions hold to structure police contracts in ways that protect officers from being disciplined for “illegal and unethical behavior” needs to be challenged, she said.
“I think it’s incredibly important for individuals to be held accountable and for those institutions in which they are embedded to hold them to account. But we routinely find that union contracts buffer individual officers from having to be accountable. We see this at the level of the Supreme Court as well, whose rulings around qualified immunity have protected law enforcement from civil suits. That needs to change.”
Other Harvard experts agree. In an opinion piece in The Boston Globe last June, Tomiko Brown-Nagin, dean of the Harvard Radcliffe Institute and the Daniel P.S. Paul Professor of Constitutional Law at HLS, pointed out the Court’s “expansive interpretation of qualified immunity” and called for reform that would “promote accountability.”
“This nation is devoted to freedom, to combating racial discrimination, and to making government accountable to the people,” wrote Brown-Nagin. “Legislators today, like those who passed landmark Civil Rights legislation more than 50 years ago, must take a stand for equal justice under law. Shielding police misconduct offends our fundamental values and cannot be tolerated.”